
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
An evaporation-crystallization process (as shown below) is used to obtain solid potassium sulfate from an aqueous salt solution. The feed contains 18.7 wt% K2SO4. The wet filter cake contains solid sulfate crystals and a 40.0 wt% salt solution. The filtrate is recycled to mix with the feed. The evaporator has a capacity of 175 kg of water evaporated per second. The filtrate has 40.0 wt% salt solution, as well, and from the water entering the evaporator, 45.0% is evaporated. In the wet filter cake, there is 10 kg of the solid crystals for every 1 kg of the salt solution.
a.) Calculate the fresh feed rate. (Include units)
b.) Determine the production rate of crystal. (Include units)
c.) Calculate the recycle ratio. (kg recycle/kg feed) Include units
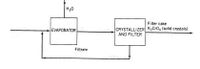
Transcribed Image Text:H20
Filter cake
CRYSTALLIZER K,Cro, (solid crystais)
AND FILTER
EVAPORATOR
Filtrate
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- In a paint manufacturing process, two different colored paints are being mixed in an infinitelylarge drum.Paint A, with a concentra�on of 30% pigment, is pumped into the drum at a rate of 10 liters perminute.Paint B, with a concentration of 17% pigment, is pumped into the drum at a rate of 17 liters perminute.Both paints have the same density of 1.0 kg/liter.If the mixture is continuously stirrred and drained from the drum at a rate of 22 liters perminute, what isthe concentration of pigment in the resulting mixture?arrow_forwardA sludge thickener is used to concentrate waste sludge before sending the thickenedsludge to a dewatering process. The thickener receives 800 m3/day of raw waste sludgeat a solid concentration of 20,000 mg/L; after thickening, the solid concentration increasesto 5%, which is then dewatered by a filter press that produces a solid cake (biosolids) witha solid concentration of 20% by weight. What is the total weight of biosolids that needs tobe hauled away from the plant each day? ( )arrow_forward2) Filtration involves the separation of solid particles from fluid through a filtering medium and ranges from simple straining to more complex operations. Depending on the objective of the filtration process, the fluid, solid or both may be useful outputs of the overall process(a)Describe the basic principles offiltration as applied in the chemical industry. Using a suitable example, explain with clear illustrationshow filtration technique can be used to separate solids from filtrates at industrial scalearrow_forward
- An evaporation-crystallization process (as shown below) is used to obtain solid potassium sulfate from an aqueous salt solution. The feed contains 18.7 wt% K2SO4. The wet filter cake contains solid sulfate crystals and a 40.0 wt% salt solution. The filtrate is recycled to mix with the feed. The evaporator has a capacity of 175 kg of water evaporated per second. The filtrate has 40.0 wt% salt solution, as well, and from the water entering the evaporator, 45.0% is evaporated. In the wet filter cake, there is 10 kg of the solid crystals for every 1 kg of the salt solution. a.) Calculate the fresh feed rate. (Include units) b.) Determine the production rate of crystal. (Include units) c.) Calculate the recycle ratio. (kg recycle/kg feed) Include unitsarrow_forwardA double effect evaporator is used to concentrate an 18% CuSO4 solution. At the end of evaporation, 26,000 kg/h of 50% CuSO4 solution were obtained. If the water evaporated in the second effect is half the water evaporated in the first effect, determine: a) The amount of solution fed into the first effect. b) The amount of water evaporated in the first and second effect. c) The amount of solution fed into the second effect, as well as its composition. Problem diagram 18% CuSO4 82% H₂O M₁ M₂ M3 X CuSO4 Y H₂O A 2 M4 = 0.5 M₂ M5 H₂O steam M6 M2 M6 is the water that condenses 26 000 kg/hr 50% CuSO4 50% H2₂Oarrow_forwardMagnesium metal, a gray solid, is heated in a crucible in the presence of oxygen. A white powder is collected from the crucible. This is an example of A) a chemical change B) a separation C) a mixture D) a physical changearrow_forward
- The following consideration(s) is/are relevant to the choice of refrigerant (SELECT ALL that apply): Vapor pressure Environmental factors Toxicity and corrosion properties Water is usually used as the refrigerantarrow_forwardTo make an instant tomato soup, a company makes soup powder from liquid step by a two-step process: concentrating the soup by removing water using a membrane to reach a concentration of 45% water, followed by a spray drying process which leads to a final moisture content of 3%. If the initial liquid tomato soup contains 9.0% solids and fat and enters the membrane separator at 4000 kg/hr, calculate: The flow-rate of the concentrated soup after membrane separation: kg/hr The flow-rate of water removed by the spray drying process (the second stage): kg/hrarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The