
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edition)
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780133594140
Author: James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
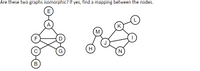
Transcribed Image Text:Are these two graphs isomorphic? If yes, find a mapping between the nodes.
E
A
K
(M
F
H
G
N
В
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- One can manually count path lengths in a graph using adjacency matrices. Using the simple example below, produces the following adjacency matrix: A B A 1 1 B 1 0 This matrix means that given two vertices A and B in the graph above, there is a connection from A back to itself, and a two-way connection from A to B. To count the number of paths of length one, or direct connections in the graph, all one must do is count the number of 1s in the graph, three in this case, represented in letter notation as AA, AB, and BA. AA means that the connection starts and ends at A, AB means it starts at A and ends at B, and so on. However, counting the number of two-hop paths is a little more involved. The possibilities are AAA, ABA, and BAB, AAB, and BAA, making a total of five 2-hop paths. The 3-hop paths starting from A would be AAAA, AAAB, AABA, ABAA, and ABAB. Starting from B, the 3-hop paths are BAAA, BAAB, and BABA. Altogether, that would be eight 3-hop paths within this graph. Write a program…arrow_forwardLet G be a graph with n vertices. If the maximum size of an independent set in G is k, clearly explain why the minimum size of a vertex cover in G is n - k.arrow_forwardPlease solve with the computer Question 2: Draw a simple undirected graph G that has 11 vertices, 7 edges.arrow_forward
- Consider an undirected graph G with 100 nodes. The maximum number of edges to be included in G so that the graph is not connected isarrow_forwardCan you help me solve this exercise? Please note that the greedy approach described in the advice paragraph does not work.arrow_forwardI have a directed graph with N nodes. How can I tell if the graph has a cycle? Your answer should be an algorithm in English. It is nice but not essential for you to give the name of the algorithm. You should describe how the algorithm works.arrow_forward
- Select the graph that is not regular. в D B D D C A Barrow_forward3. Use the graph to answer the following questions: a. Can there be a path of length bigger than 2 in the graph? Explain. b. Are there any non-trivial cycles in the graph? Explain. c. Give a trail of length 4. d. Give all self-loops in the graph.arrow_forwardWrite an algorithm using depth-first search that determines if a graph is bipartite. What is the complexity of your algorithm?arrow_forward
- A. Let G be a graph on 17 vertices. We know that G contains at most one cycle. How many edges can G contain at the most? B. The expression r is written in post-order notation (also referred to as RPN). What value does r evaluate to? r = 1 6 7 + - 5 3 + 2 * +arrow_forwardConsider the following directed graph. E N B C Which of the following are valid cycles? A, A, D A, D, C, A A, A, A, A, A C, E, B, C A E, D, C, B, E C, E, Barrow_forwardWe recollect that Kruskal's Algorithm is used to fi nd the minimum spanning tree in a weighted graph. Given a weighted undirected graph G = (V , E, W), with n vertices/nodes, the algorithm will fi rst sort the edges in E according to their weights. It will then select (n-1) edges with smallest weights that do not form a cycle. (A cycle in a graph is a path along the edges of a graph that starts at a node and ends at the same node after visiting at least one other node and not traversing any of the edges more than once.) Use Kruskal's Algorithm to nd the weight of the minimum spanning tree for the following graph.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON
Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780133594140Author:James Kurose, Keith RossPublisher:PEARSON Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science
Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...Computer EngineeringISBN:9780124077263Author:David A. Patterson, John L. HennessyPublisher:Elsevier Science Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning
Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)Computer EngineeringISBN:9781337569330Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean AndrewsPublisher:Cengage Learning Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning
Concepts of Database ManagementComputer EngineeringISBN:9781337093422Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. LastPublisher:Cengage Learning Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education
Prelude to ProgrammingComputer EngineeringISBN:9780133750423Author:VENIT, StewartPublisher:Pearson Education Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY
Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...Computer EngineeringISBN:9781119368830Author:FITZGERALDPublisher:WILEY

Computer Networking: A Top-Down Approach (7th Edi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133594140
Author:James Kurose, Keith Ross
Publisher:PEARSON

Computer Organization and Design MIPS Edition, Fi...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780124077263
Author:David A. Patterson, John L. Hennessy
Publisher:Elsevier Science

Network+ Guide to Networks (MindTap Course List)
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337569330
Author:Jill West, Tamara Dean, Jean Andrews
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Concepts of Database Management
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781337093422
Author:Joy L. Starks, Philip J. Pratt, Mary Z. Last
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Prelude to Programming
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9780133750423
Author:VENIT, Stewart
Publisher:Pearson Education

Sc Business Data Communications and Networking, T...
Computer Engineering
ISBN:9781119368830
Author:FITZGERALD
Publisher:WILEY