
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
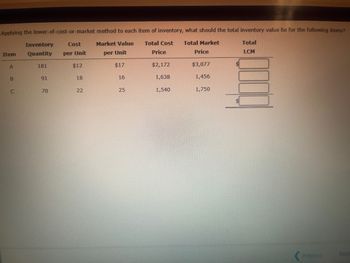
Transcribed Image Text:Applying the lower-of-cost-or-market method to each item of inventory, what should the total inventory value be for the following items?
Total Cost Total Market
Inventory
Item
Quantity
Cost
per Unit
Market Value
Total
per Unit
Price
Price
LCM
A
181
$12
$17
$2,172
$3,077
$
B
91
18
16
1,638
1,456
C
70
10
22
25
1,540
1,750
Previous
Next
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- On the basis of the following data, determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market. Assemble the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 10. Product InventoryQuantity Cost PerUnit Market Value per Unit(Net Realizable Value) Class 1: Model A 25 $113 $127 Model B 13 274 289 Model C 17 217 195 Class 2: Model D 31 70 59 Model E 39 61 45 Question Content Area a. Determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market applied to each item in the inventory. Inventory at the Lower of Cost or Market Product InventoryQuantity Costper Unit Market Valueper Unit(Net RealizableValue) Cost Market Lower ofCost orMarket Model A Model A $Model A $Model A $Model A $Model A $Model A Model B Model B Model B Model B Model B Model B Model B Model C Model C Model C…arrow_forwardLower-of-Cost-or-Market Method On the basis of the data shown below: Item InventoryQuantity Cost perUnit Market Value per Unit(Net Realizable Value) A13Y 152 $49 $52 O5T4 290 25 22 Determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market by applying lower of cost or market to each inventory item, as shown in Exhibit 9. $arrow_forward< Lower-of-Cost-or-Market Inventory On the basis of the following data, determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market. Product Adams Coolidge McKinley Garfield Lincoln Total Feedback Inventory Quantity Cost per Unit 45 13 47 23 36 $206 239 211 289 262 Market Value per Unit (Net Realizable Value) $191 232 200 296 241 $ Cost Total Market $ 26,980 X $ LCM 24,478 X Check My Work Multiply the number of units by the unit cost price and enter the total cost amount in the Cost column. Multiply the number of units by the unit market price and enter the total market amount in the Market column. Then, enter the lower of the two amounts from the Cost and Market columns in the LCM column. Finally, total the columns. The total of the LCM column shows the total lower-of-cost-or-market applied on an item-by-item basis. ?arrow_forward
- Company Z had the following information: inventory at cost of $5,100, selling value of inventory of $5,250, inventory cost of completion of $100, inventory cost of distribution of $150, normal profit margin of $2,000, and inventory replacement cost of $4,800. What is the floor amount to be used in the determination of the inventory's market value in the lower-of- cost-or-market method of inventory? O $3,000 O $5,000 O $4,800 O $5,250arrow_forwardOn the basis of the following data, determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market. Apply lower of cost or market to each inventory item. Item A B с Total Inventory Quantity 181 82 60 Cost per Unit $10 14 20 Market value per Unit $14 11 22 Cost $1,810 1,148 1,200 Total Market $2,534 902 1,320 LA LCMarrow_forwardUsing the lower of cost or market, what should the total inventory value be for the following items: Item Quantity Unit cost price Unit market price Total cost price Total market price A 200 $15 $14.50 $3,000 $2,900 B 100 $14 $15.00 $1,400 $1,500 C 50 $17 $17.50 $850 $875arrow_forward
- Lower-of-Cost-or-Market InventoryOn the basis of the following data, determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market. Assemble the data in the form illustrated in Exhibit 9. ProductInventoryQuantityUnitCost PriceUnitMarket Value per Unit(Net Realizable Value)Model A300$140$125Model B50090112Model C1506059Model D800120115Model E400140145 Inventory at the Lower of Cost or MarketProductTotal CostTotal MarketLower of Total Cost or Total MarketA$$$B C D E Total$$$arrow_forwardBased on the data below, how would the merchandise inventory appear on the balance sheet, assuming that the lower of cost or market is used and the cost is determined by the FIFO method? Total cost: $74, 300 Total market: $72,900 Lower of cost or market: $70, 400 The merchandise inventory would appear in the current assets section, as follows: Merchandise inventory - at lower of cost (FIFO) or market isarrow_forwardLower-of-Cost-or-Market Inventory On the basis of the following data, determine the value of the inventory at the lower of cost or market. Total Product Inventory Quantity Cost per Unit Market Value perUnit (Net Realizable Value) Cost Market LCM Adams 22 $51 $58 $ $ $ Coolidge 23 224 237 McKinley 27 167 152 Garfield 32 58 49 Lincoln 35 263 270 Total $ $ $arrow_forward
- On the basis of the following data, what is the value of the total inventory at the lower of cost or market? Apply lower of cost or market to each inventory item. Inventory Quantity Item Product C Product D a. $6,840 b. $6,540 c. $7,380 d. $6,300 300 420 Unit Cost Price $6 12 Unit Market Price $5 14arrow_forward16. Use the following information to calculate inventory applying LCNRV by item: Recorded cost $12 $22 $17 $42 $32 $18 Еxpected sales price $16 $24 $19 Disposal Costs $2 $5 Item A Item B Item C $2 Item D $60 $40 $6 Item E $6 Item F $24 $7arrow_forward1.At a time of declining prices, which cost flow assumption will result in the highest ending inventory? A. FIFO B. LIFO C. Weighted average D. Either A or C 2. When the cost of inventory is rising, which inventory cost flow method will produce the lowest amount of cost of goods sold? A. FIFO B. Weighted Average. C. All methods will produce the same amount of cost of goods sold. D. LIFO 200 The inventory records for Raymond Co. reflected the following Beginning Inventory @ May 1 200 units @ $1.00 First Purchase @ May 7 Second Purchase @ May 17 Third Purchase @ May 23 Sales @ May 31 B. $1.15 C. $1.14 D. $1.31 B. $130 C. $324 D. $340 300 units @ $1.10 = 400 units @ $1.20 100 units @ $1.30 = 120 900 units @ $1.50 1350 30 go 3. Determine the weighted average cost per unit for May. A. $1.22 .4.Determine the amount of cost of goods sold assuming the LIFO cost flow method. A. $1,140 B. $1,040 C. $1,000 D. $940 5. Determine the amount of gross margin assuming the FIFO cost flow method. A. $114arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education