
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynamics
8th Edition
ISBN: 9781259696527
Author: J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher: McGraw-Hill Education
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
Acetaldehyde is synthesized by the catalytic dehydrogenation of ethanol:
Fresh feed (pure ethanol) is blended with a recycle stream (95 mole% ethanol and 5%
acetaldehyde), and the combined stream is heated and vaporized, entering the reactor at 280°C.
Gases leaving the reactor are cooled to condense the acetaldehyde and unreacted ethanol. Off-gas
from the condenser is sent to a scrubber, where the uncondensed organic compounds are
removed and hydrogen is recovered as a by-product. The condensate from the condenser, which
is 45 mole% ethanol, is sent to a distillation column that produces a distillate containing 99
mole% acetaldehyde and a bottoms product that constitutes the recycle blended with fresh feed
to the process. The production rate of the distillate is 1000 kg/h. The pressure throughout the
process may be taken as 1 atm absolute.
Fresh feed (pure ethanol) is blended with a recycle stream (95 mole% ethanol and 5%
acetaldehyde), and the combined stream is heated and vaporized, entering the reactor at 280°C.
Gases leaving the reactor are cooled to condense the acetaldehyde and unreacted ethanol. Off-gas
from the condenser is sent to a scrubber, where the uncondensed organic compounds are
removed and hydrogen is recovered as a by-product. The condensate from the condenser, which
is 45 mole% ethanol, is sent to a distillation column that produces a distillate containing 99
mole% acetaldehyde and a bottoms product that constitutes the recycle blended with fresh feed
to the process. The production rate of the distillate is 1000 kg/h. The pressure throughout the
process may be taken as 1 atm absolute.
If the vapor leaving the condenser (off-gas to scrubber) is at -40 ̊C and 760 torr, what is the
molar composition of this stream?What assumption are you making when solving this problem?
molar composition of this stream?What assumption are you making when solving this problem?
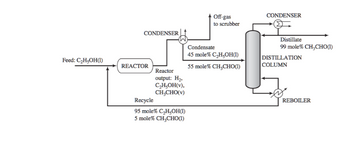
Transcribed Image Text:Feed: C₂H₂OH(1)
CONDENSER
REACTOR
Reactor
output: H₂,
C₂H₂OH(v),
CH,CHO(v)
Recycle
95 mole% C₂H,OH(1)
5 mole% CH,CHO(T)
Off-gas
to scrubber
Condensate
45 mole% C₂H-OH(1)
55 mole
CH,CHO(1)
CONDENSER
Distillate
99 mole% CH,CHOQ)
DISTILLATION
COLUMN
REBOILER
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- Ammonia is oxidized in a continuous reactor 4NH3 g + 5O2 g --> 4NO g + 6H2O g delta AHr= -904.7KJ mol The feed stream (40 mole% NH3 and 60 mole% O2 )enters the reactor at 200 degrees celsius with 80% conversion of ammonia and the products leave at 300 degrees celsius. Determine the quantity of heat required to be added or removed from the reactor.arrow_forwardAcetaldehyde is synthesized by the catalytic dehydrogenation of ethanol: Fresh feed (pure ethanol) is blended with a recycle stream (95 mole% ethanol and 5% acetaldehyde), and the combined stream is heated and vaporized, entering the reactor at 280°C. Gases leaving the reactor are cooled to condense the acetaldehyde and unreacted ethanol. Off-gas from the condenser is sent to a scrubber, where the uncondensed organic compounds are removed and hydrogen is recovered as a by-product. The condensate from the condenser, which is 45 mole% ethanol, is sent to a distillation column that produces a distillate containing 99 mole% acetaldehyde and a bottoms product that constitutes the recycle blended with fresh feed to the process. The production rate of the distillate is 1000 kg/h. The pressure throughout the process may be taken as 1 atm absolute. Calculate the flow rate of the distillate in mol/s (use the actual composition of the distillate, 99 mole% acetaldehyde and 1 mole%…arrow_forwardThe process of air conditioning in the humidifier, air at a dry bulb temperature of 30°C and RH of 10 % increases the RH to 50%. Determine the amount of water vapor added in the humidifier by dry air (kg water / kg air).arrow_forward
- Acetaldehyde is synthesized by the catalytic dehydrogenation of ethanol: Fresh feed (pure ethanol) is blended with a recycle stream (95 mole% ethanol and 5% acetaldehyde), and the combined stream is heated and vaporized, entering the reactor at 280°C. Gases leaving the reactor are cooled to condense the acetaldehyde and unreacted ethanol. Off-gas from the condenser is sent to a scrubber, where the uncondensed organic compounds are removed and hydrogen is recovered as a by-product. The condensate from the condenser, which is 45 mole% ethanol, is sent to a distillation column that produces a distillate containing 99 mole% acetaldehyde and a bottoms product that constitutes the recycle blended with fresh feed to the process. The production rate of the distillate is 1000 kg/h. The pressure throughout the process may be taken as 1 atm absolute. Assume that the vapor leaving the top tray of the distillation column is at 475 K and 1 atm, contains the same molar composition as the distillate,…arrow_forwardThe fraction recrystallized-time data for the recrystallization at 350°C of a previously deformed aluminum are tabulated here. Assuming that the kinetics of this process obey the Avrami relationship, determine the fraction recrystallized after a total time of 116.8 min. Assume y1 = 0.38 and y, = 0.73. Fraction Recrystallized Time (min) 95.2 126.6 iarrow_forwardAmmonia is oxidized in a continuous reactor 4NH3 g + 5O2 g --> 4NO g + 6H2O g delta AHr= -904.7KJ mol The feed stream (40 mole% NH3 and 60 mole% O2 )enters the reactor at 200 degrees celsius with 80% conversion of ammonia and the products leave at 300 degrees celsius. Determine the quantity of heat required to be added or removed from the reactor. The basis of calculation: 10mol/s of feed stream. given: the constant heat capacity, Cp, of NH3(g), O2(g), NO(g), and H2O(v) are 0.035, 0.029, 0.029 and 0.033KJ/ mol. degrees celsius respectively.) Cp O2 or table 8 for the calculation. can you please explaing each steparrow_forward
- Paper is being dried with recirculating air in a two-stage drying system at 1 atm. Air (State 1) enters the first dryer at 180°F, where it is adiabatically saturated to 100% relative humidity (State 2). The saturated air is then reheated to 174°F (State 3) before entering the second dryer, where it is adiabatically humidified to 80% relative humidity (State 4). This air stream is then cooled to 60°F, causing some moisture to be condensed (State 5). This is followed by a third heater to heat the air to 180°F (State 1) before it returns to the first dryer, completing the entire cycle. 1. Draw the process on the humidity chart. Label all relevant points consistent with the diagram of the process provided. 2. For each stream, determine the moisture content in air (Ib H20/lb dry air). 3. Determine the lb H20 evaporated (moisture leaving the paper and entering the air) in each dryer per lb of dry air being 100% RH TDB = 174F HEATER 1 DRYER 2 DRYER 1 80% RH 5 HEATER 2 CHILLER TDB = 180F TDB =…arrow_forwardA single effect evaporatoris being used to concentrate 8000 kg/h of tomato juice from 5% total solids to 30% total solids. The juice enters the evaporator at 25°C. The evaporator is operated with steam (80% quality) at 143.27 kPa. The vacuum inside the evaporator allows the juice to boil at 80 ° C. The specific heat of the liquid feed is 4.1 kJ/(kg°C) and the concentrated product is 3.1 kJ/(kg°C). Calculate(a) the steam requirements = Answer kg / hour.(b) steam economy for the process. Assume the condensate is discharged at 75°C. = Answer (kg of water evaporates / kg of steam)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781259696527Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark SwihartPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...Chemical EngineeringISBN:9780133887518Author:H. Scott FoglerPublisher:Prentice Hall
 Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning
Industrial Plastics: Theory and ApplicationsChemical EngineeringISBN:9781285061238Author:Lokensgard, ErikPublisher:Delmar Cengage Learning Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The
Unit Operations of Chemical EngineeringChemical EngineeringISBN:9780072848236Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter HarriottPublisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The

Introduction to Chemical Engineering Thermodynami...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781259696527
Author:J.M. Smith Termodinamica en ingenieria quimica, Hendrick C Van Ness, Michael Abbott, Mark Swihart
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY

Elements of Chemical Reaction Engineering (5th Ed...
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780133887518
Author:H. Scott Fogler
Publisher:Prentice Hall


Industrial Plastics: Theory and Applications
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9781285061238
Author:Lokensgard, Erik
Publisher:Delmar Cengage Learning

Unit Operations of Chemical Engineering
Chemical Engineering
ISBN:9780072848236
Author:Warren McCabe, Julian C. Smith, Peter Harriott
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Companies, The