
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question

Transcribed Image Text:7. An object's velocity is v = t* – 3t? where t 2 0.
a) At what time/times is the object at rest?
b) In what time range is the object moving to the left? In what time range is the object
moving to the right?
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
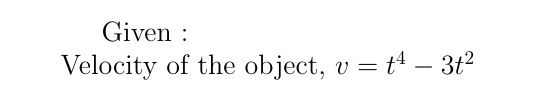
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An electron with an initial speed of 4.56x10^5m/s enters a linear particle accelerator that is3.50 cm long. In this section, the electron is accelerated to a final speed of 3.25x10^5m/s a) . Calculate the magnitude of the acceleration of the electron. b) Determine the time of accelerationarrow_forwardAn object's position in the as a function of time obeys the equation; x(t) = 14.2/t2.17 + 5.1t3 where all constants have proper SI Units. What is the speed of the object in the x direction at t = 1.93 seconds?arrow_forwardThe height of a helicopter above the ground is given by h = 3t^2+2.0t^4, where h is in meters and t is in seconds. At t=2.0s, the helicopter releases a small bag. a) Calculate the maximum height the bag reaches measured from the ground. b) How long after the bad is released, does it strike the ground? c) Calculate the speed of vag when it hits the ground.arrow_forward
- Near the end of a marathon race, the first two runners are separated by a distance of 45.6 m. The front runner has a velocity of 3.2 m/s, and the second a velocity of 4.95 m/s. a) What is the velocity of the second runner relative to the first, in meters per second? b) How many seconds earlier will the second runner reach the finish line if the front runner is 250 m from the finish line in seconds? c) What distance ahead, in meters, will the second runner be when she crosses the finish line? please answer all partsarrow_forwardYou are driving down the highway late one night at 20 m/s when a deer steps onto the road 40 m in front of you. Your reaction time before stepping on the brakes is 0.50 s, and the maximum deceleration of your car is 12 m/s2. How much distance is between you and the deer when you come to a stop? distance: m What is the maximum speed you could have and still not hit the deer? maximum speed:arrow_forward1) The motions of a car and a motorbike along a straight road are described by the velocity vs time graph provided below. The two vehicles are initially alongside each other at time t=0 s. The motorbike’s speed is 18.1 m/s and the time T is 59.9 s. a) what distance has the motorbike travelled between 0 and T (in km)? b) What distance has the car traveled between 0 and T (in km)? 2) Which of these statements is true? a. At T, the car and motorbike are at the same location. b. the acceleration of the car is constant between 0 and T c. the acceleration of the motorbike is 0 d. the acceleration of the car is 0 3) a)What is the car's average speed for the first T seconds? (in m/s) b) What is the motorbike's average speed for the first T seconds (in m/s)arrow_forward
- 3. The position of a drone as a function of time is given by m m *(t) = ( 8 i – 5 j+ 1.5 k) m + (-2 î + 4 j) t - t2j a. What is the x-position of the drone as a function of time? b. What is the y-position of the drone as a function of time? c. How far away is the drone from its starting position at t = 3s? What is the acceleration vector? e. What is the velocity vector as a function of time? f. At what time is the speed equal to 4 m/s?arrow_forwardA cyclist rides down a long straight road at a velocity (in m/min) given by v(t) = 400 - 20t, for 0≤t≤ 10. a. How far does the cyclist travel in the first 3 min? b. How far does the cyclist travel in the first 10 min? c. How far has the cyclist traveled when his velocity is 350 m/min?arrow_forwardQ:A fires a rocket beside from rest at an angle 30° and accelerates at 30 m/s2 for 3.0 s. The engine shuts off at a height 202.5 m above the ground. a) Calculate the speed of the rocket after 3s. reached? b) At what time after t = 0 will the maximum height c) What maximum height will the rocket reacharrow_forward
- An object is moving along the x-axis. At t = 0 it is at x = 0. Its x-component of velocity Vx as a function of time is given by: Vx(t) = at - Bt3, where a = 6.8 m/s2 and B = 4.0 m/s4 I. At what nonzero time t is the object again at x = 0? (Express your answer with the appropriate units.) II. At t = 1.8 s, what is the x-component of the velocity of the object? (Express your answer with the appropriate units.) III. At t = 1.8 s, what is the x-component of the acceleration of the object? (Express your answer with the appropriate units.)arrow_forwardProblem 2: Kinematics and vectors. An object is moving on the xy plane with velocities given by: V₂ x = (10.0-0.500t)1 and v = (-5.00t+0.025²) j Determine the following quantities: a. The displacement of the object as a function of time. b. The average velocity of the object from for the time interval from 0 to 10 s.arrow_forwardMotion with gravity Neglecting air resistance, the motion of an objectmoving vertically near Earth’s surface is determined by the acceleration due to gravity, which is approximately 9.8 m/s2. Suppose a stone is thrown vertically upward at t = 0 with a velocity of 40 m/s from the edge of a cliff that is 100 m above a river.a. Find the velocity ν(t) of the object, for t ≥ 0.b. Find the position s(t) of the object, for t ≥ 0.c. Find the maximum height of the object above the river.d. With what speed does the object strike the river?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON