
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
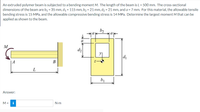
Transcribed Image Text:An extruded polymer beam is subjected to a bending moment M. The length of the beam is L = 500 mm. The cross-sectional
dimensions of the beam are b1 = 35 mm, d1 = 115 mm, b2 = 21 mm, d2 = 21 mm, and a = 7 mm. For this material, the allowable tensile
bending stress is 15 MPa, and the allowable compressive bending stress is 14 MPa. Determine the largest moment M that can be
applied as shown to the beam.
b2
a
M
d2
d1
A
B
L
b1
Answer:
M = i
N-m
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Mechanicsarrow_forwardAn extruded polymer beam is subjected to a bending moment M. The length of the beam is L = 620 mm. The cross-sectional dimensions of the beam are b₁ = 39 mm, d₁ = 94 mm, b₂ = 23 mm, d₂ = 23 mm, and a = 8 mm. For this material, the allowable tensile bending stress is 17 MPa, and the allowable compressive bending stress is 11 MPa. Determine the largest moment M that can be applied as shown to the beam. ak a ↓ a M B A Answer: M = i L N•m b₁arrow_forwardFor the overhang beam shown below, (a) draw the free body diagram of the beam, (b) draw the shear and moment diagrams, (c) find moment of inertia of its cross-section, (d) determine the maximum bending stress. (e) indicate the stress components on an infinitesimal volume element (3D stress element) located at the point. Neglect the weight of the beam. 8 kN/m 2 cm em A C 25 em B 4 m 2 m 2 cm 20 cmarrow_forward
- A rectangular beam with two notches (with radius r = 2.5 mm) is shown in Figure 1.1. The beam has dimensions w = 55 mm and d = 50 mm. The beam is subjected to a bending moment of M = 1.3 kNm and the maximum allowable bending stress in the material is 400 MPa. Determine the smallest thickness, tmin, in mm that this beam should be designed for. Stress concentration graph is provided in Figure 1.2. K₁ M 3.0 2.6 2.2 1.8 1.4 16 1.0 0 1.10 1.05 1.02 0.05 wld = ∞ W 1.5 0.10 Figure 1.1. 0.15 rld Figure 1.2. Inom 0.20 6M td² 0.25 M M 0.30arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solution ....arrow_forwardAn extruded polymer beam is subjected to a bending moment M. The length of the beam is L = 600 mm. The cross-sectional dimensions of the beam are b₁ = 36 mm, d₁ = 112 mm, b₂ = 22 mm, d₂ = 22 mm, and a = 7 mm. For this material, the allowable tensile bending stress is 15 MPa, and the allowable compressive bending stress is 9 MPa. Determine the largest moment M that can be applied as shown to the beam. b₂ ak ak ✓ a M B L A Answer: M = i N•m d₂arrow_forward
- The beam is acted upon by force F = 17 kN as shown in the figure. What is the shear force in section C in kN. Find the moment of area of the fiber 30 mm above the bottom of the beam about the neutral axis in mm3. find the shear stress in MPa at a point 30 mm above the bottom of the beam at section C.arrow_forwardExample 1 The bar is subjected to a moment of M = 17.5 N.m. If r = 5 mm, determine the maximum bending stress in the material. 80 mm 7 mm 20 mm M Marrow_forwardThe beam shown in Figure 2 is loaded in the xy and xz planes.(a) Find the y and z components of the reactions at the supports.(b) Plot the shear and bending moment diagrams.arrow_forward
- Determine the maximum shear stress acting in the fiberglass beam at the section where the internal shears force is maximum. (t1=15 mm, t2=20 mm, h=150 mm, b=50mm)arrow_forwardconsider a beam with two 60-inch-long rods. The rods have a cross section area of 0.50 in 2 . Find the axial stress in each rod, draw the shear and moment diagrams for the beam, and find the maximum stress in the beam.arrow_forwardX w MB w = 3 kN/m L = 4 m 2.4 What is the value of the bending moment at x = 2.5 m?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY