
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
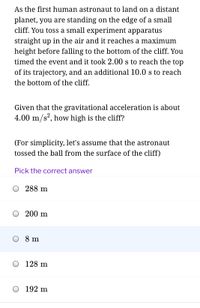
Transcribed Image Text:As the first human astronaut to land on a distant
planet, you are standing on the edge of a small
cliff. You toss a small experiment apparatus
straight up in the air and it reaches a maximum
height before falling to the bottom of the cliff. You
timed the event and it took 2.00 s to reach the top
of its trajectory, and an additional 10.0 s to reach
the bottom of the cliff.
Given that the gravitational acceleration is about
4.00 m/s?, how high is the cliff?
(For simplicity, let's assume that the astronaut
tossed the ball from the surface of the cliff)
Pick the correct answer
288 m
200 m
O 8 m
128 m
O 192 m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You have put a sonar device at the top of a frictionless inclined plane. That device allows you to measure the distance an object is from the device, as well as the speed and the acceleration of that object. If we decide that the origin (h = 0) is at the sonar device, we want to know what the height change is as we slide down the incline. For an angle below the horizontal of 9.74°, we see that our object has slid a distance 0.54 m, as measured along the incline itself. - Calculate the height change and report your answer as a negative number. (This value would be useful for calculating the change in gravitational potential energy, as we will do in the lab.) h=o earrow_forwardYou are working part-time for the GT Sports Media Complex, editing video for the women’s softball team. In one particular clip, a GT player hits a home run over the center field fence. The ball leaves the bat at a height of 4 ft, and crosses the outfield fence (220 ft away) at a height of 10 ft. Logs of the game indicate that the pitch was clocked at 68 mph as it reached the plate. Your frame-by-frame analysis of the 30-frame-per-second video indicate that the ball spent only a single frame in contact with tha bat, and another 126 frames travelling to the outfield fence. A quick internet seach tells you that a typical college softball weighs 0.4 lb. How many pounds of average force act on the ball during ocntact with the bat?arrow_forwardA ball is suspended from a light 1.3 m string . The string makes an angle of 24 degrees with the vertical. The ball is then kicked up and to the right such that the string remains taut the entire time the ball swings upwards. This kick gives the ball an initial velocity of 1.1m/s. What will be the speed, in meters per second, of the ball when it reaches its lowest point (θ = 0)? What will be the maximum angle, in degrees, the string will make with the vertical?arrow_forward
- A person throws a ball with speed 102 m/s at a 45° angle. How many seconds faster would the ball arrive if the person threw the ball at the same speed and the same distance but made the trip in two identical bumps. Assume that there is no loss of speed at the bounce. Hint: Use R = v2/g * sin(2θ) and t=2*vy(sinθ)/g.arrow_forwardAn object is dropped from rest and falls 180m during 15s of free fall. Did this occur on the moon (g=1.6m/s/s), earth (g=9.8m/s/s), or Jupiter(g=26.0m/s/s)?arrow_forwardYou shoot a ball straight up with an initial speed of 8490 m/s. When the surface of the earth, what is the speed of the ball? O 2146 m/s reaches a height of 4.0 x 10 6 m above O 2956 m/s O 3546 m/s 4009 m/s 4588 m/s O 4876 m/sarrow_forward
- You are on a planet that has an acceleration due to gravity of g = 7.0 m/s? and want to jump safely into the methane lakes below after leaping from a 11.2 meter high-cliff. If there is a ledge right at the bottom of this cliff that you want to avoid, so as to land safely in the liquid methane, that is 1.13 m wide, and assuming your initial velocity is directed entirely along the x-axis, how fast (in m/s) do you need to be running in order to land in the liquid methane?arrow_forwardThe Hulk, on the 75th story of Stark Tower (225 m off the ground), sees Tony drop his penny. He catches the penny and throws it back to Tony. What is the minimum speed necessary for Hulk's throw in order for the penny to reach Tony? (Note: nobody bothers trying to get Mjolnir back to Thor. He's on his own.)arrow_forwardOK, this is the last time for one of these crazy adventures. THIS time, though, there is a window in the floor, and you can see that you re in a rocket which has just taken off from the surface of an alien planet. By taking careful measurements out that window you determine that the rocket is accelerating upward at 7.42 m/s^2. When you drop a ball from a height of 1.74 m, it hits the floor 0.254 s later. What is the value of g for the alien world below you? 1. 63.8 m/s^2 55.2 m/s^2 3 79.1 m/s^2 4 46.5 m/s^2arrow_forward
- OK, this is the last time for one of these crazy adventures. THIS time, though, there is a window in the floor, and you can see that you re in a rocket which has just taken off from the surface of an alien planet. By taking careful measurements out that window you determine that the rocket is accelerating upward at 9.60 m/s^2. When you drop a ball from a height of 1.20 m, it hits the floor 0.362 s later. What is the value of g for the alien world below you? 16.5 m/s^2 8.7 m/s^2 28.1 m/s^2 18.4 m/s^2arrow_forwardOK, this is the last time for one of these crazy adventures. THIS time, though, there is a window in the floor, and you can see that you re in a rocket which has just taken off from the surface of an alien planet. By taking careful measurements out that window you determine that the rocket is accelerating upward at 7.11 m/s^2. When you drop a ball from a height of 1.08 m, it hits the floor 0.213 s later. What is the value of g for the alien world below you? 49.0 m/s^2 60.8 m/s^2 40.5 m/s^2 57.4 m/s^2arrow_forwardA bird flies at a velocity of 10.00 m/s straight into the wind. If it takes the bird 22 minutes to travel 6 km relative to earth, what is the velocity of the wind? If the bird turns around and flies with the wind how long will it take to return 6 km?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON