
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
An object begins at position x = 0 and moves one-dimensionally along the x-axis with a velocity v expressed as a function of time t according to the graph above. At what time does the object pass through x = 0 again?
A: Between 10 s and 20 s
B: Between 20 s and 30 s
C: At 30 s exactly
D: Between 30 s and 40 s
E: After 40 s
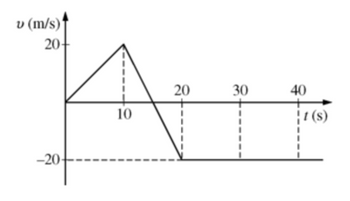
Transcribed Image Text:The image displays a velocity-time graph for an object's motion. Below is a detailed explanation of the graph:
### Axes:
- **Vertical Axis (y-axis):** Represents velocity \( v \) in meters per second (m/s), ranging from -20 m/s to 20 m/s.
- **Horizontal Axis (x-axis):** Represents time \( t \) in seconds (s), marked from 0 to 40 seconds.
### Graph Description:
1. **Time 0 to 10 seconds:**
- The velocity increases from 0 to 20 m/s, forming a straight, upward slope.
- This indicates constant acceleration.
2. **Time 10 to 20 seconds:**
- The velocity decreases from 20 m/s back to 0 m/s, forming a straight, downward slope.
- This indicates constant deceleration back to rest.
3. **Time 20 to 30 seconds:**
- The velocity continues decreasing to -20 m/s, forming another straight, downward slope.
- This represents a continuation of deceleration past rest to a negative velocity, indicating a change in direction.
4. **Time 30 to 40 seconds:**
- The velocity remains constant at -20 m/s.
- This indicates uniform motion in the reverse direction.
Overall, the graph outlines a sequence of acceleration, deceleration, change in direction, and uniform motion.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 7 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A plot of velocity versus time for a car for the first 15 seconds of motion is shown in the diagram below. v, m/s 60 The distance traveled during these 15 seconds is: O 1.5 km O 650 m O 450 m O 275 m O 85 m 40 10 5 10 15 t, sarrow_forwardCan i get help step by step with this problem?arrow_forwardAt time t, the position of a body moving along the s-axis is s=−t^3+12t^2−36t m. a. Find the body's acceleration each time the velocity is zero. b. Find the body's speed each time the acceleration is zero. c. Find the total distance traveled by the body from t=0 to t=3.arrow_forward
- In class, we used a numerical method to determine the velocity of an object at 0s and = t = 2.00 s given that the object had started from rest at t accelerated at a rate given by a(t) = (8.00 m/s^)t². Here's what we did: 1. Divided t into four intervals of 0.5 s each. 2. For each interval, calculated the average a. These were the numerical values we obtained for each time interval: 1 0.25 0.50 i t (s) a; (m/s²) After summing the values according to: 2 0.75 4.50 3 1.25 12.50 lim ã‚At, 2 V₂v₁ = limast. t₁ At→0 we arrived at the approximate value v = 21.0 m/s. 4 1.75 24.50 a (m/s²) 32.00+ 24.00 16.00 8.00 0 ā₁ 0 ā2 az as 0.50 1.00 1.50 2.00 t (s) 21.33 m/s. We then proceeded to integrate to obtain the analytical solution, which was v = Using the same numerical method, divide t into eight and then sixteen intervals to calculate the approximate value for v at t = 2.00 s. This should demonstrate that with more sampling, the AUC (area under the curve) value converges toward the analytical…arrow_forwardThe Beretta Model 92S (the standard-issue U.S. army pistol) has a barrel 127 mmmm long. The bullets leave this barrel with a muzzle velocity of 349 m/sm/s. 1) What is the acceleration of the bullet while it is in the barrel, assuming it to be constant? Express your answer in meters per second squared. 2) What is the acceleration of the bullet while it is in the barrel, assuming it to be constant? Express your answer as a multiple of acceleration due to gravity g. 3) For how long is the bullet in the barrel? Express your answer in seconds.arrow_forwardAt t=0 an object has a velocity of 35 m/s and a steady acceleration of -10 m/s2. Make a sketch of velocity vs. time for this motion from t=0 to t=5 s. Make a sketch of acceleration vs. time for this motion from t=0 to t=5 s. Does the object change directions between 0 and 6 s?arrow_forward
- Consider the following descriptions of the vertical motion of an object subject only to the acceleration due to gravity. Begin with the acceleration equation a(t) = v'(t) = g, where g= - 9.8 m/s. a. Find the velocity of the object for all relevant times. b. Find the position of the object for all relevant times. c. Find the time when the object reaches its highest point. What is the height? d. Find the time when the object strikes the ground. A softball is popped up vertically (from the ground) with a velocity of 25 m/s. а. v(t) b. s(t) = %3D c. The object's highest point is m at time t= S. (Simplify your answers. Round to two decimal places as needed.) d. t= (Simplify your answer. Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardAt t=0 an object has a position of 1 m and has a steady velocity of -2.5 m/s. What will be the object’s position at t = 6 seconds? Make a sketch of position vs. time for this motion from t=0 to t=6 s. Make a sketch of velocity vs. time for this motion from t=0 to t=6 s. Does the object change directions between 0 and 6 s?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON