
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
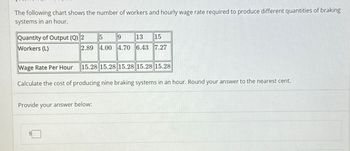
Transcribed Image Text:The following chart shows the number of workers and hourly wage rate required to produce different quantities of braking
systems in an hour.
15
9
13 15
2.89 4.00 4.70 6.43 7.27
Quantity of Output (Q) 2
Workers (L)
Wage Rate Per Hour 15.28 15.28 15.28 15.28 15.28
Calculate the cost of producing nine braking systems in an hour. Round your answer to the nearest cent.
Provide your answer below:
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- please read the question carefully as there are multiple questions with the same graphs that is shown on the imagearrow_forwardCan you assist in filling out this chart?arrow_forwardLet's explore how rising costs helped to kill off most printed newspapers after the Internet became available in the mid-1990s. Imagine that you are a newspaper publisher in the year 2004. You are in the middle of a one-year factory rental contract that requires you to pay $700,000 per month, and you have contractual salary obligations of $1,250,000 per month that you can't get out of. You also have a marginal printing cost of $0.25 per paper as well as a marginal delivery cost of $0.10 per paper. Instructions: Enter your answers rounded to two decimal places. a. If sales fall by 20 percent from 1,000,000 newspapers per month to 800,000 newspapers per month, what happens to the AFC per newspaper? AFC per newspaper rises from $ to $ b. What happens to the MC per newspaper? MC per newspaper does not change c. What happens to the minimum amount that you must charge to break even? It rises from $ to $arrow_forward
- 2. A production process using two inputs, labor and capital is Q = 5LK where Q is output per day. MPK = 5L and MPL = 5K. The wage (w) = $150 per hour and (r) = $1,000 per hour. Determine the least cost combination of K and L when the desired output is 1,000 What is the minimum cost of producing 1,000 per day?arrow_forwardThe following cost data are for a firm in the short run: Output Total Cost 0 $400 1 500 2 550 3 600 4 650 5 700 What is the firm's average variable cost at an output of 5 units? $30 $60 $120 $140arrow_forwardThe following cost data are for a firm in the short run: Output Total Cost 0 $400 1 500 2 550 3 600 4 650 5 700 What is the firm's average variable cost at an output of 5 units? $30 $60 $120 $140arrow_forward
- Question 15 of 20 Output Marginal Labor (Q) Product 15 1 2 50 15 4 70 5 60 In the table above, when the firm produces with 3 units of Labor, its Output (Q) is: 65 75 80 60arrow_forwardThe table below shows cost data for WipeOutSki Company, which manufactures skis for beginners. If the company’s fixed costs are $30, what is the marginal cost X? Quantity Variable Cost Fixed Cost Total Cost Average Variable Cost Average Total Cost Marginal Cost 0 0 $30 1 $10 $30 2 $25 $30 X 3 $45 $30 4 $70 $30 5 $100 $30 6 $135 $30 Group of answer choices $15 $55 $5arrow_forwardThe cost structure of a manufacturer of micro- chips is described in the table that follows. The firm's fixed costs equal $10,000 per day. Calculate the average variable cost, average fixed cost, and average total cost at each output level. Output (microchips per day) Total Cost of Output ($ thousands) 10 25 60 50 95 75 150 100 220 125 325 150 465arrow_forward
- A weaver working with a handloom is able to produce 11 yards of fabric per day. The typical weaver is paid £10 for a day's work. A loom powered by a steam engine is able to produce 82 yards of fabric per day. The powered loom still needs a worker to operate it, earning £10 per day, but also needs 24 pounds of coal to power it. At what price per pound of coal does the cost of producing fabric by power loom equal the cost of producing it by handloom? Round your final answer to two decimal places.arrow_forwardJ 7 please do it in 30 minutes please urgently... I'll give you up thumb definitelyarrow_forwarddefine total fixed costsarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education