
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An object's position can be modeled with the following function: s(t) = 2cos(2πt) +t^2, where t is measured in seconds. What will the object's acceleration be after 2 seconds?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
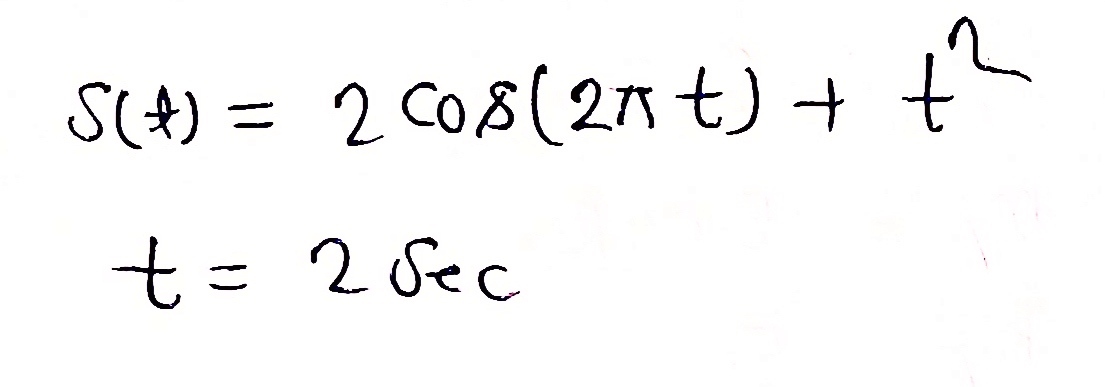
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An object's position as a function of time in one dimension is given by the expression; 3.8t2 + 2.3t + 8.15 where are constants have proper SI Units. What is the object's position at t = 2.57?arrow_forwardthe earth is approximately 1.5x10^8 km from the sun. how many minutes does it take light to travel from the sun to the earth? light travels at a speed of 3.00 x10^10 m/sarrow_forwardAn equation describing displacement (in meters) as a function of time (in seconds) of a rocket propelled motorcycle moving up a hill is given by: x(t) = 13.5t – 0.5t³ + 7 Where 0arrow_forwardA particle moves so that its position (in meters) as a function of time (in seconds) is r = î + 5t2 j + 5t k. (Use the following as necessary: t.) (a) Write an expression for its velocity as a function of time. V = m/s (b) Write an expression for its acceleration as a function of time. a = m/s?arrow_forwardAn object's position as a function of time in one dimension is given by the expression; 3.89t2 + 2.22t + 7.48 where are constants have proper SI Units. What is the object's average velocity between the times t = 3.16 s and t = 8.38 s? with everything in 3 sig figsarrow_forwardYou are driving 65.0 miles/hour and you see a police car, so you slow down to 42.5 miles/hour. It takes you 3 seconds to do this. What is your deceleration? (I asked this one before, but someone plugged in -22.5 miles/hr x 2.237 m/s / 1 mile an hour which I didn't understand)arrow_forwardA point particle of mass m = 1.8 kg moves according to the position function: r(t) = xtai + ytbj + ztck, where t denotes time and x, y, z, a, b, and c are constants such that the exponents are positive integers and the position function has the dimension of length. Part (a) We can write the particle’s velocity function in the form v(t) = ntdi + otej + ptgk. Enter an expression for n in terms of x, y, z, a, b, and c. Part (b) The particle’s velocity function will have the form v(t) = ntdi + otej + ptgk. Enter an expression for d in terms of x, y, z, a, b, and c. Part (c) Here is a set of parameter values for the motion of the particle: m = 1.8 kg, x = 1.8 m/s0, y = 2.4 m/s1, z = 0.15 m/s2, a = 0, b = 1, c = 2. Calculate the x-component of the particle’s angular momentum, in units of kg˙m2/s, about the origin at time t = 1 s. Part (d) Use the same set of parameter values (m = 1.8 kg, x = 1.8 m/s0, y = 2.4 m/s1, z = 0.15 m/s2, a = 0, b = 1, c = 2) to calculate the y-component of…arrow_forwardA soccer ball starts from rest and accelerates with an acceleration of 0.385 m/s2 while moving down a 8.50 m long inclined plane. When it reaches the bottom, the ball rolls up another plane, where, after moving 14.75 m, it comes to rest. (a) What is the speed of the ball at the bottom of the first plane (in m/s)? (Round your answer to at least two decimal places.) m/s (b) How long does it take to roll down the first plane (in s)? (c) What is the magnitude of the acceleration along the second plane (in m/s?)? m/s2 (d) What is the ball's speed 8.20 m along the second plane (in m/s)? m/s (e) What If? You change the angles of the two inclines in such a manner that the new acceleration down the first incline is a, new down = 2a initiel down and up the second incline is a, new un x initial up, What is the ball's speed 8.20 m up the second plane (in m/s)? 2 m/sarrow_forwardThe x component of the velocity of an object moving along the x axis is given as vy = 4t – 3t where vy is in meters per sec and t in seconds. The x component of its average velocity over the interval of time from t =0 to t= 2 sec is: O -2m/s O 2 m/s O -4m/sarrow_forwardA boat running at its top speed takes 3.0 hours to travel 12 km down a river. It then takes 5.0 hours to return to its starting place. What is the velocity of the river? (Answer should look like '0.35 km/h'. I know bad units.)arrow_forwardAn object's position in the X-direction as a function of time is given by the expressio%3B x(t) = 5t2 + 2t where are quantities have proper SI Units. What is the object's average velocity in the x-direction between the times t = 1.71 s and t = 2.37 s. Just enter the number rounded to 3 significant figures and assume it has proper SI Units.arrow_forwardv(t) = 4t3 + 10t m/s. The initial position is r = 3 m. 3. A one dimensional problem. Assume v = Determine the position and acceleration at time t = 3sec.arrow_forwardarrow_back_iosSEE MORE QUESTIONSarrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON