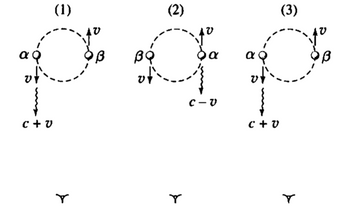
As seen in the image provided, a double-star system with stars of equal mass rotate in circular orbits around their mutual center of mass that is halfway between them. One of the stars (α) is bright. The other star (β) is its unseen dark companion. Our line of sight passes through the orbital plane such that once in every period, α approaches head-on, and once ever period it recedes directly away. The same is true for β. Suppose light always moves at speed c relative to the source that emits it (i.e., if v is the orbital speed of each star, light travels toward us at speed c + v from α when it is headed toward us, and at speed c - v when it is headed away from us, as depicted).
The double-star system is a distance d away from Earth. How long would take light to get to Earth from α if the light is emitted when α is (i) coming toward us, and (ii) moving away from us?
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

- 2. A ladder 6.00 m long leans against a wall inside a spaceship. From the point of view of a person on the ship, the base of the ladder is 2.10 m from the wall, and the top of the ladder is 5.62 m above the floor. The spaceship moves past the Earth with a speed of 0.86c in a direction parallel to the floor of the ship. Find the angle the ladder makes with the floor, as seen by an observer on Earth. 239119 16 ociarrow_forwardYou are driving down a two-lane country road, and a truck in the opposite lane is traveling toward you. Suppose that the speed of light in a vacuum is c = 69 m/s. Determine the speed of the truck relative to you when (a) your speed is 25 m/s and the truck’s speed is 35 m/s and (b) your speed is 5.0 m/s and the truck’s speed is 55 m/s. The speeds given in parts (a) and (b) are relative to the ground.arrow_forwardThe spectrum of a sun-like star is monitored and it is noticed that a spectral absorption line of wavelength A = 589 nm shifts periodically with a period equal to 10 days. The amplitude of the shift AX = ±1 × 10¬4 nm. The sun-like star has a mass M, = 2 × 1030 kg. Assuming that the periodic shifting of spectral lines is due to an unseen orbiting planet, estimate its mass. Express your answer in Earth massesarrow_forward
- One of the wavelengths of light emitted by hydrogen atoms under normal laboratory conditions is l = 656.3 nm, in the red portion of the electromagnetic spectrum. In the light emitted from a distant galaxy this same spectral line is observed to be Doppler-shifted to l = 953.4 nm, in the infrared portion of the spectrum. How fast are the emitting atoms moving relative to the earth? Are they approaching the earth or receding from it?arrow_forwardA rocket ship traveling near the speed of light appears to a stationary observer to shorten with speed. A rocket with a length of 200 meters will appear to a stationary observer to have a length of 200 Sqrt[1-r^2]meters, where r is the ratio of the velocity of the ship to the speed of light. What is the apparent length of the rocket ship if it is traveling at a speed that is 99% off the speed of light?arrow_forwardusing the parallax method (p = 0.77) and the standard candle method (apparent magnitude = 11.13; absolute magnitude = 15.60) to compute the distance to Proxima Centuari, both produce a result of about 4 light years. From a scientific and an inductive reasoning point of view why is getting about the same answer viewed as extremely significant from the standpoints of inductive reasoning and probable truth What is the concept of making inductive arguments stronger that applies? Answer here. What do these methods tell us about the size of the universe we live in compared to the universe Tycho and the people of his time thought they lived in?arrow_forward
- A laser pointer is placed on a platform that rotates at a rate of 19 revolutions per minute. The beam hits a wall 8 m away, producing a dot of light that moves horizontally along the wall. Let 0 be the angle between the beam and the line through the searchlight perpendicular to the wall. How fast is this dot moving when 0 = Wall π ? 6 8 m Laser (Use decimal notation. Give your answer to one decimal place.) velocity of the dot: m/minarrow_forwardConsider the case of two kids, Sam and Peter, riding a train and playing catch in an empty car. The train is moving to the right at 10 m/s. The kids can throw the ball at a speed of 5 m/s. The side of the car is transparent and a poodle named Max can see the boys playing inside. What is the speed and direction of Sam’s throw to Peter, according to Max? Explain.arrow_forwardConsider a thought experiment performed in free space. In the experiment, a small cube C of mass m is placed at the centre of a large and highly massive disc D and a ball B of mass M revolves in circular path of radius R around the centre of the disc. The plane of the circle is perpendicular to the plane of the dise as shown in the figure. Intensity of the gravitational field of the disc near its centre is g. What should be range of coefficient of friction between the cube and the disc so that the cube remains motionless?arrow_forward
- Consider a spiral galaxy that is moving directly away from Earth with a speed V = 3.040×105 m/s at its center, as shown in the figure. The galaxy is also rotating about its center, so that points in its spiral arms are moving with a speed v = 6.950×105 m/s relative to the center. A) If light with a frequency of 7.543×1014 Hz is emitted in both arms of the galaxy, what frequency is detected by astronomers observing the arm that is moving toward the Earth? (Measurements of this type are used to map out the speed of various regions in distant, rotating galaxies.) Express your answer using four significant figures. B) If light with a frequency of 7.543×1014 Hz is emitted in both arms of the galaxy, what frequency is detected by astronomers observing the arm that is moving away from Earth? Express your answer using four significant figures.arrow_forwardIn the red shift of radiation from a distant galaxy, a certain radiation, known to have a wavelength of 434 nm when observed in the laboratory, has a wavelength of 462 nm. (a)What is the radial speed of the galaxy relative to Earth? (b) Is the galaxy approaching or receding from Earth?arrow_forwardThe distance to a star is approximately 4.43 ✕ 1018 m. If this star were to burn out today, in how many years would we see it disappear? (b) How long does it take sunlight to reach Earth? in minutes(c) How long does it take for a microwave radar signal to travel from Earth to the Moon and back? (The distance from Earth to the Moon is 3.84 ✕ 105 km.)in secondsarrow_forward