
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Transcribed Image Text:□
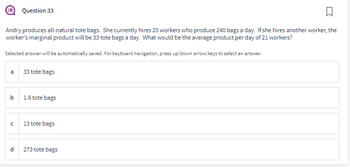
Andry produces all-natural tote bags. She currently hires 20 workers who produce 240 bags a day. If she hires another worker, the
worker's marginal product will be 33 tote bags a day. What would be the average product per day of 21 workers?
Selected answer will be automatically saved. For keyboard navigation, press up/down arrow keys to select an answer.
a
b
C
Question 33
d
33 tote bags
1.6 tote bags
13 tote bags
273 tote bags
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 10. Recently, some college alumni started a moving service for students living on campus. They have three employees and are debating hiring a fourth. The hourly wage for an employee is $18 per hour. An average moving job takes four hours. The company currently does three moving jobs per week, but with one more employee, the company could manage five jobs per week. The company charges $80 for a moving job. What would be the new employee’s marginal product of labor? What is the value of that marginal product? Should the moving service hire a fourth worker?arrow_forwardThe Zippy Paper Company has no control over either the price of paper or the wage it pays its workers. The following table shows the relationship between the number of workers Zippy hires and total output, with all other inputs being held constant. In the following table, for each quantity of labor input, fill in the marginal product (MP) and marginal revenue product (MRP) for Zippy. (Note: When the price doubles, this will also double the marginal revenue product.) Labor Input Total Output Marginal Product Marginal Revenue Product (Workers per day) (Boxes of paper per day) (Boxes of paper per day) Price = $10 Price = $20 (Dollars) (Dollars) 0 0 1 25 2 45 3 60 4 70 5 75 6 77 Assume that the selling price of paper is $10 per box. If the wage rate is $125.00 per day, Zippy will hire ______workers. Continue to assume that the selling…arrow_forwardThe diagram below shows an agricultural production function. 900- 800- 700- 600- 500- 400- 300- 200- 100- 400 800 1200 1600 2000 2400 2800 Number of farmers Kilogrammes of grain produced (thousands)arrow_forward
- Assume that the average product for six workers is fifteen. If the marginal product of the seventh worker is eighteen. A)marginal product is rising b)marginal product is falling c)average product is rising d)average product is fallingarrow_forwardUse the table below. Marginal Total Total Marginal Product revenue Workers Produce Revesue per Product Price (5) product per (Output) hours ($) hour 2,50 25 25 2.50 63 62.50 36 11 2.50 90 27.50 45 2.50 113 22.50 50 2.50 125 12.50 55 is 2.50 138 12.50 How many workers would the firm hire if it were required to pay a wage of $25 per hour? O 2 3. Osarrow_forwardEdie chooses to work 90 hours per week when the wage rate is $16 per hour. If she is offered time-and-a-half ($24 per hour) for “overtime work” (i.e., hours in excess of 90 per week), will she choose to work longer hours? Support your results with a diagram.arrow_forward
- If the marginal product of labor is 50 per day, and if the market is $4.50, calculate the marginal revenue product.arrow_forwardIf the marginal product of labor increases because of a technological advancement, it will likely cause a fall in the number of workers employed. an increase in the price of output produced by labor. a fall in the wage paid to labor. an increase in demand for labor. an increase in the supply of labor.arrow_forwardFord Motors 2010-2019 Explain how the company uses high-skilled and low-skilled labor? Most companies will use some mix of both, but most companies will rely more heavily on one or the other.arrow_forward
- Bob White argues that if his wage went up from $10/hour to $20/hour he would still be able to pay rent and feed his family even if he worked half as many hours. So, if his wage increased he would want to work proportionally less. What is strange about Bob White's labor supply curve? it is very elastic it is very inelastic it slopes down it is verticalarrow_forwardA baker uses labor (L) and raw materials (M) to produce mini Muhlenberg Mule sugar figurines (q). The process is fairly simple as workers only must make the sugar mixture and pour the mixture into the mule molds. The baker’s production function is as follows f(L, M) = L 0.50M. Let wL and wM denote the prices of a unit of L and M, respectively. (a) Write the firm’s cost minimization problem if it wants to produce q units of output. (b) Write the Lagrangian function that describes the cost minimization problem. (c) Derive the long run conditional factor input demands for L and M as a function of wL, wM, and q; L ∗ (wL, wM, q) and M∗ (wL, wM, q). (d) Suppose wL = $25 and wM = $2. Determine the cost-minimizing combination of inputs if the baker wants to produce 200 mules. (e) Using wL = $25 and wM = $2 and the demand functions from part (c), write the firm’s long run cost function CLR(q).arrow_forwardLabor (workers per day) Total Product (per day) 10 4000 11 4389 12 4752 13 5083 14 5376 15 5625 The firm can hire as many workers as they want at the prevailing market wage of $150 a day per worker. In addition, the firm pays $200 a day for equipment. Enter ONLY numbers. No comma, units, or decimals. 1. What is the marginal product of the 12th worker? 2. What is the average product of hiring 12 workers? 3. What is the total variable cost per day if 12 workers are hired ? 4. What is the total fixed cost per day if 12 workers are hired?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education