
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
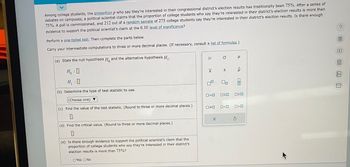
Transcribed Image Text:Among college students, the proportion p who say they're interested in their congressional district's election results has traditionally been 75%. After a series of
debates on campuses, a political scientist claims that the proportion of college students who say they're interested in their district's election results is more than
75%. A poll is commissioned, and 212 out of a random sample of 275 college students say they're interested in their district's election results. Is there enough
evidence to support the political scientist's claim at the 0.10 level of significance?
Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below.
Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.)
(a) State the null hypothesis H, and the alternative hypothesis H₁.
HO
H₁ :0
(b) Determine the type of test statistic to use.
(Choose one) ▼
(c) Find the value of the test statistic. (Round to three or more decimal places.)
0
(d) Find the critical value. (Round to three or more decimal places.)
(e) Is there enough evidence to support the political scientist's claim that the
proportion of college students who say they're interested in their district's
election results more than 75%?
OYes No
1
Н
|x
0=0
☐☐
X
O
S
00
OSO
P
ô
010
ロマロ
Ś
>O
0<0
? 圖 □图 □ □
199
Aa
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- From the U.S. Census Bureau's American Community Survey in 2019 it was found that 33.13% of United States residents over the age of 25 had an educational attainment of a bachelor's degree or higher. In the District of Columbia, the percentage of residents over the age of 25 who had attained a bachelor's degree or higher was 59.67%. An investigator for the U.S. Census Bureau took a random sample of seven residents from the District of Columbia and asked them their highest educational degree they had obtained. When there is no data set posted for an investigation, open a blank StatCrunch page by clicking "Open StatCrunch" on the StatCrunch home page. a) Verify that the sample from the District of Columbia satisfies the conditions of the binomial experiment. Write one sentence to check each requirement in context of the investigation. b) Assuming the sample from the District of Columbia is a binomial experiment, build the probability distribution in a single table and include the table in…arrow_forwardIn the Star and Tribune newspaper, there is an article entitled "1 in 8 school buses fail tests." The article says that the overall statewide proportion of school buses that fail safety tests is 9%. However, one bus company has a higher rate of over 12%. Assume that we want a new estimate for the statewide proportion of school buses that fail the safety inspection. We take a sample of 500 buses and find that 90 buses fail the safety inspection. Based on the new sample data, I construct this 90% confidence interval estimate for p: 152 < p < .208. Explain what this confidence interval means. O I am 90% sure that the number of buses that fail the inspection is between.152 and .208. O I am 95% sure that the true proportion of buses that fail the inspection is between .152 and .208. O I am 90% sure that the proportion of buses in this sample that fail the inspection is between .152 and .208. O I am 90% sure that the true proportion of buses that fail the inspection is between .152 and .208.arrow_forwardAccording to a survey, basketball is most popular among younger fans (aged 18-29) while baseball and football are most popular for fans 30 years of age or older. Suppose that in a survey of 2,500 randomly selected adults in the United States, respondents are asked to provide their favorite sport to watch out of basketball, baseball, and football. The results of the survey appear below. Favorite Professional Sport to Watch Respondent's Age Range Basketball 18-29 30-54 18-29 30-54 55+ 55+ 250 Total # 185 155 Basketball X X (a) Develop a joint probability table and use it to answer the following questions. Favorite Professional Sport to Watch Respondent's Age Range X Baseball X 110 270 215 Football Baseball X X X 235 x 685 395 Football X X X X Total x x x 1 (b) Construct the marginal probabilities for each of the professional sports leagues (basketball, baseball, and football). basketball baseball footballarrow_forward
- A dentist wants to a conduct a survey via telephone to determine what percent of all adults in their city floss daily. Which of these is the best example of response bias? Some people might not answer their phone after repeated calls. People with unlisted phone numbers or people with cell phones might be left out of the sample. Some people might refuse to tell a stranger on the phone about their flossing habits. Some people might feel pressured to say they floss even though they don’t.arrow_forwardWhether or not to continue a Mardi Gras Parade through the downtown area of a certain town is a hotly debated topic. The parade is popular with students and many residents, but some celebrations have led to complaints and a call to eliminate the parade. The local newspaper conducted online and telephone surveys of its readers and was surprised by the results. The online survey site received more than 300 responses, with more than 60% favoring continuing the parade, while the telephone response line received more than 150 calls, with more than 90% favoring banning the parade. What factors may have contributed to these very different results? (Select all that apply.) O People waver between two opinions. O Different subpopulations used the website and the telephone. O People were forced to lie about their preferences. The size of samples is too small to avoid chance variation.arrow_forwardIn 2014, Scotland was considering independence from England, going so far as to take a referendum vote. One opinion poll taken at the time showed that 51% of Scots favored "independence." In another poll taken at that same time, only 34% favored being "separate" from England. The primary reason these results differed by so much is that a. samples will usually differ just by chance due to random sampling. b. the wording of questions has a big effect on poll results. c. more follow-up efforts reduced the nonresponse rate of the second poll. d. the sample sizes are different, so the margins of error are different.arrow_forward
- Your local school board wants to determine the proportion of people who plan on voting for the school levy in the upcoming election. They conduct a random phone poll, where they contact 150 individuals and ask them whether or not they plan on voting for the levy. Of these 150 respondents, 78 people say they plan on voting for the levy. The school board wants to determine whether or not the data supports the idea that more than 50% of people plan on voting for the levy. Calculate the p-value for the one-sided Hypothesis test described in this example. (Hint: Find the test statistic and then use the tables to find the p-value.) 0.20 < p-value < 0.30 0.6879 0.3121 greater than 0.5 0.4899arrow_forwardThe city of Raleigh has 10200 registered voters. There are two candidates for city council in an upcoming election: Brown and Feliz. The day before the election, a telephone poll of 400 randomly selected registered voters was conducted. 197 said they'd vote for Brown, 176 said they'd vote for Feliz, and 27 were undecided.Give the sample statistic for the proportion of voters surveyed who said they'd vote for Brown. Note: The proportion should be a fraction or decimal, not a percent.197400 This sample statistic suggests that we might expect of the 10200 registered voters to vote for Brown.arrow_forwardThe Bureau of Labor Statistics reports that the official unemployment rate for Black people was 10.4% and 4.7% for White people in February 2015. Select all correct answers for this question. O The samples of white and black people are independent. The explanatory variable is the unemployment rate. The response variable is the unemployment rate. The response variable is race.arrow_forward
- By a small margin, Facebook remains the top choice of social media over all ages, with 29% using Facebook most often among those using social media sites. However, more visually oriented social networks such as Snapchat and Instagram continue to draw in younger audiences. When asked "Which one social networking brand do you use most often?" the results in the table show the top brands chosen by Americans aged 12-34 who currently use any social networking site or service. Social M edia Site Faceboo k Snapchat Instagra m Twitter Percentage That Use Most Often 29 28 26 6 20 (a) What is the sum of the percentages for these top social media sites? Give your answer as an exact number. Macmillan Learning top social media sites: What percent of Americans aged 12-34 use other social media sites most often? Give your answer as an exact number. other social media sites: do %arrow_forwardAmong college students, the proportion p who say they’re interested in their congressional district’s election results has traditionally been 65% . After a series of debates on campuses, a political scientist claims that the proportion of college students who say they’re interested in their district’s election results is more than 65% . A poll is commissioned, and 194 out of a random sample of 270 college students say they’re interested in their district’s election results. Is there enough evidence to support the political scientist's claim at the 0.05 level of significance? Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) State the null hypothesis H0 and the alternative hypothesis H1 . H0: H1: (b) Determine the type of test statistic to use. ▼(Choose one) (c) Find the value of the test statistic.…arrow_forwardAmong students at a nearby college, the proportion who say they're interested in their congressional district's election results has traditionally been 65%. After a series of gripping debates on campus, a political scientist claims that the proportion, p, of students at the college who say they're interested In their district's election results is now greater than 65%. A poll is commissioned, and 181 out of a random sample of 250 students at the college say they're interested in their district's election results. Is there enough evidence to support the political scientist's cdaim at the 0.10 level of significance? Perform a one-tailed test. Then complete the parts below. Carry your intermediate computations to three or more decimal places and round your answers as specified in the table. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) State the null hypothesis H. and the alternative hypothesis H,. H, :0 H :0 (b) Determine the type of test statistic to use. (Choose one) ▼ (c) Find the…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman