
FINANCIAL ACCOUNTING
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781259964947
Author: Libby
Publisher: MCG
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Analyse the effect of the actions below on the debt/equity ratio. Assume current debt/equity ratio is 0.5.
(v) Issuing new equity
(vi) Account receivable collected
(vii) Sell goods on book value, on cash basis
(viii) Pay off the company’s long term bank loan
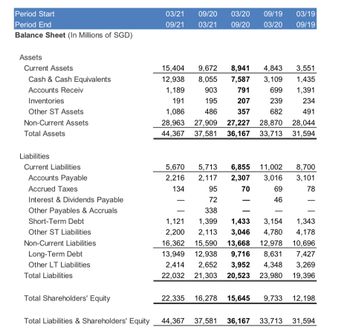
Transcribed Image Text:Period Start
Period End
Balance Sheet (In Millions of SGD)
Assets
Current Assets
Cash & Cash Equivalents
Accounts Receiv
Inventories
Other ST Assets
Non-Current Assets
Total Assets
Liabilities
Current Liabilities
Accounts Payable
Accrued Taxes
Interest & Dividends Payable
Other Payables & Accruals
Short-Term Debt
Other ST Liabilities
Non-Current Liabilities
Long-Term Debt
Other LT Liabilities
Total Liabilities
Total Shareholders' Equity
Total Liabilities & Shareholders' Equity
03/21
09/21
15,404 9,672 8,941 4,843
12,938
8,055
7,587
3,109
1,189
903
791
191
195
207
1,086
486
357
28,963
27,909
27,227 28,870 28,044
44,367 37,581 36,167 33,713 31,594
09/20 03/20 09/19 03/19
03/21
09/20
03/20 09/19
5,670
2,216 2,117
134
22,335
3,551
1,435
699 1,391
239
234
682
491
44,367
5,713 6,855 11,002
2,307 3,016
70
95
72
338
1,121
1,399
1,433
3,154
2,200 2,113
3,046 4,780
16,362
15,590 13,668 12,978 10,696
13,949 12,938
8,631
7,427
9,716
3,952 4,348 3,269
2,414 2,652
22,032 21,303 20,523 23,980 19,396
69
46
8,700
3,101
78
1,343
4,178
16,278 15,645 9,733 12,198
37,581 36,167 33,713 31,594
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Debt Equity Ratio is used to measure the company's total debt in relation to the equity i.e. amount invested by the owners and retained earnings over time. A debt-equity ratio of 1 to 1.5 is considered ideal depending on the type of industry.
A Debt-Equity ratio of 1.5 means that for every $1 of equity, the company has $1.5 of debt. This is considered to be ideal because more of equity can be costly and inefficient for the company and more of debt would mean financial trouble for the company.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, accounting and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Analyse the effect of each of the following transactions on the current ratio, quick ratio, debt-to-equity ratio and earnings per share. assume that the current ratio, quick ratio and debt-to-equity ratio are each greater than 1 and that earnings per share are positive. determine if the ratio increases decrease or are unchanged. consider each transaction independently of all the other transactions. Repaid short-term loans payable of $51 000. Purchased inventory of $48 000 on cash. Made repayments of $78 000 on the long-term loan. Declared, but did not pay, a $31 000 cash dividend on shares. Borrowed an additional $56 000 on the long-term loan. Sold short-term investments recorded in the balance sheet at $30 000 for $28 000. Issued 140 000 shares at the beginning of the financial period for cash of $168 000. Received $6000 owing in cash from a customer.arrow_forwardIf a company has a current ratio of 1.5:1, what effects will the borrowing of cash by long-term debt and collection of accounts receivable have on the ratio? Decrease and decrease ) Decrease and no effect Increase and increase Increase and no effectarrow_forwardA bank loan approved for the business that has been paid into the bank account will have the following impact on the accounting equation. Group of answer choices Increase equity and increase asset Decrease an asset and decrease a liability Decrease an asset and decrease stockholders’ equity Increase an asset and increase a liabilityarrow_forward
- Match each definition that follows with the term (a–h) it defines. Question 7 options: a company's ability to make interest payments and repay debt at maturity focuses on a company’s ability to generate net income useful for comparing one company to another or to industry averages use debt to increase the return on an investment measures the risk that interest payments will not be made if earnings decrease the percentage analysis of the relationship of each component in a financial statement to a total within the statement a percentage analysis of increases and decreases in related items on comparative financial statements an analysis of a company’s ability to pay its current liabilities 1. solvency 2. leverage 3. times interest earned 4. horizontal analysis 5. vertical analysis 6. common-sized financial statements 7. current position analysis 8.…arrow_forwardHow do firms use current liabilities, including accounts payable, accruals, lines of credit, commercial paper and short-term loans, to finance current assets?arrow_forwardWhich of the following ratios would a lender find most useful in monitoring a borrower's ability to make loan payments? () PE ratio Return on assets Total asset turnover Inventory turnover () Cash coverage ratio Previous Page Next Page Page 6arrow_forward
- If a company is worried about having enough cash to pay interest to their bondholders, rent to their landlords and wages to their employees. they are having:a. Solvency issuesb. Liquidity issuesc. Duration matching issuesarrow_forwardWhich of the following is not classified among the financing activities in a statement of cash flows? a Long-term borrowing. b Payment of dividends to stockholders. c Short-term borrowing. d Payment of interest to creditors.arrow_forwardUsing the data from Years n and n-1 below, answer the following questions. What are the company's assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity in Year n and n- I? What story does the balance sheet tell about changes in short term investments from Year n-1 to Year n? What story does the balance sheet tell about changes in notes payable from Year n-I to Year n? What is the company's net income in Year n and n-I? please provide answer and explain in detail for all answer all requirements with all working answer in textarrow_forward
- Indicate if the following transactions increase or decrease cash and classify the transactions as Operating, Investing or Financing Activities Enter I For increase and D for decrease. Enter O for Operating, I for Investing, and F for Financing. 1. Pay taxes D O 2. Collect cash from customers I O 3. Issue common stock F 4. Take out a loan from a bank 5. Purchase stock in another company I 6. Sell government debt security 7. Buy a patent 8. Retire a bonds payable 9. Pay dividends 10. Pay insurance 11. Pay interest on a loan 12. Pay principal on a loan 13. Pay salaries 14. Repurchase treasury stock 15. Sell a copyright to another firm 16. Pay suppliers for inventory 17. Dividend payments received from stock investment. 18. Interest payments received from investment in government debt securities.arrow_forwardPrepare the balance sheet and income statement by rearranging the above items. Note: Be sure to list the assets and liabilities in order of their liquidity. Enter all amounts as positive values. Cash Receivables Inventories BALANCE SHEET Assets Liabilities and Shareholders' Equity $ 15 Payables $ 35 35 Debt due for repayment 25 50 Total current assets $ 100 Total current liabilities $ 60 Property, plant, and equipment 520 Long-term debt Total liabilities 350 $ 410 Net fixed assets Total assets $ 520 Shareholders' equity 90 $ 620 Total liabilities and shareholders' equity $ 500arrow_forwardGuys could you please help me: I'm attaching AT&T's Balance Sheet and Income Statement for the analysis.I'd really appreciate help with the following: Perform a vertical financial analysis incorporatingi. Debt ratioii. Debt to equity ratioiii. Return on assetsiv. Return on equityv. Current ratiovi. Quick ratiovii. Inventory turnoverviii. Days in inventoryix. Accounts receivable turnoverx. Accounts receivable cycle in daysxi. Accounts payable turnoverxii. Accounts payable cycle in daysxiii. Earnings per share (EPS)xiv. Price to earnings ratio (P/E)xv. Cash conversion cycle (CCC), andxvi. Working capitalxvii. Explain Dupont identity, apply it to your selected company, interpret thecomponents in Dupont identity.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
AccountingAccountingISBN:9781337272094Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning,
Accounting Information SystemsAccountingISBN:9781337619202Author:Hall, James A.Publisher:Cengage Learning, Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON
Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...AccountingISBN:9780134475585Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. RajanPublisher:PEARSON Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Intermediate AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259722660Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M ThomasPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Financial and Managerial AccountingAccountingISBN:9781259726705Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting PrinciplesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781337272094
Author:WARREN, Carl S., Reeve, James M., Duchac, Jonathan E.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Accounting Information Systems
Accounting
ISBN:9781337619202
Author:Hall, James A.
Publisher:Cengage Learning,

Horngren's Cost Accounting: A Managerial Emphasis...
Accounting
ISBN:9780134475585
Author:Srikant M. Datar, Madhav V. Rajan
Publisher:PEARSON

Intermediate Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259722660
Author:J. David Spiceland, Mark W. Nelson, Wayne M Thomas
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Financial and Managerial Accounting
Accounting
ISBN:9781259726705
Author:John J Wild, Ken W. Shaw, Barbara Chiappetta Fundamental Accounting Principles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education