
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
an you please answer drop down question, A, and B
A.
H0 =
p1 or μ1 (=,<,>, ≠ ) p2 or μ2
H1=
p1 or μ1 (=,<,>, ≠ ) p2 or μ2
B. Z or T
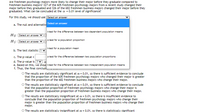
Transcribed Image Text:Are freshmen psychology majors more likely to change their major before they graduate compared to
freshmen business majors? 327 of the 605 freshmen psychology majors from a recent study changed their
major before they graduated and 326 of the 682 freshmen business majors changed their major before they
graduated. What can be concluded at the a = 0.01 level of significance?
For this study, we should use Select an answer
Select an answer
a. The null and alternativ
t-test for the difference between two dependent population means
Ho: Select an answer
z-test for a population proportion
H1: Select an answer
t-test for a population mean
b. The test statistic ? V
c. The p-value =
z-test for the difference between two population proportions
d. The p-value is ?V a
e. Based on this, we shoul t-test for the difference between two independent population means
f. Thus, the final conclusi.
The results are statistically significant at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude
that the proportion of the 605 freshmen psychology majors who changed their major is greater
than the proportion of the 682 freshmen business majors who change their major.
The results are statistically significant at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude
that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their major is
greater than the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their major.
O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.01, so there is insufficient evidence to
conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their
major is greater than the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their
major.
O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.01, so there is statistically significant
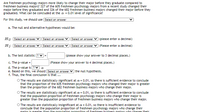
Transcribed Image Text:Are freshmen psychology majors more likely to change their major before they graduate compared to
freshmen business majors? 327 of the 605 freshmen psychology majors from a recent study changed their
major before they graduated and 326 of the 682 freshmen business majors changed their major before they
graduated. What can be concluded at the a = 0.01 level of significance?
For this study, we should use Select an answer
a. The null and alternative hypotheses would be:
Ho: Select an answer
Select an answer
Select an answer
(please enter a decimal)
Hj: Select an answer
Select an answer
| (Please enter a decimal)
Select an answer
b. The test statistic ? v=
(please show your answer to 3 decimal places.)
c. The p-value =
(Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.)
d. The p-value is ?V a
e. Based on this, we should Select an answer
) the null hypothesis.
f. Thus, the final conclusion is that ...
O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude
than the proportion of the 682 freshmen business majors who change their major.
O The results are statistically significant at a = 0.01, so there is sufficient evidence to conclude
that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their major is
that the proportion of the 605 freshmen psychology majors who changed their major is greater
greater than the population proportion of freshmen business majors who change their major.
O The results are statistically insignificant at a = 0.01, so there is insufficient evidence to
conclude that the population proportion of freshmen psychology majors who change their
maior is areater than the ponulation pronortion off freshmen business maiors who change their
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Grades for Keyla Hernandez Bac x A ALEKS - Keyla Hemandez Baca www-awu.aleks.com/alekscgi/x/Isl.exe/1o_u-lgNslkr7j8P3H-liGQxpKIf4w-aQ-rw-zRhgRnayfmbBs65spE7xc4HUZ9GGhbh9fvh3qAPbDgWDIOH asuprep.org bookmarks C Infinite Campus Dashboard C Clever | Portal Courses Earned A. S Simplenote O Launch Meeting - Z O Greek Myths Harry Potter 1-Go O STATISTICS AND PROBABILITY Counting principle with repetition allowed Suppose each license plate In a certaln state has two digits, followed by two letters, followed by two digits. The letters Q and U are not used. So, there are 24 letters and 10 digits that are used. Assume that the letters and digits can be repeated, How many license plates can be generated using this format? license plates Expnation Checkarrow_forward#6arrow_forwarda researcher wants to determine the average amount of minutes it takes for the medicine to reduce the pain for adult males. The researcher contacted 107 subjects to participate in the study, n=but only got results from 79 of the subjects. The average time it took for the medicine to reduce headache pain of these subjects was 27 minutes. What is the population? What is the sample? What tis the parameter? What is the symbol for this parameter? What is the statistics? What is the symbol for this statistics?arrow_forward
- please answer in text form and in proper format answer with must explanation , calculation for each part and steps clearlyarrow_forwardQuestion-based on, "area of sectors". Also, how to find the area of the sector too... I have tried it but both answers are incorrect.arrow_forwardMatch the linear correlation coefficient value that best approximate each given scatter diagram. The scales on the x-axis and y-axis are the same for each scatter diagram. Explanatory (1) Explanatory (II) Explanatory (IV) Explanatory (111) Response Response Response Responsearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman