
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
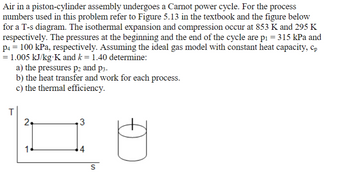
Transcribed Image Text:Air in a piston-cylinder assembly undergoes a Carnot power cycle. For the process
numbers used in this problem refer to Figure 5.13 in the textbook and the figure below
for a T-s diagram. The isothermal expansion and compression occur at 853 K and 295 K
respectively. The pressures at the beginning and the end of the cycle are p₁ = 315 kPa and
p4 = 100 kPa, respectively. Assuming the ideal gas model with constant heat capacity, cp
= 1.005 kJ/kg-K and k = 1.40 determine:
T
a) the pressures p2 and p3.
b) the heat transfer and work for each process.
c) the thermal efficiency.
2+
16
3
4
S
Đ
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Air (Rair = 0.287 ) as an ideal gas flows through the turbine and heat exchanger arrangement kg-K, shown below. Steady-state data are given on the figure. Stray heat transfer and kinetic and potential energy effects can be ignored. Sketch a T - s diagram of processes 1-4 and determine: (a) The entropy production of turbine 1 [3.2 kW /K] (b) The isentropic efficiency of turbine 1 [75%] (c) The exit temperature of turbine 2 if its isentropic efficiency is nr, = 0.85 [960 K] (d) The entropy production within the intermediate heat exchanger [3.2 kW/K] W1 = 10,000 kW Wn= ? Turbine Turbine P3= 4.5 bar T3 = ? T = 1100 K P2=5 bar P4 = 1 bar Air wwww www 2 4 T = 1400 K Pi = 20 bar Ts = 1480 K 5 Ps = 1.35 bar ms = 1200 kg/min Heat exchanger V T = 1200 K P6 =1 bar %3D Air inarrow_forwardAn engine has the Lenoir thermodynamic cycle as shown in the figure. Given: 1 mol of ideal gas CP,m = 3.5 R P1 = 2 atm ; P2 = 5 atm V1 = 3000 cm3 ; V3 = 6000 cm3 Find the following: Temperature at (P1, V1), (P2, V2), and (P2, V1) QH and Qc (Note; QH comes from Process 1->2; Proces 2-3 is considered isentropic efficiency of the enginearrow_forwardPlease explain each steparrow_forward
- A working fluid in a closed loop undergoes the following cycle: • 1-2 Isentropic compression • 2-3 Isobaric heat addition • 3-4 Isentropic expansion • 4-1 Isobaric heat rejection Identify the temperature-entropy (T-s) diagram that illustrates this cycle. T 2. 1 2 3 3 4 4 S 2 1 2 1 3 3 4 4 Sarrow_forwardstream? Q2/ An ideal gas initially at 600 K and 10 bar undergoes a four step mechanically reversible cycle in a closed system. In step 1-2, pressure decreases isothermally to 3 bar; in step 2-3, pressure decreases at constant volume to 2 bar; in step 3-4, volume decreases at constant pressure; and in step 4-1, the gas returns adiabatically to its initial state. Assum C₂=(7/2) R and C₂ = (5/2) R. Calculate Q, W, AU, and 4H for each step of the cycle?arrow_forwardHi I need help with parts of a thermo practice problem 2 kg of air in a piston cylinder initially at P1=101 kPa, T1= 300 K undergoes a cycle made up of three processes: 1-2 Isothermal compression until the volume is (1/15) of its original value.2-3 Constant Pressure heating3-1 Isentropic Expansion back to the initial state Assume air is an ideal gas with constant specific heats with the following values: Cpo=1.027kJ/kgK; Cvo= 0.740 kJ/kgK; R=0.287 kJ/kgK; ɣ=1.388 Fill in the processes table below and show all work.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY