
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
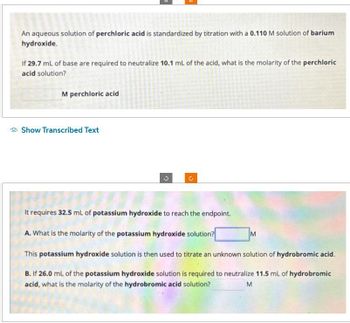
Transcribed Image Text:An aqueous solution of perchloric acid is standardized by titration with a 0.110 M solution of barium
hydroxide.
If 29.7 mL of base are required to neutralize 10.1 mL of the acid, what is the molarity of the perchloric
acid solution?
M perchloric acid
Show Transcribed Text
G
It requires 32.5 mL of potassium hydroxide to reach the endpoint.
A. What is the molarity of the potassium hydroxide solution?
This potassium hydroxide solution is then used to titrate an unknown solution of hydrobromic acid.
B. If 26.0 mL of the potassium hydroxide solution is required to neutralize 11.5 mL of hydrobromic
acid, what is the molarity of the hydrobromic acid solution?
M
M
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- To determine the molarity of an unknown sulfuric acid solution in a titration, a standardized NaOH solution with a molarity of 0.138 M was given. A student used 11.8 mL of the NaOH solution to reach to the end point of the titration with a 25.0 mL sample of the unknown acid solution. What is the molarity of the unknown sulfuric acid solution?arrow_forwardA student is asked to standardize a solution of calcium hydroxide. He weighs out 0.952 g potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC8H4O4, treat this as a monoprotic acid).It requires 35.7 mL of calcium hydroxide to reach the endpoint.A. What is the molarity of the calcium hydroxide solution? This calcium hydroxide solution is then used to titrate an unknown solution of nitric acid.B. If 15.6 mL of the calcium hydroxide solution is required to neutralize 29.1 mL of nitric acid, what is the molarity of the nitric acid solution?arrow_forwardAn aqueous solution of hydroiodic acid is standardized by titration with a 0.179 M solution of barium hydroxide. If 19.1 mL of base are required to neutralize 10.1 mL of the acid, what is the molarity of the hydroiodic acid solution? ____M hydroiodic acidarrow_forward
- 5. A student conducted a titration experiment. He/she used 12.0 mL of silver nitrate (titrant) solution to reach the endpoint. If the student used 25.4 mL of the chloride (analyte) for the titration and found the concentration of chloride ions to be 2.2 M, what is the mass (in grams) of silver nitrate titrant Clic)arrow_forwardHydrobromic acid can be purchased as 50.0% solution. The density of this solution is 1.07 g mL-1. What is the molar concentration of hydrobromic acid in this solution? The molar concentration = i Marrow_forwardsolution after precipitation is complete. 68. The drawings below represent aqueous solutions. Solution A is 2.00 L of a 2.00-M aqueous solution of copper(II) nitrate. Solution B is 2.00 L of a 3.00-M aqueous solution of potas- sium hydroxide. (0) suiro Cu²+ ebro NO3 БО K+ OH™ A B a. Draw a picture of the solution made by mixing solutions A and B together after the precipitation reaction takes place. Make sure this picture shows the correct relative volume compared to solutions A and B, and the correct relative number of ions, along with the correct relative amount of solid formed. b. Determine the concentrations (in M) of all ions left in solution (from part a) and the mass of solid formed.arrow_forward
- 1. If 10. g of AgNO3 is available, what volume of 0.40 M AgNO3 solution can be prepared? Volume = mL? 2. A 7.52-g sample of a diprotic acid requires 179.0 mL of a 0.750 M NaOH solution for complete neutralization. Determine the molar mass of the acid. g/mol?arrow_forwardA student is asked to standardize a solution of potassium hydroxide. He weighs out 0.985 g potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC8H404, treat this as a monoprotic acid). It requires 36.1 mL of potassium hydroxide to reach the endpoint. A. What is the molarity of the potassium hydroxide solution? M This potassium hydroxide solution is then used to titrate an unknown solution of hydrochloric acid. B. If 18.7 mL of the potassium hydroxide solution is required to neutralize 18.3 mL of hydrochloric acid, what is the molarity of the hydrochloric acid solution? Marrow_forwardAn aqueous solution of sodium hydroxide is standardized by titration with a 0.156 M solution of nitric acid. If 12.4 mL of base are required to neutralize 22.4 mL of the acid, what is the molarity of the sodium hydroxide solution?_____M sodium hydroxidearrow_forward
- A student is asked to standardize a solution of calcium hydroxide. He weighs out 0.945 g potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC8H404, treat this as a monoprotic acid). It requires 27.4 mL of calcium hydroxide to reach the endpoint. A. What is the molarity of the calcium hydroxide solution? M This calcium hydroxide solution is then used to titrate an unknown solution of hydrochloric acid. B. If 12.3 mL of the calcium hydroxide solution is required to neutralize 29.7 mL of hydrochloric acid, what is the molarity of the hydrochloric acid solution? Marrow_forwardA student is asked to standardize a solution of sodium hydroxide. He weighs out 1.09 g potassium hydrogen phthalate (KHC8H404, treat this as a monoprotic acid). It requires 33.5 mL of sodium hydroxide to reach the endpoint. Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. A. What is the molarity of the sodium hydroxide solution? This sodium hydroxide solution is then used to titrate an unknown solution of nitric acid. Submit Answer M B. If 18.7 mL of the sodium hydroxide solution is required to neutralize 10.3 mL of nitric acid, what is the molarity of the nitric acid solution? 2 question attempts remaining Marrow_forwardA 0.02198 M AgNO3 solution is used to titrate a 25 mL sample of an unknown chloride solution. Three drops of potassium chromate solution is added to the unknown. It requires 33.59 mL of the AgNO3 solution to change the color of the solution from yellow to peach. Compute the molarity of chloride ion in the unknown. (Note tha Ag+ reacts with Cl- in a 1:1 mole ratio)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY