
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
(Repost) Dynamic force analysis for linkage
![OA
0.90
CG
Length
[m]
3.25 2.75 5.50 0.55 1.85
AB
BC
BD
2. Velocity Analysis
OE
CE
2.20 2.581 3.15
Present a clearly labelled velocity diagram;
4. Dynamic Forces Analysis
• Calculate the magnitude and direction of:
o velocity of point A;
o velocity of point B.
• Calculate angular velocities of links AB and BC.
H
3. Acceleration Analysis
• Present a clearly labelled acceleration diagram;
Calculate the magnitudes and directions of:
o acceleration of points A and B;
o angular acceleration of links AB and BC;
o accelerations of points G.
B
WOA
[deg] [rad/s]
1. Geometry Calculations
Using the given geometrical parameters above, calculate angles and Y, distance OC and any
other required angles and distances.
160.0 3.0
M BD
Mass
[kg]
3000
J BD
Mass moment of
inertia
[kg.m²]
2200
Present a clearly labelled free body diagram for each rod and the slider;
• Calculate the magnitudes and directions of all reaction forces at the instant shown using
accelerations obtained in acceleration analysis part;
Calculate the instantaneous torque, T, required to drive the mechanism at the instant
shown.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/e06819f9-dae6-4bd0-9585-26daba0604c4/825358d1-1ece-4aac-9bf6-4f63dd79646a/v5vafv5_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:OA
0.90
CG
Length
[m]
3.25 2.75 5.50 0.55 1.85
AB
BC
BD
2. Velocity Analysis
OE
CE
2.20 2.581 3.15
Present a clearly labelled velocity diagram;
4. Dynamic Forces Analysis
• Calculate the magnitude and direction of:
o velocity of point A;
o velocity of point B.
• Calculate angular velocities of links AB and BC.
H
3. Acceleration Analysis
• Present a clearly labelled acceleration diagram;
Calculate the magnitudes and directions of:
o acceleration of points A and B;
o angular acceleration of links AB and BC;
o accelerations of points G.
B
WOA
[deg] [rad/s]
1. Geometry Calculations
Using the given geometrical parameters above, calculate angles and Y, distance OC and any
other required angles and distances.
160.0 3.0
M BD
Mass
[kg]
3000
J BD
Mass moment of
inertia
[kg.m²]
2200
Present a clearly labelled free body diagram for each rod and the slider;
• Calculate the magnitudes and directions of all reaction forces at the instant shown using
accelerations obtained in acceleration analysis part;
Calculate the instantaneous torque, T, required to drive the mechanism at the instant
shown.
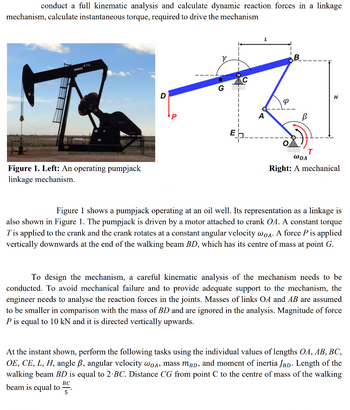
Transcribed Image Text:conduct a full kinematic analysis and calculate dynamic reaction forces in a linkage
mechanism, calculate instantaneous torque, required to drive the mechanism
470
Figure 1. Left: An operating pumpjack
linkage mechanism.
D
G
E
A
Φ
B
B
T
H
WOA
Right: A mechanical
Figure 1 shows a pumpjack operating at an oil well. Its representation as a linkage is
also shown in Figure 1. The pumpjack is driven by a motor attached to crank OA. A constant torque
T' is applied to the crank and the crank rotates at a constant angular velocity wOA. A force P is applied
vertically downwards at the end of the walking beam BD, which has its centre of mass at point G.
To design the mechanism, a careful kinematic analysis of the mechanism needs to be
conducted. To avoid mechanical failure and to provide adequate support to the mechanism, the
engineer needs to analyse the reaction forces in the joints. Masses of links OA and AB are assumed
to be smaller in comparison with the mass of BD and are ignored in the analysis. Magnitude of force
P is equal to 10 kN and it is directed vertically upwards.
At the instant shown, perform the following tasks using the individual values of lengths OA, AB, BC,
OE, CE, L, H, angle ß, angular velocity wOA, mass mBD, and moment of inertia JBD. Length of the
walking beam BD is equal to 2-BC. Distance CG from point C to the centre of mass of the walking
BC
beam is equal to
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 9 images

Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Apologies but unsure how values for Vb (2.64) and the other value 4.08 were actually calculated from the velocity diagram
Transcribed Image Text:conduct a full kinematic analysis and calculate dynamic reaction forces in a linkage
mechanism, calculate instantaneous torque, required to drive the mechanism
470
Figure 1. Left: An operating pumpjack
linkage mechanism.
D
G
E
A
Φ
B
B
T
H
WOA
Right: A mechanical
Figure 1 shows a pumpjack operating at an oil well. Its representation as a linkage is
also shown in Figure 1. The pumpjack is driven by a motor attached to crank OA. A constant torque
T' is applied to the crank and the crank rotates at a constant angular velocity wOA. A force P is applied
vertically downwards at the end of the walking beam BD, which has its centre of mass at point G.
To design the mechanism, a careful kinematic analysis of the mechanism needs to be
conducted. To avoid mechanical failure and to provide adequate support to the mechanism, the
engineer needs to analyse the reaction forces in the joints. Masses of links OA and AB are assumed
to be smaller in comparison with the mass of BD and are ignored in the analysis. Magnitude of force
P is equal to 10 kN and it is directed vertically upwards.
At the instant shown, perform the following tasks using the individual values of lengths OA, AB, BC,
OE, CE, L, H, angle ß, angular velocity wOA, mass mBD, and moment of inertia JBD. Length of the
walking beam BD is equal to 2-BC. Distance CG from point C to the centre of mass of the walking
BC
beam is equal to
![OA
0.90
CG
Length
[m]
3.25 2.75 5.50 0.55 1.85
AB
BC
BD
2. Velocity Analysis
OE
CE
2.20 2.581 3.15
Present a clearly labelled velocity diagram;
4. Dynamic Forces Analysis
• Calculate the magnitude and direction of:
o velocity of point A;
o velocity of point B.
• Calculate angular velocities of links AB and BC.
H
3. Acceleration Analysis
• Present a clearly labelled acceleration diagram;
Calculate the magnitudes and directions of:
o acceleration of points A and B;
o angular acceleration of links AB and BC;
o accelerations of points G.
B
WOA
[deg] [rad/s]
1. Geometry Calculations
Using the given geometrical parameters above, calculate angles and Y, distance OC and any
other required angles and distances.
160.0 3.0
M BD
Mass
[kg]
3000
J BD
Mass moment of
inertia
[kg.m²]
2200
Present a clearly labelled free body diagram for each rod and the slider;
• Calculate the magnitudes and directions of all reaction forces at the instant shown using
accelerations obtained in acceleration analysis part;
Calculate the instantaneous torque, T, required to drive the mechanism at the instant
shown.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/e06819f9-dae6-4bd0-9585-26daba0604c4/12ba5bfe-6ad0-4520-8d1a-6ec0b965fe65/o8cyttl_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:OA
0.90
CG
Length
[m]
3.25 2.75 5.50 0.55 1.85
AB
BC
BD
2. Velocity Analysis
OE
CE
2.20 2.581 3.15
Present a clearly labelled velocity diagram;
4. Dynamic Forces Analysis
• Calculate the magnitude and direction of:
o velocity of point A;
o velocity of point B.
• Calculate angular velocities of links AB and BC.
H
3. Acceleration Analysis
• Present a clearly labelled acceleration diagram;
Calculate the magnitudes and directions of:
o acceleration of points A and B;
o angular acceleration of links AB and BC;
o accelerations of points G.
B
WOA
[deg] [rad/s]
1. Geometry Calculations
Using the given geometrical parameters above, calculate angles and Y, distance OC and any
other required angles and distances.
160.0 3.0
M BD
Mass
[kg]
3000
J BD
Mass moment of
inertia
[kg.m²]
2200
Present a clearly labelled free body diagram for each rod and the slider;
• Calculate the magnitudes and directions of all reaction forces at the instant shown using
accelerations obtained in acceleration analysis part;
Calculate the instantaneous torque, T, required to drive the mechanism at the instant
shown.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
Confused where the value 2.64 came for vb. You say vb equals 2.64 but also 4.08
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Questions
Read through expert solutions to related follow-up questions below.
Follow-up Question
Apologies but unsure how values for Vb (2.64) and the other value 4.08 were actually calculated from the velocity diagram

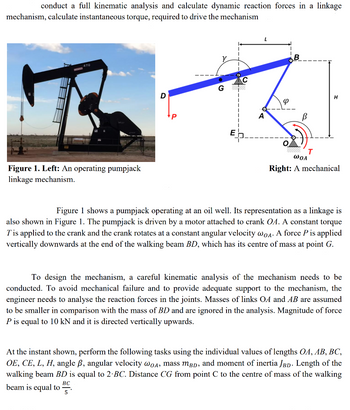
Transcribed Image Text:conduct a full kinematic analysis and calculate dynamic reaction forces in a linkage
mechanism, calculate instantaneous torque, required to drive the mechanism
470
Figure 1. Left: An operating pumpjack
linkage mechanism.
D
G
E
A
Φ
B
B
T
H
WOA
Right: A mechanical
Figure 1 shows a pumpjack operating at an oil well. Its representation as a linkage is
also shown in Figure 1. The pumpjack is driven by a motor attached to crank OA. A constant torque
T' is applied to the crank and the crank rotates at a constant angular velocity wOA. A force P is applied
vertically downwards at the end of the walking beam BD, which has its centre of mass at point G.
To design the mechanism, a careful kinematic analysis of the mechanism needs to be
conducted. To avoid mechanical failure and to provide adequate support to the mechanism, the
engineer needs to analyse the reaction forces in the joints. Masses of links OA and AB are assumed
to be smaller in comparison with the mass of BD and are ignored in the analysis. Magnitude of force
P is equal to 10 kN and it is directed vertically upwards.
At the instant shown, perform the following tasks using the individual values of lengths OA, AB, BC,
OE, CE, L, H, angle ß, angular velocity wOA, mass mBD, and moment of inertia JBD. Length of the
walking beam BD is equal to 2-BC. Distance CG from point C to the centre of mass of the walking
BC
beam is equal to
![OA
0.90
CG
Length
[m]
3.25 2.75 5.50 0.55 1.85
AB
BC
BD
2. Velocity Analysis
OE
CE
2.20 2.581 3.15
Present a clearly labelled velocity diagram;
4. Dynamic Forces Analysis
• Calculate the magnitude and direction of:
o velocity of point A;
o velocity of point B.
• Calculate angular velocities of links AB and BC.
H
3. Acceleration Analysis
• Present a clearly labelled acceleration diagram;
Calculate the magnitudes and directions of:
o acceleration of points A and B;
o angular acceleration of links AB and BC;
o accelerations of points G.
B
WOA
[deg] [rad/s]
1. Geometry Calculations
Using the given geometrical parameters above, calculate angles and Y, distance OC and any
other required angles and distances.
160.0 3.0
M BD
Mass
[kg]
3000
J BD
Mass moment of
inertia
[kg.m²]
2200
Present a clearly labelled free body diagram for each rod and the slider;
• Calculate the magnitudes and directions of all reaction forces at the instant shown using
accelerations obtained in acceleration analysis part;
Calculate the instantaneous torque, T, required to drive the mechanism at the instant
shown.](https://content.bartleby.com/qna-images/question/e06819f9-dae6-4bd0-9585-26daba0604c4/12ba5bfe-6ad0-4520-8d1a-6ec0b965fe65/o8cyttl_thumbnail.png)
Transcribed Image Text:OA
0.90
CG
Length
[m]
3.25 2.75 5.50 0.55 1.85
AB
BC
BD
2. Velocity Analysis
OE
CE
2.20 2.581 3.15
Present a clearly labelled velocity diagram;
4. Dynamic Forces Analysis
• Calculate the magnitude and direction of:
o velocity of point A;
o velocity of point B.
• Calculate angular velocities of links AB and BC.
H
3. Acceleration Analysis
• Present a clearly labelled acceleration diagram;
Calculate the magnitudes and directions of:
o acceleration of points A and B;
o angular acceleration of links AB and BC;
o accelerations of points G.
B
WOA
[deg] [rad/s]
1. Geometry Calculations
Using the given geometrical parameters above, calculate angles and Y, distance OC and any
other required angles and distances.
160.0 3.0
M BD
Mass
[kg]
3000
J BD
Mass moment of
inertia
[kg.m²]
2200
Present a clearly labelled free body diagram for each rod and the slider;
• Calculate the magnitudes and directions of all reaction forces at the instant shown using
accelerations obtained in acceleration analysis part;
Calculate the instantaneous torque, T, required to drive the mechanism at the instant
shown.
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Follow-up Question
Confused where the value 2.64 came for vb. You say vb equals 2.64 but also 4.08
Solution
by Bartleby Expert
Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Problem 4-6a The link lengths (a, b, c, d) and the value of 2 for a crank-rocker linkage are defined as 2, 7, 9, 6, 30°, respectively. Draw the scaled linkage. Find all possible solutions (both open and crossed) for angles 03 and 04 graphically. Орen B A LNCS 4 a GCS र 4 4" Crossed (This is not the scaled kinematic diagram.) Problem 4-7a Repeat Problem 4-6a except solve by the vector loop method.arrow_forwardI only need help with the last two parts (not the mobility)arrow_forwarddraw the final resultsarrow_forward
- herr solving pls very urgentarrow_forwardShow how you would find the velocity of each point (no values given just the equation) for an overlapping/superimpose 4 bar linkage. Find the equation for 0 degree.arrow_forwardi need to solve part b pls quickk very urgent part (a) is solvedarrow_forward
- Problem 4-14a Find the worst value of the transmission angle for a crank-rocker linkage with link lengths (a, b, c, d) of 2, 7, 9, 6, respectively.arrow_forwardFor the four-bar linkages below, indicate whether they are Grashof type 1 or 2 and whether they are crank-rocker, dourble-crank, or double-rocker mechanisms. A t 7" 8" 6" 5" (a) 5" (b) 7" 8" 4" 6" (c)arrow_forwardTopic: Grashof's Law - Four Bar Linkage MechanismWhat are the different links and how to identify which is which?Please watch this video for reference: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h8bz4ni6mdY&t=145sarrow_forward
- Q3. You should draw a three DoF (Degree of freedom) eight link (n=8) mechanism with revolute joints. You should verify DoF mechanism using mobility formulations.arrow_forwardPls i need her solving with count the nb in grapharrow_forwardi need her solving all part with count the number of link and full joint on the graph very urgent and what means the character of assemblyarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY