
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
11th Edition
ISBN: 9780134580999
Author: Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher: PEARSON
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
Amylose n + Water → Amylosen-1 + Glucose
(See attached image of
1) If amylose and amylase are left together in solution in a test tube for a long period of time, what will be left in the test tube at the end?
2) In an experiment amylase activity is measured immediately and 10 minutes after addition to a solution of amylose. Assume 10 minutes is enough time for amylose to act on all available substrate molecules in the solution.
a) What colour would you expect to observe if you added iodine at the 0 minute time point?
b) What colour would you expect to observe if you added iodine at the 10 minute time point?
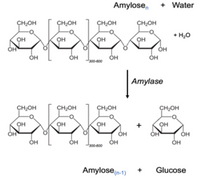
Transcribed Image Text:Amylose,
+ Water
ÇH;OH
CH2OH
ÇH;OH
ÇH;OH
+ H20
OH
OH
он
он
он
Он
он
он
00-000
Amylase
ÇH2OH
ÇH2OH
ÇH;OH
ÇH;OH
он
он
он
+
OH
ÓH
он
ÓH
он
он
он
Amylose(n-1)
Glucose
+
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, biology and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Which of the following is TRUE under the following conditions: the enzyme concentration is 2.5 nM, substrate concentration is 75 nM, the KM = 150 nM, and the Vmax = 20 nmol/min a) The rate of the reaction is 20 nmol/min! b) The rate of the reaction is between 10 nmol/min and 20 nmol/min. c) The rate of the reaction is 10 nmol/min. d) The rate of the reaction is below 10 nmol/min. e) The rate cannot be determined from the above information.arrow_forwardYou begin to study enzyme Z, which catalyzes a simple reversible reaction that interconverts compound S and compound P. You observe that the ∆G´° for the S to P conversion to be –6 kJ/mol, and that compound S has ∆G´° for binding to enzyme Z of –15 kJ/mol, while compound P has a ∆G´° for binding to enzyme Z of –13 kJ/mol. Please explain the effect of enzyme Z on conversion of S to P. (Your answer should include a graph qualitatively showing energy versus reaction progress; however, you still need to explain youranswer in words!) not sure how to make the correct graph.arrow_forward8arrow_forward
- Determine whether the following reactions will be spontaneous under standard biochemical conditions. Include calculations for Delta G in your answer. Use Table 13-7 in your textbook to help you.a) 2NADH + 2H+ + O2 --> 2NAD+ + 2H2Ob) Malate + FAD --> Oxaloacetate + FADH2c) Pyruvate + H2S --> Lactate + Sarrow_forwardThe KM values for the reaction of chymotrypsin with two different substrates are given in the table below. Considering this information, which substrate has the lower apparent affinity for the enzyme? Which substrate is likely to give a lower value for Vmax? Substrate N-acetylvaline ethyl ester N-acetyltyrosine ethyl ester KM (M) 8.8 X 10-² 6.6 X 10-4 N-acetylvaline ethyl ester has the lower apparent affinity for the enzyme; it will also likely to give a lower Vmax: N-acetyltyrosine ethyl ester has the lower apparent affinity for the enzyme; it will also likely to give the lower V₁ max. N-acetylvaline ethyl ester has the lower apparent affinity for the enzyme; N- acetyltyrosine ethyl ester is likely to give the lower Vmax: N-acetyltyrosine ethyl ester has the lower apparent affinity for the enzyme; N- acetylvaline will likely to give the lower Vmax. None of the above statements are correct.arrow_forwardTwo reactions are shown below. These reactions are directly coupled in cells by an enzyme called hexokinase, which is a key enzyme in glycolysis. It is generally the case that reactions that are directly coupled by enzymes share some common reactants. What is the net reaction when these two reactions are combined? Glucose + Inorganic Phosphate + ATP + Water → Glucose 6-phosphate + ADP Glucose + ATP + Water → Glucose 6-phosphate + ADP + Inorganic Phosphate Glucose + ATP → Glucose 6-phosphate + Inorganic Phosphate Glucose + ATP → Glucose 6-phosphate + ADParrow_forward
- This is a picture of the catalysis of alcohol by ADH with an inhibitor binding as an aldehyde analog. I have two questions. First, what would the enzyme be classified as and why? Also, what would the steps of this mechanism be?arrow_forwardThe pKa for histidine is pKa = 6.1 while that for cysteine is pKa = 8.0 2. Assume that both histidine and cysteine are catalytic groups for a particular enzyme. Assume also that the side chain of cysteine must be in the deprotonated form. Estimate the pH at which the catalytic activity of this enzyme is the maximum and sketch a pH-activity graph.arrow_forwardConsider the following chemical equation whose delta(G) = 9kcal/mol: AC + BD ---> AB + CD what are the reactants and what are the products is this reaction spontaneous? How do you know? Is energy released or consumed by this reaction? If an enzyme, which catalyzes this reaction is added, what will happen to delta (G) If this reaction is coupled to another reaction, whose delta(G) is -12 kcal/mol, what will be the net delta(G) value? will the overall reaction be spontaneousarrow_forward
- Can you please help solve this problem?arrow_forwardGiven the tri-acylglyceride (TAG) below as source of energy when administered from an organism's diet, H,C-O HC-0 H,C-o [A] Show the calculated maximum amount of ATP that could be generated by the full oxidation of the compound. Illustrate where the ATPS are derived from (show the reactions and enzymes involved). You can use general structure of the FFA in the reactions involved in the process. (B) Discuss the fate of the glycerol. (C] One of the FFAS derived from the TAG has the same carbon number as glucose. Compare the maximum yield of ATP derivable from this FFA as compared to the ATP yield from glucose.arrow_forwardWrite the balanced reaction catalyzed by phophoenolpyruvate carboxylase (P PC). Remember to add any cofactors, and to draw the structure formulas (a line-bond representation is fine) for the main substrate and product of the reaction.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON
Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)BiologyISBN:9780134580999Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. HoehnPublisher:PEARSON Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax
Biology 2eBiologyISBN:9781947172517Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann ClarkPublisher:OpenStax Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,
Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781259398629Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa StouterPublisher:Mcgraw Hill Education, Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company
Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)BiologyISBN:9780815344322Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter WalterPublisher:W. W. Norton & Company Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.
Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & PhysiologyBiologyISBN:9781260159363Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, CynthiaPublisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co. Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education
Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)BiologyISBN:9781260231700Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael WindelspechtPublisher:McGraw Hill Education

Human Anatomy & Physiology (11th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780134580999
Author:Elaine N. Marieb, Katja N. Hoehn
Publisher:PEARSON

Biology 2e
Biology
ISBN:9781947172517
Author:Matthew Douglas, Jung Choi, Mary Ann Clark
Publisher:OpenStax

Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781259398629
Author:McKinley, Michael P., O'loughlin, Valerie Dean, Bidle, Theresa Stouter
Publisher:Mcgraw Hill Education,

Molecular Biology of the Cell (Sixth Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9780815344322
Author:Bruce Alberts, Alexander D. Johnson, Julian Lewis, David Morgan, Martin Raff, Keith Roberts, Peter Walter
Publisher:W. W. Norton & Company

Laboratory Manual For Human Anatomy & Physiology
Biology
ISBN:9781260159363
Author:Martin, Terry R., Prentice-craver, Cynthia
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Publishing Co.

Inquiry Into Life (16th Edition)
Biology
ISBN:9781260231700
Author:Sylvia S. Mader, Michael Windelspecht
Publisher:McGraw Hill Education