
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
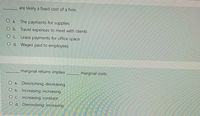
Transcribed Image Text:are likely a fixed cost of a firm.
O a. The payments for supplies
O b. Travel expenses to meet with clients
O c. Lease payments for office space
O d. Wages paid to employees
marginal returns implies
marginal costs.
O a. Diminishing; decreasing
O b. Increasing: increasing
Oc. Increasing; constant
O d. Diminishing: increasing
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure at right illustrates short-run cost curves for a firm. Based on this figure, which of the following is true? O A. A is the total cost curve, B is the marginal cost curve, and C is the total fixed cost curve. O B. A is the average variable cost curve, B is the total fixed cost curve, and C is the average total cost curve. O C. A is the total cost curve, B is the total variable cost curve, and C is the total fixed cost curve. O D. A is the total cost curve, B is the total variable cost curve, and C is the marginal cost curve. O E. A is the average variable cost curve, B is the average total cost curve, and C is the marginal cost curve. Quantity сarrow_forward4. The shape of a firm's long-run average cost curve depends o how costs vary with scale of operation. Draw a long-run average cost curve for a firm that exhibits economies of scale, constant returns to scale, and diseconomies of scale. Identify each of these sections of the cost curve and explain why each section exemplifies its specific type of return to scale.arrow_forwardQUESTION 18 Table Average Average Average Total Total Fixed Variable Marginal Quantity Fixed Variable Cost Cost Cost Cost Cost Cost Cost $50 S50 SO -- -- -- 1 $150 A C D E F G H I S120 J K 3 M P $120 R Refer to Table. Based on the information given in the above table, the value of F will be O a. $200 O b.$50 O c. $150 O d. $100arrow_forward
- Consider the three figures below, depicting possible cost functions for a firm. The horizontal axis measures output in all figures, while the vertical axis measures dollars. A B Which of the following statements are correct? Choose one or more: ⒸA. Figure A could represent the average total cost. OB. Figure B could represent the average total cost. C. Figure C could represent the average total cost. OD. If Figure B represents the average variable cost, then Figure C could not represent the average total cost. OE. If Figure B represents the marginal cost, then Figure C cannot represent the average total cost.arrow_forwardWhich of the following statements is correct? OA. Accounting profit is typically larger than economic profit. O B. Accounting profit equals the firm's revenues minus all of its costs, implicit and explicit. OC. Economic profit equals the firm's revenues minus its explicit costs O D. All of the abovearrow_forward5,000 Total Cost 10,000 O a.) The profit is maximized. Profit Total Revenue b.) The firm should increase output 15,000 Based on this graph, which of the following statements is true at an output of 7,000 indicated by the green line? Output Oc.) The slopes of the total revenue and total cost curves are equal. O d.) The cost is rising faster than the revenue.arrow_forward
- A firm has a fixed production cost of $1,000 and a constant marginal cost of production of $700 per unit produced. What is the firm's total cost function? O A. TC = 1,000 + (700q) O B. TC = 1,000 + (700q). OC. TC = 700q. O D. TC = 1,000. The firm's average total cost (ATC) of production is O A. ATC = 1,000 + (700q). OB. 1,000 + (700q) ATC = Oc. 1,000 ATC = O D. ATC = 700q. O E. ATC = 700. If the firm wanted to minimize the average total cost, would it choose to be very large or very small? Explain. OA. very small because the average total cost of production rises with output. O B.- very large because the average variable cost of production falls with output. OC. very small because the average fixed cost of production rises with output. O D. very small because the total cost of production rises with output. O E. very large because the average total cost of production falls with output.arrow_forwardhould a competitive firm ever produce when it is losing money? Why or why not? D A. No, the firm should shutdown if it is making an accounting loss. O B. No, the firm should shutdown if it is making an economic loss. O C. Yes, as long as revenue can cover total variable costs plus any portion of fixed costs. O D. Yes, as long as revenue can cover some portion of total variable costs.arrow_forward4.arrow_forward
- Please please a answer both I will ratearrow_forward. What are the firm's fixed costs?$ c. What is the variable cost of producing 475 units of output (use least-cost)?$ d. How many units of the variable input should be used to maximize profits?e. What are the maximum profits this firm can earn?$ f. Over what range of the variable input usage do increasing marginal returns exist?From ___ to ____g. Over what range of the variable input usage do decreasing marginal returns exist?From ___ to ___h. Over what range of input usage do negative marginal returns exist?From ___ to ___ . What are the firm's fixed costs?$ c. What is the variable cost of producing 475 units of output (use least-cost)?$ d. How many units of the variable input should be used to maximize profits?e. What are the maximum profits this firm can earn?$ f. Over what range of the variable input usage do increasing marginal returns exist?From to g. Over what range of the…arrow_forwardPlease answer both and give explanation of correct and incorrect options and get likearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education