
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
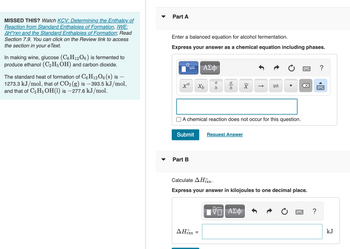
Transcribed Image Text:**Educational Content on Alcohol Fermentation and Enthalpy Calculations**
**Introduction to Alcohol Fermentation**
In winemaking, glucose (\(C_6H_{12}O_6\)) undergoes fermentation to produce ethanol (\(C_2H_5OH\)) and carbon dioxide (\(CO_2\)). This process can be represented by a balanced chemical equation, which you are tasked to formulate.
**Part A: Writing a Balanced Chemical Equation**
To express the chemical reaction for alcohol fermentation, input your balanced equation, including the phases of each substance, into the form provided. Ensure all atoms are accounted for on both sides of the equation. For example:
- Glucose: \(C_6H_{12}O_6(s)\)
- Ethanol: \(C_2H_5OH(l)\)
- Carbon Dioxide: \(CO_2(g)\)
**Part B: Calculating the Standard Enthalpy Change (\(\Delta H^\circ_{rxn}\))**
In this section, calculate the standard enthalpy change (\(\Delta H^\circ_{rxn}\)) for the reaction. Use the given standard heats of formation:
- \(C_6H_{12}O_6(s)\): \(-1273.3 \, \text{kJ/mol}\)
- \(CO_2(g)\): \(-393.5 \, \text{kJ/mol}\)
- \(C_2H_5OH(l)\): \(-277.6 \, \text{kJ/mol}\)
Enter your calculated value in kilojoules, rounded to one decimal place, using the formula for enthalpy change based on the standard heats of formation.
---
**Note**: The text also references resources for further study:
- *KCV: Determining the Enthalpy of Reaction from Standard Enthalpies of Formation*
- *IWE: \(\Delta H^\circ_{rxn}\) and the Standard Enthalpies of Formation*
- Section 7.9 in your eText
These resources will deepen your understanding of enthalpy calculations in chemical reactions.
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1
Fermentation of ethanol can be done from the glucose.
We have to write the balance chemical equation for fermentation of Ethanol.
Secondly we have to calculate the ∆H0 value of the reaction.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A 50 ml solution of 1.2M HCl at 24.1OC is mixed with 50 ml of 1.2M NaOH, also at 24.1oC, in a coffee-cup calorimeter. After the reaction occurs, the temperature of the resulting mixture is 29.8OC. The density of the final solution is 1.05 g/ml. Calculate the molar heat of neutralization. Assume the specific heat of the solution is 4.184 J/g-OC. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 32.5 J/oC. NaOH(aq) + HCl(aq) → NaCl(aq) + H2O(l)arrow_forwardA 5.1-gram piece of gold jewelry isremoved from water at 100.0°C and placed in a coffee-cup calorimeter containing 16.9 gof water at 22.5°C (specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g · °C). The equilibrium (final)temperature of the water and jewelry is 23.2°C. The calorimeter constant is known fromcalibration experiments to be 1.54 J/°C. What is the specific heat (in J/g · °C) of this pieceof jewelry? If the tabulated value of the specific heat of gold is 0.129oC, is the jewelrypure gold?arrow_forward31. When a 0.740-g sample of trinitrotoluene (TNT), C7H5N2O6, is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature increases from 23.4 °C to 26.9 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 534 J/°C, and it contains 675 mL of water. How much heat was produced by the combustion of the TNT sample?arrow_forward
- Use the References to access important values if needed for this question. A student determines the heat of dissolution of solid potassium bromide using a coffee-cup calorimeter of negligible heat capacity. When 6.36 g of KBr(s) is dissolved in 115.00 g of water, the temperature of the solution drops from 25.00 to 22.71 °C. Based on the student's observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution of KBr(s) in kJ/mol. Assume the specific heat of the solution is 4.184 J/g°C. AHdissolution = kJ/mol Submit Answer 5 question attempts remainingarrow_forwardWhen a solid dissolves in water, heat may be evolved or absorbed. The heat of dissolution (dissolving) can be determined using a coffee cup calorimeter. Thermometer Cardboard or In the laboratory a general chemistry student finds that when 3.38 g of CuCl,(s) are Styrofoam lid dissolved in 114.10 g of water, the temperature of the solution increases from 25.37 to 27.99 °C. The heat capacity of the calorimeter (sometimes referred to as the calorimeter constant) was determined in a separate experiment to be 1.60 J/°C. Nested Styrofoam cups Based on the student's observation, calculate the enthalpy of dissolution of CuCl2(s) in kJ/mol. - Reaction occurs in Assume the specific heat of the solution is equal to the specific heat of water. solution. AHdissolution kJ/mol kc Cengage Lnarrow_forwardA 10.0-g sample of ammonium nitrate, NH4NO3, is added to 100.0 mL of water (density = 1.00 g/mL) in a Styrofoam calorimeter. The initial temperature of water and calorimeter is 25.0 oC. When the solid completely dissolves, the final temperature of the solution is 18.4 oC. (a) Calculate heat lost by water and by the calorimeter. (Heat capacity of calorimeter is 15 J/oC and the specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g.oC)(b) What is the total amount of heat (in Joules) absorbed by the system (the dissolution of solid NH4NO3). (c) Write an equation for the dissolution of NH4NO3(s) and calculate its molar enthalpy of dissolution, Hdissol. expressed in kJ/mol.arrow_forward
- 1. How much energy (in kJ) is required to change the temperature of 1.00 kg Fe from 25.0 °C to 1515 °C? The specific heat capacity of iron is 0.449 J/g·C. 2. MgO reacts with water to form Mg(OH)2. If 5.00 g MgO is combined with 100.0 g H2O in a coffee cup calorimeter, the temperature of the resulting solution increases from 22.3 °C to 32.9 °C. Calculate the enthalpy change (kJ) for the reaction per mole of MgO. Assume that the specific heat capacity of the solution is 4.18 J/g·C. 3. Commercial cold packs consist of solid ammonium nitrate and water. NH4NO3 absorbs 25.69 kJ of heat per mole dissolved in water. In a coffee-cup calorimeter, 3.40 g NH4NO3 is dissolved in 100.0 g of water at 21.0 °C. What is the final temperature of the solution? Assume that the solution has a specific heat capacity of 4.18 J/g·Carrow_forwardThe combustion of hydrogen-oxygen mixtures is used to produce very high temperatures (ca. 2500 °C) needed for certain types of welding operations. Consider the reaction to be H₂(g) + ½O₂(g) → H₂O(g) ∆H° = -241.8 kJ/mol What is the quantity of heat evolved, in kilojoules, when a 180 g mixture containing equal parts of H₂ and O₂ by mass is burned?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY