
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
thumb_up100%
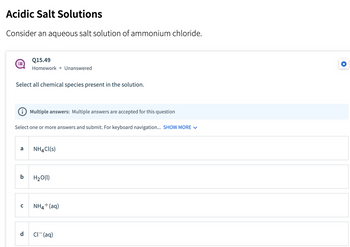
Transcribed Image Text:### Acidic Salt Solutions
**Consider an aqueous salt solution of ammonium chloride.**
---
**Q15.49**
Homework • Unanswered
Select all chemical species present in the solution.
**Multiple answers:** Multiple answers are accepted for this question.
Select one or more answers and submit. For keyboard navigation... **SHOW MORE**
- **a** NH₄Cl(s)
- **b** H₂O(l)
- **c** NH₄⁺(aq)
- **d** Cl⁻(aq)
This question asks students to identify the chemical species that are present in a solution when ammonium chloride (NH₄Cl) is dissolved in water. The options include the solid ammonium chloride, liquid water, and the aqueous ions that result from the dissolution process. Students need to select all that apply based on their understanding of solubility and dissociation in aqueous solutions.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Given 0.01 M solutions of each of the following acids, which solution would have the lowest pH? -117 Hypoiodous acid (HOI), K = 2.3 x 10 Hypobromous acid (HOBr), K = 2.5 x 10 Lactic acid (HC₂H₂O₂), K = 1.3 x 10 Chlorous acid (HClO₂), K = 1.1 x 10²arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwritten solutionarrow_forward1. A typical acid-base reaction involves an acid (losing proton) and a base (gaining proton) as reactant and corresponding conjugate base (product from acid losing proton) and conjugate acid (product from base gaining proton) as product. Acid + Base Û Conjugate Base + Conjugate Acid Look at the following acid-base reactions and identify reactant acid, base and product conjugate base, conjugate acid. (a) HC1 + OH Û H₂O + CI Acid Base (b) HNO, + OH Û H₂O + NO, Acid Base ; Base ; Conjugate Acid Acid Base Base ; Conjugate Acid (c) NH, + H,O Ô NH+OH ; Base ; Conjugate Acid ; Conjugate ; Conjugate ; Conjugatearrow_forward
- 4th Edition McQuarrie Rock Gallogly versity Science Books presented by Macmillan Learning Calculate the pH of the resulting solution if 27.0 mL of 0.270 M HCl(aq) is added to 37.0 mL of 0.270 M NaOH(aq). pH = Calculate the pH of the resulting solution if 27.0 mL of 0.270 M HCl(aq) is added to 17.0 mL of 0.370 M NaOH(aq). pH = O 8: Question Source: McQuarrie, Rock, And Gallogly 4e - General Chemistry | Publisher: University Science Books 5:53 PM 68°F (1) 6/2/2022arrow_forwardUse the References to access important values if needed for this question. Classify each of the following as a strong acid or a weak acid. Indicate how each should be written in aqueous solution. For example, should chlorous acid be represented as HClO2 or as H++ ClO2? phosphoric acid In solution, this acid should be written as hydrochloric acid In solution, this acid should be written as acetic acid- In solution, this acid should be written asarrow_forwardPlease type this, dont write it on a paper!arrow_forward
- The pH of a 1.3 M solution of hydrocyanic acid (HCN) is measured to be 4.55. Calculate the acid dissociation constant K, of hydrocyanic acid. Round your answer to 2 significant digits. a. K = 0 Continuearrow_forward$ 4 [Review Topics] [References] Calculate the [OH-] of each of the following solutions at 25°C. Identify each solution as neutral, acidic, or basic. Also calculate the pH and pOH of each of these solutions. [+] = 1.0 × 107 M [OH-] = The solution is pH = pOH = b. [H] = 9.8 x 10-16 M [OH-] = The solution is pH = pOH = 000 R F Submit Answer a. F4 % 5 Show Hint T G FS ^ Retry Entire Group 9 more group attempts remaining 6 v Y M MacBook Air F6 M H 87 & U J * 00 8 ( 9 K O BORS v 1 O L F10 P DIO 1108 chat A - 4) Previous F11 SAVAGE X FENTY... + A = C. 11 Next Save and Exit Show All } deletarrow_forwardWrite the chemical formual of acid: Cl-(aq0+HS04-(aq) HCI(AQ+SO42-(aq)arrow_forward
- Strong acids and strong bases ionize 100% in aqueous solution. HCl is a strong acid. In solution we write it as H"(aq) + Cl (aq). - HF is a weak acid. In solution we write it as HF(aq). - KOH is a strong base. In solution we write it as K*(aq) + OH (aq). - NH3 is a weak base. In solution we write it as NH3(aq). Exception: Since Ca(OH), is only slightly soluble we write it as Ca(OH)2(s). Below is a list of the 6 strong acids and 6 strong bases you should know. All other acids and bases are considered weak. Strong Bases LIOH, NaOH, КОН Strong Acids HCІ, HBr, HI HNO3 Ca(OH)2 (slightly soluble) HCIO4 Ba(OH)2 H2SO4 Sr(ОН)2arrow_forwardWhich of the following chemical formulas corresponds to a base? HCl; KOH; H2SO4; HNO3arrow_forwardWhen carbon dioxide gas dissolves in water, it reacts with the water to form carbonic acid. This is why soft drinks have a low pH, and soda water is often recommended as a mild cleaning agent. It is also why there is concern that rising levels of atmospheric carbon dioxide may cause the Earth's oceans to become more acidic. Here is the reaction between carbon dioxide gas and water: H₂O(1) + CO₂(g) H₂CO3(aq) Suppose an engineer decides to study the rate of this reaction. He prepares four reaction vessels with 152.7 g of water and 34.3 g of carbon dioxide gas each. The volume and temperature of each vessel is shown in the table below. Arrange the reaction vessels in decreasing order of initial rate of reaction. In other words, select a "1" next to the vessel in which the engineer can reasonably expect the initial rate of reaction to be highest, a "2" next to the vessel in which the initial rate of reaction would be next highest, and so on. vessel volume temperature A B C D 8.0 L 1.0 L…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY