
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
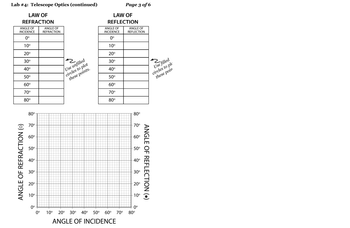
Transcribed Image Text:Lab #4: Telescope Optics (continued)
LAW OF
REFRACTION
ANGLE OF
INCIDENCE
0⁰
10⁰
20⁰
30°
40°
50⁰
60°
70⁰
80°
ANGLE OF REFRACTION (0)
80⁰
70⁰
60°
50⁰
40⁰
30⁰
20⁰
10⁰
0⁰
0⁰
ANGLE OF
REFRACTION
/Use unfilled
circles to plot
these points.
Page 3 of 6
LAW OF
REFLECTION
ANGLE OF
INCIDENCE
0⁰
10⁰
20⁰
30⁰
40°
50⁰
60⁰
70⁰
80⁰
ANGLE OF
REFLECTION
80⁰
-70°
60°
50°
40°
30°
-20°
-10°
·0⁰
10⁰ 20⁰ 30⁰ 40⁰ 50⁰ 60⁰ 70⁰ 80⁰
ANGLE OF INCIDENCE
Use filled
circles to pl
these poin
ANGLE OF REFLECTION ()
Transcribed Image Text:Lab #4: Telescope Optics (continued)
Page 5 of 6
Make a refracting telescope using the lenses in the white envelopes on the lab table as follows:
• Carefully insert the thin lens in one of the lens holders.
Alternatively, you may hold it securely between your fingers
as shown in the figure at right. Insert the thick lens into
a lens holder or hold it securely.
THICK
LENS
• Align the lenses so that you can look through both in the direction of the paper on the wall
labeled "NORTH". While keeping the thick lens close to your eye, move the thin lens slowly
toward or away from the thick lens. At some point, the word "NORTH" should come into focus.
1) Is the image you see upside down & reversed?,
2) Is the size of the image larger than what you see with the naked eye?
3) Do you notice anything peculiar around the edges of the letters and paper?
Complete the chart on the next page. Your instructor will distribute concave mirrors
and binoculars. A Newtonian reflecting telescope is located in the northwest corner
of the lab room.
• To measure the diameter, place the lens or concave mirror on the ruler at right.
Use a meter stick to measure the diameter of the Newtonian telescope's tube.
• To compute the radius, divide the diameter by two.
• To find the area, square the radius and multiply it by J (~3.14).
• To find the Light Gathering Power (LGP) as eye area equivalents, divide the area
of the lens or mirror by the area of the lens of the human eye.
• To find the Resolving Power (RP), use the following relationship:
Resolving power of lens or mirror in degrees =
Diameter of eye's lens in cm x 0.02⁰
Diameter of lens or mirror in cm
• To measure the focal lengths of the lenses, mount them in the optical bench as
shown in the diagram below and adjust the screen until a focused image appears on
the screen. The distance between the screen and lens is the focal length. Note: Keep
the light source as far from the lens as possible. You can also use light from a source
outside such as reflected light from a distant building or from a streetlight. For the
concave mirror, reflect the light back to its source and find the point where the light
is brought to a focus. Use a meter stick to measure the length of the Newtonian
telescope's tube.
screen
lens in
holder
light
source
THIN
LENS
optical bench
To find the Magnifying Power (MP), divide the focal length of the objective lens or
mirror by the focal length of the eyepiece.
centimeters
O
N
لا
00
10
Expert Solution
arrow_forward
Step 1

Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A ray of light would change direction when (Check all that apply): A.) Changing mediums at an angle of 90° from the surface B.) changing mediums when directly in line with the surface normal C.) incident on a shiny, smooth surface D.) changing mediums at an angle of less than 90° from the surfacearrow_forward#1arrow_forwardWaves and Opticsarrow_forward
- Part 3 - Keplerian Telescope A telescope magnifies far-off images. Rays hitting the objective are almost parallel and are focused to form an inverted, real image at the focal point of the eyepiece. The eyepiece refracts the light so the rays leave the eyepiece again almost parallel. The object remains inverted, and so the angular magnification is defined as M= -B/a, where the angles are shown in Figure 2. objective eyepiece f. f. f. F e F. h inverted image at infinity Figure 2: A Keplerian telescope, invented by Johannes Kepler in 1611, uses two converging lenses as shown. An objective with focal length fo and an eyepiece with focal length fe focus nearly parallel light rays from a distant object into an inverted image of much smaller size than the object. 1. Assume that a and ß are small angles (much less than 1 radian). Using the ray diagram shown in Figure 2 and considering two appropriate triangles, show that M = -fo/ fe.arrow_forwardPHY.3 What is the focal length of a flint glass converging lens with radii of curvature 4cm and 5cm ? The lens from question 2 is used to produce the image of anobject 0.9 meters in front of the le a. At what distance from the lens is the object's image?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON