
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
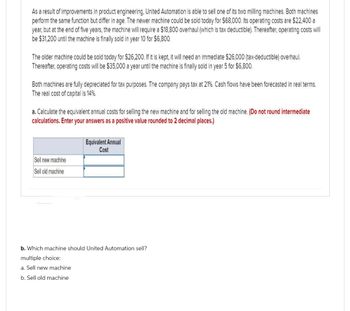
Transcribed Image Text:As a result of improvements in product engineering, United Automation is able to sell one of its two milling machines. Both machines
perform the same function but differ in age. The newer machine could be sold today for $68,000. Its operating costs are $22,400 a
year, but at the end of five years, the machine will require a $18,800 overhaul (which is tax deductible). Thereafter, operating costs will
be $31,200 until the machine is finally sold in year 10 for $6,800.
The older machine could be sold today for $26,200. If it is kept, it will need an immediate $26,000 (tax-deductible) overhaul.
Thereafter, operating costs will be $35,000 a year until the machine is finally sold in year 5 for $6,800.
Both machines are fully depreciated for tax purposes. The company pays tax at 21%. Cash flows have been forecasted in real terms.
The real cost of capital is 14%.
a. Calculate the equivalent annual costs for selling the new machine and for selling the old machine. (Do not round intermediate
calculations. Enter your answers as a positive value rounded to 2 decimal places.)
Sell new machine
Sell old machine
Equivalent Annual
Cost
b. Which machine should United Automation sell?
multiple choice:
a. Sell new machine
b. Sell old machine
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Builtrite is considering the purchase of a new five-year machine worth $90,000. It will cost another $10,000 to install the machine and Builtrite will need to keep an extra $9,000 in inventory on hand due to the machine's efficiency. The current machine being used is 5 years old and originally cost $60,000 and is being depreciated down to zero over a 10-year period. If the current machine were sold today, it could be sold for $45,000. In five years, the new machine is estimated to have a salvage value of $36,000. Two employees will need to be trained for the new machine at a cost of $4000. The new machine is expected to produce $80,000 in annual savings. Builtrite is in the 34% tax bracket. What is the terminal cash flow for the new machine? O $23.760 O $31,800 O $32,760arrow_forwardBuiltrite is considering purchasing a new machine that would cost $60,000 and the machine would be depreciated (straight line) down to $0 over its five-year life. At the end of four years, it is believed that the machine could be sold for $30,000. The current machine being used was purchased 3 years ago at a cost of $40,000 and it is being depreciated down to zero over its 5-year life. The current machine's salvage value now is $12,000. The new machine would increase EBDT by $56,000 annuall Builtrite's marginal tax rate is 34%. What is the TCF associated with the purchase of this new machine if it is sold at the end of year 4? Ⓒ$30,000 $23,880 $20,500 $19,800arrow_forwardBig Rock Brewery currently rents a bottling machine for $51,000 per year, including all maintenance expenses. The company is considering purchasing a machine instead and is comparing two alternate options: option a is to purchase the machine it is currently renting for $160,000, which will require $20,000 per year in ongoing maintenance expenses, or option b, which is to purchase a new, more advanced machine for $250,000, which will require $19,000 per year in ongoing maintenance expenses and will lower bottling costs by $13,000 per year. Also, $36,000 will be spent upfront in training the new operators of the machine. Suppose the appropriate discount rate is 9% per year and the machine is purchased today. Maintenance and bottling costs are paid at the end of each year, as is the rental of the machine. Assume also that the machines are subject to a CCA rate of 45% and there will be a negligible salvage value in 10 years' time (the end of each machine's life). The marginal corporate tax…arrow_forward
- Calligraphy Pens is deciding when to replace its old machine. The machine's current salvage value is $3,050,000. Its current book value is $1,800,000. If not sold, the old machine will require maintenance costs of $710,000 at the end of the year for the next five years. Depreciation on the old machine is $360,000 per year. At the end of five years, it will have a salvage value of $155,000 and a book value of $0. A replacement machine costs $4,650,000 now and requires maintenance costs of $380,000 at the end of each year during its economic life of five years. At the end of the five years, the new machine will have a salvage value of $745,000. It will be fully depreciated by the straight-line method. In five years, a replacement machine will cost $3,650,000. The company will need to purchase this machine regardless of what choice it makes today. The corporate tax rate is 25 percent and the appropriate discount rate is 7 percent. The company is assumed to earn sufficient revenues to…arrow_forwardA construction company is considering acquiring a new earthmover. The purchase price is $110,000, and an additional $25,000 is required to modify the equipment for special use by the company. The equipment falls into the MACRS seven-year classification (the tax life), and it will be sold after five years (the project life) for $50,000. The purchase of the earthmover will have no effect on revenues, but the machine is expected to save the firm $68,000 per year in before-tax operating costs, mainly labor. The firm's marginal tax rate is 25%. Assume that the initial investment is to be financed by a bank loan at an interest rate of 10% payable annually. Determine the after-tax cash flows by using the generalized cash flow approach and the worth of the investment for this project if the firm's MARR known to be 12%. Click the icon to view the MACRS depreciation schedules. Click the icon to view the interest factors for discrete compounding when /= 10% per year. Click the icon to view the…arrow_forwardRequired: 1. Prepare a comparative income statement covering the next five years, assuming: a. The new machine is not purchased. b. The new machine is purchased. (Negative amounts should be indicated by a minus sign. Do not round intermediate calculations.) Total expenses w Transcribed Text of purchasing the new machine Keep Old Machine S Minimum saving in costs 5 Years Summary Buy New Machine Ĉ Difference 2. Compute the net advantage of purchasing the new machine using only relevant costs in your analysis. (Do not round intermediate calculations.) Check my work 3. What is the minimum saving in annual operating costs that must be achieved in order for the president to consider buying the new machine?arrow_forward
- Wildhorse Inc. wants to purchase a new machine for $38,790, excluding $1,500 of installation costs. The old machine was purchased 5 years ago and had an expected economic life of 10 years with no salvage value. The old machine has a book value of $2,200, and Wildhorse Inc. expects to sell it for that amount. The new machine will decrease operating costs by $9,000 each year of its economic life. The straight-line depreciation method will be used for the new machine for a 6-year period with no salvage value. Click here to view PV table. (a) Determine the cash payback period. (Round cash payback period to 2 decimal places, e.g. 10.53.) Cash payback period (b) years Determine the approximate internal rate of return. (Round answer to O decimal places, e.g. 13%. For calculation purposes, use 5 decimal places as displayed in the factor table provided.) Internal rate of return %arrow_forwardGranfield Company has a piece of manufacturing equipment with a book value of $41,500 and a remaining useful life of four years. At the end of the four years the equipment will have a zero salvage value. The market value of the equipment is currently $22,300. Granfield can purchase a new machine for $123,000 and receive $22,300 in return for trading in its old machine. The new machine will reduce variable manufacturing costs by $19,300 per year over the four-year life of the new machine. The total increase or decrease in net income by replacing the current machine with the new machine (ignoring the time value of money) is: Multiple Choice $77,200 decrease $23,500 increase $53,050 increase $23,500 decrease $19,200 decreasearrow_forwardBig Rock Brewery currently rents a bottling machine for $50,000 per year, including all maintenance expenses. The company is considering purchasing a machine instead and is comparing two alternate options: option a is to purchase the machine it is currently renting for $165,000, which will require $24,000 per year in ongoing maintenance expenses, or option b, which is to purchase a new, more advanced machine for $260,000, which will require $16,000 per year in ongoing maintenance expenses and will lower bottling costs by $10,000 per year. Also, $36,000 will be spent upfront in training the new operators of the machine. Suppose the appropriate discount rate is 7% per year and the machine is purchased today. Maintenance and bottling costs are paid at the end of each year, as is the rental of the machine. Assume also that the machines are subject to a CCA rate of 30% and there will be a negligible salvage value in 10 years' time (the end of each machine's life). The marginal corporate tax…arrow_forward
- Need-Based Accounting Corp. has just purchased 10 photocopiers for a total cost of $500,000. The CCA rate for these photocopiers is 20%. The company plans to use these photocopiers for 10 years. By the end of the 10th year, the company expects to move into new imaging system that will no longer require the photocopiers, and the asset pool will then be closed. If the company can sell the photocopiers for $50,000 in 10 years’ time, what amount of terminal loss/CCA recapture can be claimed after the photocopiers have been sold? Assume that half-year rule applies. Please show all calculation steps:arrow_forwardSantana Rey is considering the purchase of equipment for Business Solutions that would allow the company to add a new product to its computer furniture line. The equipment is expected to cost $280,000 and to have a five-year life and no salvage value. It will be depreciated on a straight-line basis. Business Solutions expects to sell 100 units of the equipment’s product each year. The expected annual income related to this equipment follows. Sales $ 385,000 Costs Materials, labor, and overhead (except depreciation) 193,000 Depreciation on new equipment 56,000 Selling and administrative expenses 32,000 Total costs and expenses 281,000 Pretax income 104,000 Income taxes (30%) 31,200 Net income $ 72,800 Required: (1) Compute the payback period. (2) Compute the accounting rate of return for this equipment.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education