
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
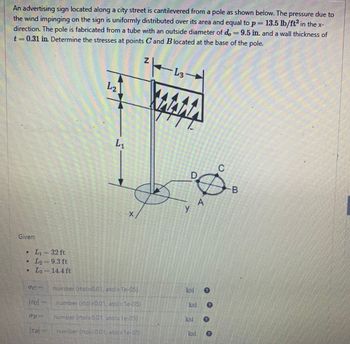
Transcribed Image Text:An advertising sign located along a city street is cantilevered from a pole as shown below. The pressure due to
the wind impinging on the sign is uniformly distributed over its area and equal to p= 13.5 lb/ft² in the x-
direction. The pole is fabricated from a tube with an outside diameter of d = 9.5 in. and a wall thickness of
t = 0.31 in. Determine the stresses at points Cand B located at the base of the pole.
Given:
L₁-32 ft
L₂-9.3 ft
L3
CONSE
TC
TB
= 14.4 ft
Incity
L₂
L₁
number (rtol-0.01, atol-Te-05)
number (rtol-0.01, atol=1e-05)
number (rtol-0.01, atol=1e-05) -
number (rtol-001, atol-le-05)
L3 →
MAMA
y
C
Ø
A
D
ksi e
-B
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 16 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A compound cylinder is made by shrinking a jacket with an outer diameter of 200 mm on a hollow cylinder with diameter of 100 mm and 150 mm. When the compound cylinder is subjected to an internal pressure of 35MNm-2, the maximum circumferential stress in both cylinders is the same. Calculate the maximum stress developed at the internal diameter of the jacket.arrow_forwardThe pipe shown has an outer diameter of 200 mm and a wall thickness of 10 mm. The length a is 1600 mm and length b is 800 mm (b is from the center of the pipe to the application of the load). There is an applied load of 25 kN as pictured and the pipe contains a static fluid pressurized at 2 MPa (this causes normal stresses in both the hoop and long directions). Determine the normal and shear stresses on the side of the pipe at point K which is coplanar with the yz-plane. K Use the following cross-sectional properties: A = 12· 103 mm² J = 54· 106 mm4 Qmax = 180 · 103 mm3 I = Iy = 27· 106 mm4 V 25 kNarrow_forwardضحقهشمتلوظhelparrow_forward
- Example: A cylinder has an internal diameter of 230 mm, has walls 5 mm thick and is 1 m long. It is found to change in internal volume by 12.0 x m' when filled with a liquid at a pressure p. If E = 200GN/m2 and y= p.25, and assuming rigid end plates, determine: (a) the values of hoop and longitudinal stresses; (c) the necessary change in pressure p to produce a further increase in internal volume of (longitudinal) are assumed; 15 %. The liquid may be assumed incompressible.arrow_forwardThe closed thin-walled tank has an inner radius of r and wall thickness t and contains a gas of pressure of p. The state of stress at point "a" on the surface of the tank is represented by stress components with an unknown stress element rotation angle of 0. Note that, the two normal stress components for x'y' system (note: not xy system!) are known: ox, = 120 MPa and Oy = 180 MPa, but the shear stress component (T,) is unknown. Determine: (1) the principal stresses at point a ; (2) Tx'yı ; (3) rotation angle of 0 . y 180 MPa 120 MPа х 0 = ? a Tyy = ? tank cross section stress state at point aarrow_forwardA composite square member of varying sizes is subjected to axial forces along its centerline, as shown. The members' cross-sectional dimensions, from smaller to larger, are 50 mm ´ 50 mm, 75 mm ´ 75 mm, and 100 mm ´ 100 mm, respectively. (a) What are the normal stresses (in MPa) induced in the bar material at Section A-A, Section B-B, Section C-C? (b) What are the changes in the axial (4.28 ft), width (100mm), and thickness (100 mm) direction (in mm), at Section C-C? Assume n = 0.25 and E = 200,000 MPa., 1 ft = 0.3048 marrow_forward
- Example 2 : 200N Pi-40ON SONUTION: o mm • Dete mine an equivalent force-couple syster at the center of the transverse section passing through H. Evaluate the normal and shearing stresse at H/ 250 mm D. 30 mm 100 m • Betermine the principal planes and calculate the principal stresses. A single horizontal force P,of 600N magnitude soppliad to endD of lever ABD. Determine (a) the normal and shearing stresses on an element at point H having sides parallel to the x and y axes, (b) the principal planes and principal stresses at the point H. mchr's cin' mohr's arclearrow_forwardHow do I calculate for sigma seam? Thank youarrow_forwardCan you please solve this homework problem with step by step solutionarrow_forward
- The cylinder for a hydraulic press has an inside diameter of 300 mm and an outside radius of 260 mm. Find the maximum shear stress in the cylinder for an internal pressure of 221 MPa.arrow_forwardA hollow shaft with an outside diameter of 3.2 in. and an inside diameter of 2.6 in. is subjected to both a torque of T = 614 lb-ft and an axial tension load of P = 7410 lb, as shown. (a) Determine the principal stresses (σp1 > Op2) and the maximum shear stress Tmax at point H on the surface of the shaft. (b) Show the stresses of part (a) and their directions in an appropriate sketch. H (1) I X Barrow_forwardNeglecting the weight of the bracket, calculate the three principal stresses, and absolute maximum shear stress at point A on the cross section of the bracket at section a-a. Calculated for you: I, = 0.79948 in“, cross sectional area is 0.875 in². 0.5 in. 0.25 in. "T TA 500 lb X 0.25 in.→||– -||-0.25 in. 6 in. 1.5 in.1.5 in. ↑. Section a – a 12 in.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY