
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
#69 help
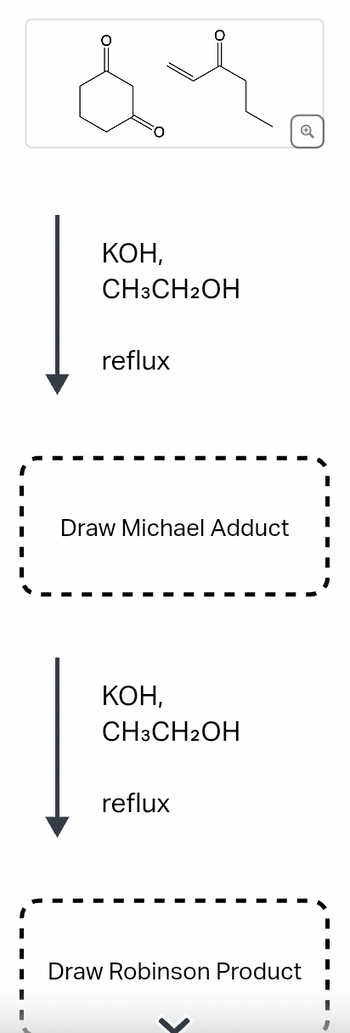
Transcribed Image Text:### Image Transcription for Educational Website
**Chemical Reaction Sequence**
1. **Initial Compounds:**
- The image displays two chemical structures. The first is a six-membered cyclohexanone ring with a ketone group. The second compound is a methyl vinyl ketone, characterized by the presence of a vinyl group attached to a ketone.
2. **Reagents and Conditions:**
- **KOH, \( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{OH} \), reflux**
- The reaction is carried out under reflux conditions with potassium hydroxide (KOH) in ethanol (\( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{OH} \)) as the solvent.
3. **First Product:**
- **Draw Michael Adduct**
- This step involves a Michael addition reaction, where the enolate ion of the cyclohexanone adds to the α,β-unsaturated carbonyl compound (methyl vinyl ketone).
4. **Second Reaction Step:**
- The same reagents and conditions are used again: **KOH, \( \text{CH}_3\text{CH}_2\text{OH} \), reflux**.
5. **Final Product:**
- **Draw Robinson Product**
- The final product forms through a series of reactions, including intramolecular aldol reaction and subsequent dehydration, leading to the formation of the Robinson annulation product.
This sequence showcases the use of alkali and alcohol in promoting organic reactions for the formation of complex cyclic structures from simpler precursors.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Ether groups are formed when alcohols are treated with acid. Consider the following question that focuses on acid-catalyzed ether formation using alcohol functional groups. There are 3 unique ether products will be formed when the following reaction is performed. Draw the product of the above reaction that has six carbon atoms and an ether functional group. **Be sure to include all lone pairs of electrons.**arrow_forwardDraw the organic product formed when 1-hexyne is treated with [1] NH,; [2] CH,CH,Br. Click the "draw structure" button to launch the drawing utility. draw structure...arrow_forwardView the first compound name provided in Table 6. Follow the steps below and draw each part of the structure on a piece of paper. Determine the number of carbons present in the compound based on the base name. Draw the carbon chain and include any double or triple bonds if indicated in the suffix of the base name. Number each carbon. The carbons can be numbered from left to right or right to left. Draw any substituents on the corresponding carbon atom for which is indicated in the name. Refer to Figures 3 and 4 in the background for a visual representation of numbered carbons with corresponding substituents. Check that each carbon atom has a total of 4 bonds.arrow_forward
- Classify each of the following organic reactions in the table below. Reaction Type (Check all that apply.) ÇH; CH,—CH=CH—CH—CH,—CH, “དཔ_)ཡ་ཡ་¨-6,-]"་ཡ་6,-་ད —་ “68="-་་-་ F;C H O OH CH; ཙ ་ ། H,C—CH—CH,—C—O─—CH—CH¥ O0 CH3 Ongdition O Elimination COBgbstitution Ar H O Addition O Elimination O Substitution ཅཏ-"-་་,་ཡང་ཡང"-ང་",, ༩-་་-་“,ཡདི་ ཡད་ CH; CH; CH; Addition O Elimination O Substitution O Addition O Elimination O Oxidation O Reduction Substitution ×arrow_forwardPlease help me check if the information below is correct for both the types of reactions and the special rules or laws to predict predominant products for alcohols. If not please insert the correct information. Please make the information in jot notes. TYPES OF REACTIONS ALCOHOL: Dehydration: This is a reaction where an alcohol loses a water molecule to form an alkene. For example, when ethanol is treated with an acidic catalyst, such as sulfuric acid, it undergoes dehydration to form ethene (CH2=CH2) and water. Oxidation: In this reaction, an alcohol is converted to either a carbonyl compound or a carboxylic acid. For example, primary alcohols can be oxidized to aldehydes or carboxylic acids, while secondary alcohols can be oxidized to ketones. Tertiary alcohols are not oxidized under normal conditions. Esterification: This reaction involves the formation of an ester from an alcohol and a carboxylic acid in the presence of an acid catalyst. For example, when ethanol is…arrow_forwardFor each of the following ethers, fill in the blank with the IUPAC NAME of the ether. butoxy)butane ****||||O (R)-1-(sec- HINT: the straight butane is the parent chain of the fourth one, with an (R)-sec-butoxy group attached at carbon 1arrow_forward
- [Review Topics] [References] Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. Draw a structural formula for the missing organic reactant in the esterification reaction below. ? + CH3OH è *** • You do not have to consider stereochemistry. • You do not have to explicitly draw H atoms. CH4 OCH3 + H₂O CH₂CH3 Yarrow_forwardThe starting materials for this reaction are ethylene glycol and terephthalic acid. The letters A and B represent organic groups that are unreactive. What reactive organic functional group does ethylene glycol (containing the A functional group) contain? Enter its name.arrow_forwardWhich of the following chemical equations depicts an alkylation reaction? C6H6() + CH3Cl() → C6H5CH3() + HCl(g) 2 CH3OH() + 3 O2(g) → 2 CO2(g) + 4 H2O() C6H12() → C6H10() + H2(g) CH2ClCH2Cl(g) + H2(g) → CH3CH3(g) + Cl2(g) CHClCHCl(g) → CH2ClCH2Cl(g)arrow_forward
- 2. Please fill in missing reactants, reagents, reaction conditions, or products in the provided blank boxes OMe ...-CF2-CF2-CF2-CF2-CF2-...arrow_forwardThe highlighted part of this antimalarial is an.... A) Alcohol CH3 H B) Ester H3C» C) Ether "CH3 D) Ketone E) None of the abovearrow_forwardPls help ASAP. Pls do all asked questions. Pls draw this compound.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY