
ENGR.ECONOMIC ANALYSIS
14th Edition
ISBN: 9780190931919
Author: NEWNAN
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
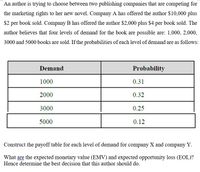
Transcribed Image Text:An author is trying to choose between two publishing companies that are competing for
the marketing rights to her new novel. Company A has offered the author $10,000 plus
$2 per book sold. Company B has offered the author $2,000 plus $4 per book sold. The
author believes that four levels of demand for the book are possible are: 1,000, 2,000,
3000 and 5000 books are sold. If the probabilities of each level of demand are as follows:
Demand
Probability
1000
0.31
2000
0.32
3000
0.25
5000
0.12
Construct the payoff table for each level of demand for company X and company Y.
What are the expected monetary value (EMV) and expected opportunity loss (EOL)?
Hence determine the best decision that this author should do.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 6 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, economics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Cheryl Druehl Retailers, Inc., must decide whether to build a small or a large facility at a new location in Fairfax. Demand at the location will either be low or high, with probabilities 0.6 and 0.4, respectively. If Cheryl builds a small facility and demand proves to be high, she then has the option of expanding the facility. If a small facility is built and demand proves to be high, and then the retailer expands the facility, the payoff is $230,000. If a small facility is built and demand proves to be high, but Cheryl then decides not to expand the facility, the payoff is $183,000. If a small facility is built and demand proves to be low, then there is no option to expand and the payoff is $250,000. If a large facility is built and demand proves to be low, Cheryl then has the option of stimulating demand through local advertising. If she does not exercise this option, then the payoff is $45,000. If she does exercise the advertising option, then the response to advertising will…arrow_forwardThelma is indifferent between $100 and a bet with a 0.6 chance of no return and a 0.4 chance of $200. If U(0) = 20 and U(200) = 220, then U(100) = :arrow_forwardChannels 7 and 10 are the only television networks. They want to capture as much of the market as possible because it helps them earn more advertising revenue. Each channel can choose to show a cooking or a reality show on Sunday night. If they both airing cooking shows or both airing reality shows, Channel 10 gets 60% of the market. If Channel 10 is showing a cooking show and Channel 7 is showing a reality show, Channel 10 gets 70% of the market. If Channel 10 is showing a reality show and Channel 7 is showing a cooking show, Channel 7 gets 45% of the market. In a sequential game, Channel 7 moves first. What is true? Group of answer choices Channel 7 will choose reality. Channel 7 has a second mover advantage. Channel 10 will choose cooking. Channel 10 will choose reality. Channel 7 will choose cooking.arrow_forward
- Soft selling occurs when a buyer is skeptical of the usefulness of a product and the seller offers to set a price that depends on realized value. For example, suppose a sales representative is trying to sell a company a new accounting system that will, with certainty, reduce costs by 10%. However, the customer has heard this claim before and believes there is only a 20% chance of actually realizing that cost reduction and a 80% chance of realizing no cost reduction. Assume the customer has an initial total cost of $200. According to the customer's beliefs, the expected value of the accounting system, or the expected reduction in cost, is $____ . Suppose the sales representative initially offers the accounting system to the customer for a price of $12.00. The information asymmetry stems from the fact that the ______(sales rep or buyer) has less information about the efficacy of the accounting system than does the ______(sales rep or buyer) . At this price, the…arrow_forwardConsider the following interaction between a student and a company. The student is either serious or lazy with probabilities 1/3 and 2/3 respectively. The student knows if they are serious or not, but the company does not. Initially, the student decides whether to revise for exams or not. Revising has a cost of 1 for a serious student and 3 for a lazy one. The company observes the student's exam result (that is, whether they have made the effort to revise), and based on this, offers a salary of 3 (for a serious student) or 1 (for a lazy student). The student learns of the proposed salary and can then either accept (and earn the salary) or refuse (and earn O). They also lose the revision effort if they worked. The company's gain is equal to the student's productivity (4 if they are serious, 2 if not) minus the salary if the student accepts the offer, and O otherwise. 1. Represent the game in extensive form. 2. Show that the game has a unique perfect Bayesian Equilibrium, and provide the…arrow_forwardThe ultimatum game is a game in economic experiments. The first player (the proposer) receives a sum of money and proposes a fair proposal (F - 5;5) or unfair proposal (U - 8;2). The second player (the responder) chooses to either accept (A) or reject (R) this proposal. If the second player accepts, the money is split according to the proposal. If the second player rejects, neither player receives any money. 1 A 5:5 2 F R 0:0 U A 8:2 2 1. Find the subgame perfect Nash Equilibrium using backward induction. R 0;0arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON
Principles of Economics (12th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134078779Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. OsterPublisher:PEARSON Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON
Engineering Economy (17th Edition)EconomicsISBN:9780134870069Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick KoellingPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)EconomicsISBN:9781305585126Author:N. Gregory MankiwPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning
Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving ApproachEconomicsISBN:9781337106665Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike ShorPublisher:Cengage Learning Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...EconomicsISBN:9781259290619Author:Michael Baye, Jeff PrincePublisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Principles of Economics (12th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134078779
Author:Karl E. Case, Ray C. Fair, Sharon E. Oster
Publisher:PEARSON

Engineering Economy (17th Edition)
Economics
ISBN:9780134870069
Author:William G. Sullivan, Elin M. Wicks, C. Patrick Koelling
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Economics (MindTap Course List)
Economics
ISBN:9781305585126
Author:N. Gregory Mankiw
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics: A Problem Solving Approach
Economics
ISBN:9781337106665
Author:Luke M. Froeb, Brian T. McCann, Michael R. Ward, Mike Shor
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Managerial Economics & Business Strategy (Mcgraw-...
Economics
ISBN:9781259290619
Author:Michael Baye, Jeff Prince
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education