
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
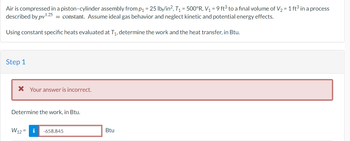
Transcribed Image Text:Air is compressed in a piston-cylinder assembly from p₁ = 25 lb/in², T₁ = 500°R, V₁ = 9 ft³ to a final volume of V₂ = 1 ft³ in a process
described by pv¹.25 = constant. Assume ideal gas behavior and neglect kinetic and potential energy effects.
Using constant specific heats evaluated at T₁, determine the work and the heat transfer, in Btu.
Step 1
* Your answer is incorrect.
Determine the work, in Btu.
W12=
i -658.845
Btu
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- QUESTION II: 0.5 m of air at Ti = 67 °C, P1 = 700 kPa undergoes a polytropic expansion to a final pressure of 350 kPa. The process follows pV3 = constant and the work done by the air is 175 kJ. Assuming ideal gas behavior for the air, and neglecting kinetic and potential energy effects, determine: (a) the final temperature, in °C. (b) the heat transfer, in kJ. Airarrow_forwardA closed, rigid tank is filled with only saturated vapor (water), initially at 20 bar, is cooled until the pressure is 3 bar. Show the process of the water on a sketch of the T-v diagram and evaluate the heat transfer, in kJ/kg a. Locate the states on the T-v coordinate and process. b.Write your energy balance equation to evaluate the heat transfer c. Determine the specific internal energy at state 1 (u1 )in kJ/kg d. Determine the quality x at state 2 e. Determine the specific internal energy at state 2 (u2) in kJ/kgf. Determine the energy transfer by heat/mass during the process (kJ/kg)arrow_forwardPlease explain wellarrow_forward
- A mass of 3 kilograms of air in a piston-cylinder assembly undergoes two processes in series from an initial state where p1 = 1.5 MPa, T1 = 264°C: Process 1–2: Constant-temperature expansion until the volume is twice the initial volume. Process 2–3: Constant-volume heating until the pressure is again 1.5 MPa.Assuming ideal gas behavior, determine the temperature at state 3, in kelvin.arrow_forwardOne-tenth kmol of carbon monoxide (CO) in a piston- cylinder assembly undergoes a process from p1 = 150 kPa, T1 = 300 K to p2 = 500 kPa, T2 = 370 K. For the process, W = -300 kJ. Employing the ideal gas model, determine: (a) the heat transfer, in kJ. (b) the change in entropy, in kJ/K.arrow_forwardQUESTION II: 0.5 m' of air at T1 = 67 °C, P1 = 700 kPa undergoes a polytropic expansion to a final pressure of 350 kPa. The process follows pV3 = constant and the work done by the air is 175 kJ. Assuming ideal gas behavior for the air, and neglecting kinetic and potential energy effects, determine: (a) the final temperature, in °C. (b) the heat transfer, in kJ. Airarrow_forward
- Need correctly..arrow_forwardA piston-cylinder assembly contains Refrigerant 22, initially a saturated vapor at 5 bar. The refrigerant undergoes a process for which the pressure-specific volume relationship is pv = constant to a final pressure of 20 bar. Kinetic and potential energy effects can be neglected. a. For your schematic, provide a rough sketch of your system, with arrows indicating direction of work and heat (i.e, in or out of the system) b. Determine the work and heat transfer for the process, each in (kJ/kg)arrow_forwardEither solve all parts or leave it unsolved ... I vll upvotearrow_forward
- 3. Air is contained within a piston-cylinder assembly The cross sectional area of the piston is 0.01 m². Initially the piston is at 1 bar and 25°C, 10 cm above the base of the cylinder. In this state, the spring exerts no force on the piston. The system is then reversibly heated to 100°C. As the spring is compressed, it exerts a force on the piston according to: F=-kx where k= 50,000 N/m and x is the displacement length from its uncompressed position. Determine the work done. a. -166 J b. -216 J c. 166 J d. 216 Jarrow_forward2. An ideal gas in a piston/cylinder system undergoes a process in which the specific volume is increased. In which process is the most work done for the same volume change? a. Isobaric process b. Isothermal process C. Isentropic process, k = 1.4 d. Polytropic process, n = 2 e. Cannot tell from this informationarrow_forwardawuIs 2 kg of air undergoes a power cycle undergocs a power cycle consisting of the following processes: Process 1-2: Constant-temperature expansion from p, = 4 bar, v, = 1 m³ /kg, to p2 = 2 bar, v2 = 2 m3/kg. Process 2-3: Constant-pressure compression to T3 = 696.9 K. Process 3-1: Constant-volume heating to state 1. Assume ideal gas behavior and neglect kinetic and potential energy effects. Show that T; = 1393.7 K and find T Sketch the cycle on a T-v diagram and label the states. Find the work done and heat transferred during cach process to complete this chart: b C. Process W (kJ) Q (kJ) iti 1-2 2-3 3-1 TOTAL Find the thermal efficiency of the cycle. For an energy balance on the entire cycle (1-2-3-1), what should the change in system energy be? Does that hold in this case? Add a Caption Pedro Castaño shared with you > Wednesday • Feb 23, 2022•7:24 PM Adjust IMG_7188 Apple iPhone 12 Pro Max НEIF Wide Camera – 26 mm f1.6 3 MP • 1914 × 1728 • 3.5 MB iarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY