
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Angie March owns a catering company that stages banquets and parties for both individuals and companies. The business is seasonal,
with heavy demand during the summer months and year-end holidays and light demand at other times. Angle has gathered the
following cost information from the past year:
A.)
Identify the high and low points
(Activity level) $
High
Low
Using the high-low method, compute the overhead cost per labor hour and the fixed overhead cost per month. (Round variable cost
to 2 decimal places, eg. 15.25 and fixed cost 5 O decimal places, e.g. 5,275.)
Variable cost = $________ per labor hour.
Fixed cost=$____________
B.)
Angie has booked 4,200 labor hours for the coming month. How much overhead should she expect to incur?
Total Cost =$______
C.)
If Angie books one more catering job for the month, requiring 350 labor hours. how much additional overhead should she expect
to incur?
Additional overhead= $_________
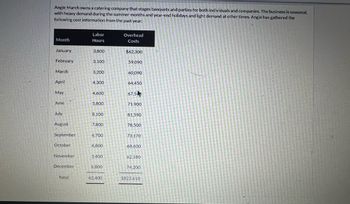
Transcribed Image Text:Angie March owns a catering company that stages banquets and parties for both individuals and companies. The business is seasonal,
with heavy demand during the summer months and year-end holidays and light demand at other times. Angie has gathered the
following cost information from the past year:
Month
January
February
March
April
May
June
July
August
September
October
November
December
Total
Labor
Hours
3,800
3,100
3,200
4,300
4,600
5,800
8,100
7,800
6,700
4,800
3,400
6,800
62,400
Overhead
Costs
$62,300
59,090
60,090
64,450
67,5
71,900
81,590
78,500
73,170
68,600
62,180
74,200
$823.610
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Benson Trophies makes and sells trophies it distributes to little league ballplayers. The company normally produces and sells between 5,000 and 11,000 trophies per year. The following cost data apply to various activity levels. Required Complete the preceding table by filling in the missing amounts for the levels of activity shown in the first row of the table. (Round your intermediate calculations and per unit amounts to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardSophia's Restaurant served 5,500 meals last quarter. Sophia recorded the following costs with those meals. Variable costs: Ingredients used Direct labor Indirect materials and supplies Utilities Fixed costs: Managers' salaries Rent Depreciation on equipment (straight-line, time basis) Other fixed costs $15,250 11,500 Total variable costs Total fixed costs Total costs Unit costs 6,300 2,700 24,500 20,500 4,500 5,670 Required: Unit variable costs and total fixed costs are expected to remain unchanged next quarter. Calculate the unit cost and the total cost if 4,950 meals are served next quarter. (Round "Unit costs" answer to 2 decimal places.)arrow_forwardJoyce Murphy runs a courier service in downtown Seattle. She charges clients $0.60 per mile driven. Joyce has determined that if she drives 2,400 miles in a month, her total operating cost is $700. If she drives 3,500 miles in a month, her total operating cost is $810. Required: 1. Using the high-low method, determine Joyce's variable and fixed operating cost components. 2. Complete the contribution margin income statement for Joyce's service assuming she drove 1,550 miles last month. (Assume this falls within the relevant range of operations). Complete this question by entering your answers in the tabs below. Required 1 Required 2 Using the high-low method, determine Joyce's variable and fixed operating cost components. (Round your cost per unit answer to 2 decimal places.) Variable Cost per Mile Driven Fixed Costarrow_forward
- Given the following cost and activity observations for Bounty Company's utilities, use the high-low method to determine Bounty's variable utilities cost per machine hour. Round your answer to the nearest cent. Cost Machine Hours March $3,142 15,489 April 2,691 10,041 May 2,810 11,509 4 June 3,881 18,009 a. $0.15 b. $1.05 O c. $1.64 Od. $1.01 10:21 PM 670002 K 63°Farrow_forwardFinch Trophies makes and sells trophies it distributes to little league ballplayers. The company normally produces and sells between 6,000 and 12,000 trophies per year. The following cost data apply to various activity levels: Required Complete the following table by filling in the missing amounts for the levels of activity shown in the first row of the table. Note: Round "Cost per unit" answers to 2 decimal places. Number of Trophies Total costs incurred Fixed Variable Total costs Cost per unit Fixed Variable Total cost per trophy $ 84,000 48,000 $ 132,000 $ $ 6000 $ 14.00 8.00 22.00 $ 8000 0 $ 0.00 $ 10000 0 0.00 $ $ 12000 0 0.00arrow_forwardCould you please answer all the reuired fields correctly.arrow_forward
- The managing director of a consulting group has the accompanying monthly data on total overhead costs and professional labor hours to bill to clients. Complete parts a through c. Click the icon to view the monthly data. a. Develop a simple linear regression model between billable hours and overhead costs. Overhead Costs = +xBillable Hours X Monthly Overhead Costs and Billable Hours Data (Round the constant to one decimal place as needed. Round the coefficient to four decimal places as needed. Do not include the $ symbol in your answers.) Overhead Costs Billable Hours 0 $315,000 3,000 $365,000 4,000 $395,000 5,000 $447,000 6,000 $530,000 7,000 $550,000 8,000arrow_forwardGiven the following cost and activity observations for Bounty Company's utilities, use the high-low method to determine Bounty's variable utilities cost per machine hour. Round your answer to the nearest cent. Cost Machine Hours March $3,002 15,174 April 2,664 9,624 May 2,823 12,276 June 3,621 17,777 a.$1.17 b.$0.70 c.$0.66 d.$0.12arrow_forwardCove’s Cakes is a local bakery. Price and cost information follows: Price per cake $ 14.21 Variable cost per cake Ingredients 2.33 Direct labor 1.12 Overhead (box, etc.) 0.25 Fixed cost per month $ 3,153.00 How do i find the break even sales for this problemarrow_forward
- David Manufacturing, which uses the high-low method for estimating cost function, makes a product called Kwan. The company incurs three different manufacturing cost types (A, B, and C) and has a relevant range of operation between 4,000 units and 10,000 units per month. Per-unit costs at two different activity levels for each cost type are presented below. Type A Type B Type C Total 5,000 units $7 $12.60 $4 $23.60 7,500 units $7 $8.40 $3 $18.40 Required: a) Classify each of the costs (A, B, and C) as either fixed or variable or semi-variable b) Write down a linear cost function that expresses the behavior of Shum's total manufacturing cost as a function of # of units produced. c) If Shum produces 10,000 units, what would be the total cost of manufacturing? d) If all fixed costs (or fixed components of costs) decrease by 10% and all variable costs (or variable components of costs) decrease by 10%, what would be the total cost of manufacturing for an activity level of production of 8,000…arrow_forwardStuart Trophies makes and sells trophies it distributes to little league ballplayers. The company normally produces and sells between 10,000 and 16,000 trophies per year. The following cost data apply to various activity levels: Required Complete the following table by filling in the missing amounts for the levels of activity shown in the first row of the table. Note: Round "Cost per unit" answers to 2 decimal places. Number of Trophies Total costs incurred Fixed Variable Total costs Cost per unit Fixed Variable Total cost per trophy $ 66,000 $ 42,000 $ 108,000 $ $ 10,000 $ 6.60 4.20 10.80 12,000 $' 14,000 4,20 4.20 $ 66,000 $ 66,000 $ 66,000 50,400 58,800 67,200 116,400 $ 124,800 $ 133,200 4.20 4.20 16,000 $ 4.20 4.20arrow_forwardGiven the following cost and activity observations for Bounty Company's utilities, use the high-low method to determine Bounty's variable utilities cost per machine hour. Round your answer to the nearest cent. Cost Machine Hours March $3,091 14,781 April 2,676 9,929 May 2,812 11,845 June 3,520 17,889 a.$0.49 b.$0.53 c.$0.11 d.$1.17arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education