
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
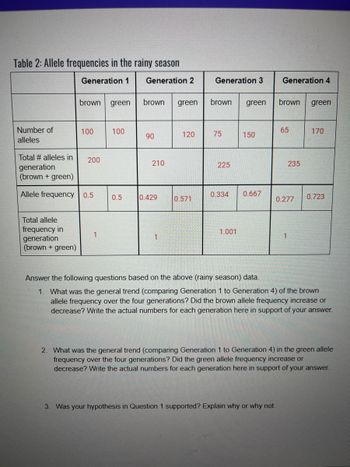
Transcribed Image Text:Table 2: Allele frequencies in the rainy season
Generation 1
Generation 2
Number of
alleles
brown green
Total allele
frequency in
generation
(brown + green)
100
Total # alleles in
generation
(brown + green)
Allele frequency 0.5
200
1
100
0.5
brown green
90
210
0.429
1
120
0.571
Generation 3
brown green
75
225
150
0.334 0.667
1.001
Generation 4
brown green
65
3. Was your hypothesis in Question 1 supported? Explain why or why not.
0.277
235
1
170
0.723
Answer the following questions based on the above (rainy season) data.
1. What was the general trend (comparing Generation 1 to Generation 4) of the brown
allele frequency over the four generations? Did the brown allele frequency increase or
decrease? Write the actual numbers for each generation here in support of your answer.
2. What was the general trend (comparing Generation 1 to Generation 4) in the green allele
frequency over the four generations? Did the green allele frequency increase or
decrease? Write the actual numbers for each generation here in support of your answer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Are these all correct? Last two questions are 8. What is the critical value? Round to two decimal places. 9. What is your conclusion from the chi-square test? option 1: Fail to reject H option 2: Reject Hoarrow_forwardIf the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what is the expected (projected) frequency of heterozygous cats in the next generation? Question 4 options: 0.68 0.89 0.435 0.84arrow_forwardIn a population of millipedes, the gene “R” determines their color. The color red is determined by the dominant “R” allele and the color orange is determined by the recessive “r” allele. A population of 100 millipedes consists of the following genotypes: 30 RR 44 Rr 26 rr Answer the following - You can represent the ratio/frequency as a fraction or a %. A. What is the genotypic ratio of this population of millipedes? B. What is the phenotypic ratio of this population of millipedes? C. What are the allele frequencies for “R” and “r” in this population of millipedes?arrow_forward
- The next several questions refer to the data given in this problem. You sample a population of leafhoppers and genotype 250 individuals at a polymorphic locus with two alleles. You obtain the following numbers: AA = 68 individuals Aa = 54 individuals aa = 128 individuals What is the expected frequency of the AA genotype if the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium( you may round your answer to 3 decimal places) What is the expected frequency of the aa genotype of the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? ( You may round your answer to 3 decimal places)arrow_forwardWhat is the chi-square value of the pumpkin population? round up and use four decimal points After doing some crosses and genotyping some individuals, you determined that the number of individuals homozygous dominant for the largest pumpkin allele is 98, 80 are heterozygous for medium size, and 20 are homozygous recessive for small size.arrow_forwardIn carnations, the red pigment (RR) is incompletely dominant to white (rr). The heterozygote (Rr) is pink. In a randomly mating field of carnations, 42 plants were red, 178 plants were pink, and 180 plants were white (total =400). What is the best estimate of the allele ferequency, for the red allele in this population?arrow_forward
- Can you please make a conclusion for this? Thank you so much! Suppose you counted 79 R_ and 33 rr. The total number of individuals you counted, N, is 112. You expect 3/4 to be R_ (84) and 1/4 to be rr (28). Are your results close enough to these ratios for you to accept the null hypothesis—that there is no real difference? Individual'sPhenotype Observed number Observed Ratio Expected Ratio Expected Number (Observed no. – Expected no.)^2 / Expected number R_ 79 2.8 3 84 (79-84) ^2 = 25/84 = 0.297 rr 33 1.18 1 28 (33-28) ^2 = 25/28 = 0.893 TOTAL: 112 Chi Square Value = 1.19 Degrees of freedom = 1arrow_forwardYou were tasked to conduct a field observation of a population with two distinct forms, which you temporarily named "Big A" and "small b." These two forms mate and produce offspring together. For each form, you tabulated the frequency distribution of lifetime offspring production, as shown in the figure. The filled bars represent the lifetime progeny frequency distribution for "Big A" and the open bars "small b." Which of the following statements is correct? 0 1 2 4 20 # of lifetime progeny "small b" is likely having a male sexual role. "Big A" is likely to have a female sexual role. "small b" is likely to be choosy. Both are likely to be competitive. frequencyarrow_forwardSample A Sample B Sample C Habitat type Sand dunes Grassland Grassland Morph Pink unbanded 1 Pink mid-banded 28 Pink many-banded 45 Yellow unbanded 23 57 Yellow mid-banded 20 12 28 Yellow many-banded 38 78 160 Brown unbanded 70 42 Brown mid-banded 15 25 Brown many-banded 103 83 Total in sample 132 301 395 a. Summarise the data on morph frequencies, allele frequencies and index of polymorphism for the three populations in a table. b. Summarise in a table the estimates of genetic differentiation (FsT) between the populations for both shell colour and banding alleles. Note that you do not need to aenerate bar charts for each of the populations. c. With reference to all the information given in Table 1 and summarised in your tables in (a) and (b), explain how each of these samples differs from the others, and which of the samples are most genetically similar to each other. It should be clear from your answer on what evidence your conclusions are based and your answer should be no more than…arrow_forward
- What is the frequency of the T allele in the current gene pool? Question 3 options: 0.68 0.435 0.52 0.84arrow_forwardThe next several questions refer to the data given in this problem. You sample a population of leafhoppers and genotype 250 individuals at a polymorphic locus with two alleles. You obtain the following numbers: AA = 68 individuals Aa = 54 individuals aa = 128 individuals What is the frequency of the A allele? (You may round your answer to 2 decimal places) What is the expected number of individuals with the AA genotype if the population is in Hardy Weinberg equilibrium? (You may round your answer to the nearest whole number) What is the expected number of individuals with the Aa genotype if the population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? (you may round your answer to the nearest whole number)arrow_forwardA species of butterfly shows variation in the length of the antennae. You measure antennae in a butterfly population and find the mean to be 15 mm. You calculate a heritability of antennae length to be 1 (h2 = 1). %3D That summer, there is a severe drought. Many of the butterflies die and only a few survive to reproduce. The surviving butterflies have a mean antennae length of 17 mm. a) What is the predicted mean limb-length of the offspring of the surviving butterflies? [ Select ] b) What type of selection was acting on antennae length in these butterflies? [ Select ] c) Five years later, you go back and measure antennae length in this butterfly population again. Every butterfly in the population has antennae measuring 16 mm. What is the heritability of antennae length in this population now? [Select ]arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education