
Structural Analysis
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781337630931
Author: KASSIMALI, Aslam.
Publisher: Cengage,
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
a. What is the value of the distributed load in beam B2 in plf (lb/ft)?
b. What is the value of each of the point loads acting on girder G1 in kips to one decimal place?
c. What is the value of the force in column C6 in the ground floor (in kips to one decimal place)?
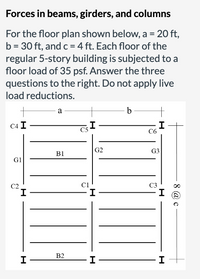
Transcribed Image Text:Forces in beams, girders, and columns
For the floor plan shown below, a = 20 ft,
b = 30 ft, andc = 4 ft. Each floor of the
regular 5-story building is subjected to a
floor load of 35 psf. Answer the three
questions to the right. Do not apply live
load reductions.
a
b
C4 I
I
C6
C5
G2
G3
B1
G1
C1
I-
C2
C3
I
I
B2
I
8
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- . A beam is constructed from a reinforced 50mm x 200mm section of timber using two L120x80x12 steel angle sections. Considering that the effort allowable stress in wood is 10 MPa, and the allowable stress in steel is 110 MPa. Determine the maximum positive and negative moment that the beam can supportarrow_forwardSituation 1. For the steel framing plan shown in Figure 1, use the tributary area method to distribute the floor loads to the supporting structural members. The girders are made of W410x46 while the beams are W360x33. Compute the maximum shear and bending moments for girders 3G-1, 3G-2, and 3G-4 by considering the following: a. the entire floor area is to carry a floor live load of 4.8 kPa and a superimposed dead load of 0.6 kPa; b. the thickness of the slab is 150 mm and framing dimensions are in mm; c. use unit weight of concrete of 23.5 kN/m3; d. include the self-weight of the beams and girders; e. your final answer should be based on the shear and moment diagrams of the corresponding girders; and f. discuss the critical and important assumptions made in your ideal model and solution. A B 1500 2000 2000 1500 1500 3G - 1 3G - 2 -I- 2. 3G - 1 3G - 2 GIRDERS CROSS-SECTION W410 x 46 BEAMS CROSS-SECTION W360 x 33 Area = 5890 mm2 Area = 4170 mm2 Figure 1 00s8 3G – 3 3B – 1 3G – 4 3B – 2…arrow_forwardWhat is the value of the force in column C5 and C6 in the ground floor (in kips to one decimal place)?arrow_forward
- What is the value of kip/ft of the uniform load on beam B1 ? What is the value in kips of the point load in the middle of Girder G1 ? What is the value in kips of the point load in the middle of Girder G2 ? What is the value in kips of the axial force in Column C2 on the first storey ?arrow_forwardWhat is the value of the force in column C4 and C2 in the ground floor? Each floor of the regular 5-story building is subjected to a floor load of 35 psf. a = 20ft, b = 30ft, and c= 4ft. b C4I C5 C6 G2 G3 BI GI C2 Ci I B2 8 @ carrow_forward3. For the three-hinge arch below, let F1 = 10 1lbs, F2 =20 lbs, H1 = 5 feet and L1 and F2 act at L1/2 from A and L2/2 from C, respectively. Determine the reactions at the supports (A & C) and the pin forces at B and write your final results in the table below for the following conditions: 1 5 feet. F1 H2 L2 Ax Ay Bx By Cx Су 2 ft 5 ft. 4 ft 4 ft. 10 ft 10 ft F Show by arrows the direction of each force. Show forces at B on member AB. F. В Hi H2 Li L2arrow_forward
- An Am. long beam is on hinged at its left end and on fixed support at its right end. Its flexural capacity is 610 kN.m. whilte its web shear capacity is 642 kN. Beam flexural rigidity is Y x 1012 N.mm². #1 What is the allowable uniformly distributed load on the beam so that the flexural capacity is not exceeded? #2 Based on web shear capacity, what is the allowable uniformly distributed load (kN/m)? #3 When the support at the left end is removed, a cantilever beam results. How much should the beam be cambered at the free end to offset the end deflection if the load W = 210 kN/m? Use: A = 8 Y=29arrow_forward17.3. A transfer girder has an overall depth of 11 ft and spans 22 ft between column supports. In addition to its own weight, it will pick up a uniformly distributed factored load of 4.0 kips/ft from the floor above and will carry a 14 x 14 in. column delivering a concentrated factored load of 270 kips from floors above at midspan. The girder width must be equal to or less than 16 in. Design the beam for the given loads. Find the girder width and the area and geometry of tie steel, and specify the placement details. Material strengths are f = 5000 psi and fy = 60,000 psi.arrow_forwardslab single /simple spanning slab spanning twoway/ double The timber structure below has a single spanning floor of grade C16 beams of weight 4.2 kN/m? and a two way spanning floor 150 mm thick of CLT flooring of density 410 kg/m3. Dimensions are as follows: Length a = 2.8 m %3D b = 4.4 m C = 4.4 m Find the reaction of the internal beam acting on the edge beam at X. Give your answer in kN to one decimal place. Do not put units in the answer box. The conversion from kg to kN is (x 9.81 / 1000)arrow_forward
- Determine the absolute shear and moment of the beam and series of concentrate loads shownarrow_forwardSITUATION 1: A precast girder of length 20 m is to be lifted at two points at equal distance from both ends. The weight of the girder is 0.10787 oz/mm. And its section modulus is 900,000 mm3. The moment should be made as small as possible. 1. Determine the distance (m) of the pick-up points from each end.arrow_forwardFigure below shows the partial steel structure floor framing plan of a hospital building. Assuming a total DL of 100 psf and an average LL 60 psf. 1. For Beam B1: Using LRFD load combinations: a. Calculate the corresponding factored loads, Wu (klf) b. Draw the shear force diagram and calculate the maximum factored shear, Vu (Demand). c. Draw the bending moment diagram and calculate the maximum factored moment, Mu (Demand). 2. For Girder G1: Using LRFD load combinations: a. Calculate the corresponding factored loads, Wu (klf) b. Draw the shear force diagram and calculate the maximum factored shear, Vu (Demand). c. Draw the bending moment diagram and calculate the maximum factored moment, Mu (Demand).arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you

 Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Structural Analysis (10th Edition)Civil EngineeringISBN:9780134610672Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...Civil EngineeringISBN:9781337705028Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam SivakuganPublisher:Cengage Learning Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Fundamentals of Structural AnalysisCivil EngineeringISBN:9780073398006Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel LanningPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
 Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Traffic and Highway EngineeringCivil EngineeringISBN:9781305156241Author:Garber, Nicholas J.Publisher:Cengage Learning


Structural Analysis (10th Edition)
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780134610672
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Principles of Foundation Engineering (MindTap Cou...
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781337705028
Author:Braja M. Das, Nagaratnam Sivakugan
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Fundamentals of Structural Analysis
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9780073398006
Author:Kenneth M. Leet Emeritus, Chia-Ming Uang, Joel Lanning
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education


Traffic and Highway Engineering
Civil Engineering
ISBN:9781305156241
Author:Garber, Nicholas J.
Publisher:Cengage Learning