
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
As energy passes from blue-absorbing chlorophylls down to red-absorbing chlorophylls,
surprisingly, no energy passes from lower energy-absorbing pigments back to higher
ones (in other words, the process is irreversible). Why might that be?
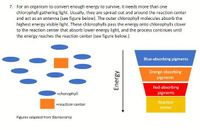
Transcribed Image Text:7. For an organism to convert enough energy to survive, it needs more than one
chlorophyll gathering light. Usually, they are spread out and around the reaction center
and act as an antenna (see figure below). The outer chlorophyll molecules absorb the
highest energy visible light. These chlorophylls pass the energy onto chlorophylls closer
to the reaction center that absorb lower energy light, and the process continues until
the energy reaches the reaction center (see figure below.)
Blue-absorbing pigments
Orange-absorbing
pigments
Red-absorbing
=chorophyll
pigments
Reaction
=reaction center
center
Figures adapted from Blankenship
Energy
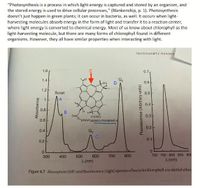
Transcribed Image Text:"Photosynthesis is a process in which light energy is captured and stored by an organism, and
the stored energy is used to drive cellular processes," (Blankenship, p. 1). Photosynthesis
doesn't just happen in green plants; it can occur in bacteria, as well. It occurs when light-
harvesting molecules absorb energy in the form of light and transfer it to a reaction center,
where light energy is converted to chemical energy. Most of us know about chlorophyll as the
light-harvesting molecule, but there are many forms of chlorophyll found in different
organisms. However, they all have similar properties when interacting with light.
PHOTOSYNTHETIC PIOMENIS
1.6
0.7
1.4
D.
0.6-
1.2
Soret
0.5
0.4
0.8
B.
H
COOCH
phytyl bacteriochlorophyll a
0.3-
0.6
0.2-
0.4
0.1
0.2
300
400
500
600
700
800
700 750 800 850 900
A (nm)
2 (nm)
Figure 4.7 Absorption (left) and fluorescence (right) spectra of bacteriochlorophyll a in diethyl ether
Absorbance
1.
Fluorescence (Arbitrary units)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You perform the leaf disc experiment using two cups of leaves, one in the light by a window in your kitchen and the other inside a closed kitchen cabinet without any light available. Based on what you know about this experiment, what would happen to the leaves in each cup? The leaves in the cup in the window will eventually float but the leaves in the cup inside the dark cabinet will not. All of the leaves in the cups will float. None of the leaves in the cups will float. The leaves in the cup in the dark cabinet will eventually float but the leaves in the cup beside the window will not.arrow_forwardWhat is the purpose of having multiple chlorophylls and what do the other pigments serve ?arrow_forwardReferring to the figure below(first picture) explain photosynthetic electron transport. Then compare the process outlined in the figure with figure 1(second picture), What are the similarities and differences?arrow_forward
- A C4 plant minimizes photorespiration by (note that we are talking about standard C4 plant, not CAM plants here) O having the light reactions and carbon reactions occur in different cells, so oxygen does not come into contact with rubisco O having the light reactions and carbon reactions occur in different cells, so carbon dioxide does not come into contact with rubisco O stomata that are only opened at night, storing oxygen in malate, and releasing oxygen during the day O stomata that are only opened at night, storing carbon dioxide in malate, and releasing carbon dioxide during the dayarrow_forwardSuppose we set up a system in a lab where plants are automatically injected with all the glucose they need to survive. What part of photosynthesis would the plants no longer need to perform? Group of answer choices a)ETC 1 b)the entire dark reaction c)the entire light reaction d)P700 e)all of itarrow_forwardWhich (look at figure) is an accessory pigment in red flowers?arrow_forward
- Rubisco can bind with CO2 or 02. When it binds with O2, it "wastes" some of the energy captured from the sun. This reaction is photorespiration and is favored at high temperatures and low CO2:02 ratios. Which of the following strategies should limit photorespiration (select all that apply). Keep stomata closed. Keep stomata open. Physically separate the light and light-independent reactions. Temporally separate CO2 uptake and fixation.arrow_forwardWhen considering the loading and unloading of photosynthate from the phloem, which of the following is FALSE? Select one: a. Apoplastic phloem unloading enables the import of sugars against their concentration gradient into sink tissue. b. In apoplastic loading, the solute potential of the companion cells is more negative than the apoplastic space nearby. c. In apoplastic loading, proton pumps create electrochemical gradients that can be used by symporter proteins to import sugars into the companion cell. d. All the statements are true. e. Symplastic loading relies on diffusion of the sugars through plasmodesmata from photosynthetic cells to the phloem cells.arrow_forwardThe substance dichlorophenyldimethylurea (DCMU) is an herbi- cide that inhibits photosynthesis by blocking electron transfer between plastoquinones in photosystem II. (a) Would you expect DCMU to interfere with cyclic photophos- phorylation? (b) Normally, DCMU blocks Oz evolution, but addition of ferri- cyanide to chloroplasts allows Oz evolution in the presence of DCMU. Explain.arrow_forward
- If a plant is removed from its natural environment and exposed to 100 percent CO2 composed of the radioisotope 14C, which of the following will not occur? Select one: a. The rate of photorespiration will remain unchanged. b. The sugars synthesized by the plant will be radioactive. c. The oxygen released will also be radioactive. d. All the carbon molecules in the RuBP molecules will eventually become 14C. e. Rubisco will eventually contain 14C.arrow_forwardPhycobiliproteins are complex proteins in cyanobacteria that absorb light energy. There are three kinds of phycobiliprotein molecules used to pass light to chlorophyll: phycoerythrin-responsible for capturing green light, phycocyanin-responsible for capturing orange-red light, and allophycocyanin-responsible for capturing red light. Since light can only penetrate to certain depths in oceans, phycobiliproteins capture the light available and pass it through various pathways of phycobiliproteins until the emitted light is red, which is absorbed by chlorophyll. Use the figure below to answer the following questions. 7.5m UV 15.0m 22.5m 30.0m. 37.5m Blue Green Red O Tomemorris 2020 Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 4.0 International license. IR 25ft 50ft 75ft 100ft 125ft a. Explain the relationship between chlorophyll absorption and wavelength. b. In addition to the pigments commonly associated with photosynthesis, a certain photosynthetic species contains two additional pigment…arrow_forwardWhich of the following lists the stages of the Calvin cycle in order, starting with the stage where carbon dioxide is added? PGAL synthesis → carbon fixation → light reactions → regeneration of RuBP carbon fixation → PGAL synthesis → regeneration of RuBP regeneration of RuBP → carbon fixation → PGAL synthesis photorespiration → PGAL synthesis → regeneration of RuBP → carbon fixationarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education