
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
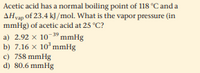
Transcribed Image Text:Acetic acid has a normal boiling point of 118 °C and a
AHvap of 23.4 kJ /mol. What is the vapor pressure (in
mmHg) of acetic acid at 25 °C?
a) 2.92 x 103º mmHg
b) 7.16 x 10*mmHg
c) 758 mmHg
d) 80.6 mmHg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Mount Rainier is the highest mountain in the U.S. state of Washington; it rises 4392 m above sealevel (which is approximately half the height of Mount Everest). If the ambient temperature is 15 °C at sealevel, determine the absolute pressure at the top of Mount Rainier. HINT: The universal gas constant in standard SI units is 8314.3 J/kmol-K Altitude (m) 8964 4392 2025 Sea level Mount Everest Mount Rainier (Washington) Clingman's Dome (Smoky Mountains National Park)arrow_forwardQUESTION 2 Under constant pressure P = 1 atm an ideal gas of 1.5 mol undergoes cooling from 120°C to 30.0°C, and = 3/2R. Please calculate q, w, AU, and AH (all units are J). Cv.m Please enter all four answers using scientific notation (E notation) with three significant figures, such as 2.30E4 (=23000). If the answer is negative, please do not forget the negative sign. If answer is zero, please just enter 0 without decimal. (1) q= (2) w= (3) AU= (4) ΔΗ=arrow_forwardSuperheated steam at 300°C and 1 bar (absolute) is to be fed to a heat exchanger. It is produced by mixing an available stream of saturated steam at 1 bar discharged from a turbine at a rate of 1150 kg/h with a second stream of superheated steam at 400°C and 1 bar. The mixing may be considered adiabatic. Calculate the amount of superheated steam at 300°C produced and the required volumetric flow rate of the 400°C steam. a. b. C. d. e. Draw a picture of your system. Label input and exit streams and include mass flow rate, temperature, and pressure. Use variables to define any unknowns. Determine enthalpies for all streams at appropriate conditions. See attached steam table. All enthalpy values in the steam table are in kJ/kg. Write the open system energy balance and eliminate unnecessary terms (include brief justifications). Determine the mass flow rate of saturated steam. Please give your answer in kg/hr. Determine the volumetric flow rate of the saturated steam. Please give your…arrow_forward
- J 5arrow_forwardA high-altitude balloon contains helium, whose molar mass is 4.00 g/mol. At theballoon’s maximum altitude, its volume is 792 m3 and the outside temperatureand pressure are -53.0 °C and 5.00 kPa, respectively. Assume that the helium in theballoon is in equilibrium with the outside air temperature and pressure.(a) Use the ideal gas law to find the amount of helium in the balloon at maximumaltitude.(b) Assuming no loss of helium, what would be the volume of the balloon when itwas launched from the ground, where the air temperature and pressure are 20.0°C and 101 kPa, respectively?(c) If the volume of the balloon when it was launched was 65.0 m3, how many molesof helium were lost during the balloon’s ascent?arrow_forwardQUESTION 2 3.8 moles of an ideal gas at 27.0°C expands isothermally from an initial volume of 20.0 dm³ to a final volume of 83.1 dm³. Calculate w (unit is J) for this process for expansion against a constant external pressure of 3.1 bar. Please write your answer in scientific E notation with 3 significant figures. If your answer is negative, please add negative sign. For example: -2.32E2. Do not write unit (J).arrow_forward
- Vapor pressure data are given here for octane, C8H18. Temperature(c) Vapor Pressure (mm Hg) 25 13.6 50 45.3 75 127.2 100 310.8 Use the Clausius–Clapeyron equation to calculate the molar enthalpy of vaporization of octane and its normal boiling pointarrow_forwardCalculate the pressure(in atm) of the saturated liquid at 71 °C.arrow_forward2 g of a saturated liquid are converted to a saturated vapor by being heated in a weighted piston-cylinder device arranged to maintain the pressure at 200 kPa. During the phase conversion, the volume of the system increases by 500 cm3, 10 kJ of heat are required, and the temperature of the substance stays constant at 80 °C. Estimate the saturation pressure (in kPa) of this substance when the temperature is 100 °C.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The