
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Topic Video
Question
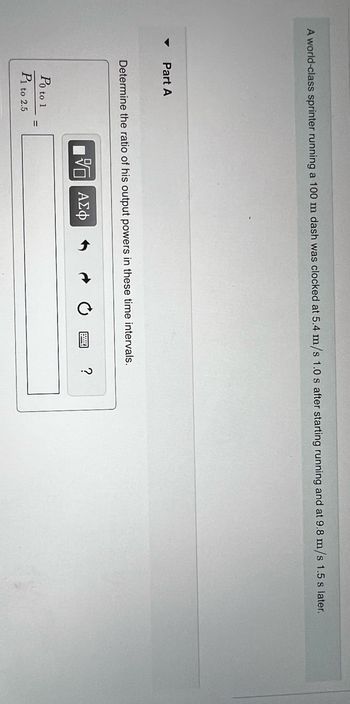
Transcribed Image Text:A world-class sprinter running a 100 m dash was clocked at 5.4 m/s 1.0 s after starting running and at 9.8 m/s 1.5 s later.
Part A
Determine the ratio of his output powers in these time intervals.
Po to 1
P1 to 2.5
15 ΑΣΦ
?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 5 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Question 18 If a quantity you calculated had units of kg. m/s, what type of quantity could it be? none of the given choices O potential energy O momentum work O kinetic energy 2 pts ◄ Previous Next ▸arrow_forwardIf a 3.58 kg object is placed on a frictionless incline of 59.5 º and released from rest, what is speed of the object down the incline after traveling a distance of 1.06 m? Enter a number rounded to 2 decimal places and assume it has proper SI units.arrow_forwardYou plan to take a trip to the moon. Since you do not have a traditional spaceship with rockets, you will need to leave the earth with enough speed to make it to the moon. Some information that will help during this problem: mearth = 5.9742 x 1024 kgrearth = 6.3781 x 106 mmmoon = 7.36 x 1022 kgrmoon = 1.7374 x 106 mdearth to moon = 3.844 x 108 m (center to center)G = 6.67428 x 10-11 N-m2/kg2 1) On your first attempt you leave the surface of the earth at v = 5534 m/s. How far from the center of the earth will you get? 2) Since that is not far enough, you consult a friend who calculates (correctly) the minimum speed needed as vmin = 11068 m/s. If you leave the surface of the earth at this speed, how fast will you be moving at the surface of the moon? Hint carefully write out an expression for the potential and kinetic energy of the ship on the surface of earth, and on the surface of moon. Be sure to include the gravitational potential energy of the earth even when the ship is…arrow_forward
- 17. A few weeks ago in lab you were releasing gliders down a tilted frictionless air track. Assume the track surface is tilted by 18 degrees from the horizontal. The glider is released from rest at t=0, and passes through a gate, which is a distance d along the track from the starting position, 0.90 seconds later. What is d (to 2 sig.figs)? A) 1.6 m B) 4.0 m 日:18° 3.8 m D) 2.5 m E) 1.2 m 9 COS 18arrow_forwardmes New... BIUA 田回, 三三 12 + 三| 1三 2. 3 2. Ryan having mass 60 kg possesses a kinetic energy of 1.3 kJ. What is his speed? 3. Steven having mass 52 kg jumps to the surface of the table which is at the height of 45 cm. Find his gravitational potential energy.arrow_forwardIf a 3.9 kg object is placed on a frictionless incline of 55.6 ° and released from rest, what is speed of the object down the incline after traveling a distance of 1.69 m? Enter a number rounded to 2 decimal places and assume it has proper Sl units.arrow_forward
- Which of the following quantities has the same dimensions as kinetic energy, mv? Note: [a] = [g] = LT²; [h] = L and [v] = LT'. та тух mvt mgh mgtarrow_forward"Energy per unit time" is a quantity called Power. Which of the following combinations has the same units as power? A length squared times mass over time squared B persimmons. C speed times mass times acceleration over time D Force times acceleration E {potential energy minus kinetic energy} times time F Force times velocity G speed squared times mass H mass time acceleration I mass squared times acceleration.arrow_forwardYou are playing a game and you push a cart to give it in. speed. The cart starts at the bottom (zero) of a ramp and after reaching the top of the ramp, the cart travels across a horizontal track w/ friction. The mass of the cart is 44 x 10^-3 kg. The ramp is 56 cm high. The length is 70 cm. What can you infer of the intial speed in (m/s)arrow_forward
- A uranium-238 nucleus undergoes a radioactive decay, 238 U 234Th + 4He. The masses are approximately 238, 234 and 4 u, where u = the atomic mass unit. The U nucleus is initially at rest. Suppose the He nucleus has speed v. Then what is the kinetic energy of the Th nucleus? Parameters: ] u = 1.66 x 10-27 kg; v = 9.000×106 m/s. (in J) A: 2.942x10-15 B: 3.678x10-15 OC: 4.597x10-15 D: 5.746x10-15 OE: 7.183x10-15 F: 8.978x10-15 OG: 1.122x10-14 OH: 1.403x10-14arrow_forwardAt the Earth's surface, a projectile is launched straight up at a speed of 7.7 km/s. To what height will it rise? Ignore air resistance. 3.00E6 X Your response differs from the correct answer by more than 10%. Double check your calculations. m Need Help? Read Itarrow_forwardIf a particle is moving, it has kinetic energy. Kinetic energy is the energy of motion, and it depends on the speed and mass of the particle. It is given by the formula Ek = 1/2*mv2, where Ek is the kinetic energy, m is the mass, and v is the speed of the particle. The formula for kinetic energy has some important features to keep in mind. Kinetic energy, and every other type of energy as well, is a scalar quantity, given by only a single number. Energy does not have a "direction", unlike a vector quantity. (This is in contrast to the vector quantity momentum, which you might have already studied.) Kinetic energy, in particular, is always a positive number. (Note the speed v is the magnitude of the vector velocity, and therefore is positive. But even if it were a negative number, squaring it would always lead to a positive result.) Kinetic energy depends on the square of the speed. (This is in contrast to the magnitude of momentum, mv, a quantity you may have already studied, which…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON