
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781337091992
Author: N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
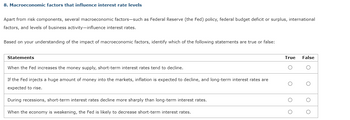
Transcribed Image Text:## 8. Macroeconomic Factors that Influence Interest Rate Levels
Apart from risk components, several macroeconomic factors—such as Federal Reserve (the Fed) policy, federal budget deficit or surplus, international factors, and levels of business activity—influence interest rates.
Based on your understanding of the impact of macroeconomic factors, identify which of the following statements are true or false:
| Statements | True | False |
|------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------|------|-------|
| When the Fed increases the money supply, short-term interest rates tend to decline. | | |
| If the Fed injects a huge amount of money into the markets, inflation is expected to decline, and long-term interest rates are expected to rise. | | |
| During recessions, short-term interest rates decline more sharply than long-term interest rates. | | |
| When the economy is weakening, the Fed is likely to decrease short-term interest rates. | | |
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The table below shows the amount of savings and borrowing in a market for loans to purchase homes, measured in millions of dollars, at various interest rates. InterestRate QuantitySupplied QuantityDemanded5% 98 2216% 129 1917% 160 1608% 178 1429% 196 12410% 214 106 What is the equilibrium interest rate and quantity of loaned funds? r = % Q = Suppose there is a decrease in demand of money, what will happen to interest rates and quantity? Increase in Interest Rates, Increase in Quantity?Increase in Interest Rates, Decrease in Quantity?Decrease in Interest Rates, Increase in Quantity?Decrease in Interest Rates, Decrease in Quantity?arrow_forward3. Most global markets have been reporting severe contractions, which mainly responding to the COVID-19 pandemic. The situation is worsened by the decrease in people’s confidence in the government as policymakers, spreading a wave of pessimism towards the future prospect of the economy. Explain how such wave of pessimism, ceteris paribus, may lead to short-term economic fluctuations, which will eventually work to push the economy back towards its long-run equilibrium. Use relevant diagrams to support your answer.arrow_forwardIdentify the effect of recession in the economy on either demand or supply curve and the equilibrium interest rates. kindly use a graph in your explanation.arrow_forward
- Urgently needarrow_forward33) Which of the following is NOT true according to classical macroeconomics theory? Given output and the interest rate, the price level adjusts to balance the supply of, and demand for, money. Output is determined by the supplies of capital and labor and the available production technology. For any given level of output, the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply of, and demand for, money. For any given level of output, the interest rate adjusts to balance the supply of, and demand for, loanable funds.arrow_forwardhi, this is macroeconomics question. i need answer ASAP!arrow_forward
- 3. Suppose that the economy is well described by the New-Keynesian with partial sticky prices. Assume that the ZLB on nominal interest rate is binding. In your answer below, keep in mind the consumers' and firms' optimal decisions that give rise to the model and explain how and why agents' decisions change. a) Bank runs generate a large increase in spreads ft in the economy. What are the effects on aggregate outcomes (Y, P, r)? How does it compare to the case where the ZLB is not binding? Use diagram to support your answer b) The Central bank, as lender of last resort, decides to inject large amounts of money into financial institutions. Analyse the transmission mechanism of this policy action as well as its effects on output and price level.arrow_forward1. Refer to the figure below. An increase in interest rate would cause: Price level, P AD₂ B AD ADO Aggregate output, Y A) the aggregate demand curve to shift from AD₁ to AD2 B) the economy to move from Point A to Point B C) the aggregate demand curve to shift from AD₁ to ADo D) neither a shift of the aggregate demand curve nor a change in real GD³arrow_forward72arrow_forward
- Suppose the current economy requires $7 million for transactions. The table below shows the interest rate and asset demand. Interest Rate (%) 12% 10% 8% 6% 4% 2% Multiple Choice What is the total transaction demand when the interest rate is 4 percent? о о о $7 million $6 million $8 million Asset Demand (in millions of Dollars) $3 $6 $9 $22 million $12 $15 $18arrow_forwardWhat happens to the interest rates on bonds during recessions. I am confused becaus During an economic downturn,income and wealth are falling and thus the demand for bonds fall at every price level– the demand curve shifts to the left. Does this decrease the price of bonds meaning higher interest rates? Or an alternartive explanation: In recessions the government tends to cut interest rates in order to stimulate economic activity by creating incentive for banks to lower their rates on loans to consumers and firms, encouraging consumption and investment. This can lead to the interest rates on assets falling. Bonds are often a safe haven during recessionary periods because they offer a fixed income stream in times of uncertainty, and thus they may be favoured to other types of assets invesmtents increasing demand for bonds. The increase in demand Increases price of bonds thus decreases interest rates. or in terms of supply: the supply of bonds may fall because there is less incentive to…arrow_forward8. Macroeconomic factors that influence interest rate levels Apart from risk components, several macroeconomic factors—such as Federal Reserve (the Fed) policy, federal budget deficit or surplus, international factors, and levels of business activity—influence interest rates. Based on your understanding of the impact of macroeconomic factors, identify which of the following statements are true or false: Statements True False When the Fed increases the money supply, short-term interest rates tend to decline. Actions that lower short-term interest rates will always lower long-term interest rates. Long-term interest rates are not as sensitive to booms and recessions as are short-term interest rates. The Federal Reserve’s ability to use monetary policy to control economic activity in the United States is limited because US interest rates are highly dependent on interest rates in other parts of the world.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781337091992Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781285165912Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...EconomicsISBN:9781337091985Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...EconomicsISBN:9781285165875Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305971509Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning

Essentials of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781337091992
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781285165912
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Brief Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Cours...
Economics
ISBN:9781337091985
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Economics, 7th Edition (MindTap Cou...
Economics
ISBN:9781285165875
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Principles of Macroeconomics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305971509
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning