
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
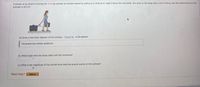
Transcribed Image Text:A woman at an airport is towing her 13.0-kg suitcase at constant speed by puling on a strap at an angle e above the horizontal. She puls on the strap with a 28.0-N force, and the friction force on the
suitcase is 20.0 N.
(a) Draw a free-body diagram of the suitcase. Cheose Fe no ie selected
This answer has not been graded yet
(b) What angle does the strap make with the horizontal?
(c) What is the magnitude of the normal force that the ground exerts on the suitcase?
Need Help?
Weh
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- To maintain a constant speed, the force provided by a car's engine must equal the drag force plus the force of friction of the road (the rolling resistance). The density of air is 1.2 kg/m. (a) What are the drag forces in newtons at 75 km/h and 104 km/h for a Toyota Camry? (Drag area = 0.70 m? and drag coefficient = 0.28.) at 75 km/h at 104 km/h (b) What are the drag forces in newtons at 75 km/h and at 104 km/h for a Hummer H2? (Drag area = 2.44 m2 and drag coefficient = 0.57.) at 75 km/h at 104 km/h N Additional Materialsarrow_forwardA 29.0-kg block is initially at rest on a horizontal surface. A horizontal force of 77.0N is required to set the block in motion, after which a horizontal force of 63.0 N is required to keep the block moving with constant speed. (a) Find the coefficient of static friction between the block and the surface. (b) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction between the block and the surface. Need Help? Watch It Read Itarrow_forwardwo blocks are positioned on surfaces, each inclined at the same angle of 52.3 degrees with respect to the horizontal. The blocks are connected by a rope which rests on a frictionless pulley at the top of the inclines as shown, so the blocks can slide together. The mass of the black block is 3.16 kg, and the coefficient of kinetic friction for both blocks and inclines is 0.440. Assume static friction has been overcome and that everything can slide. What is must be the mass of the white block if both blocks are to slide to the LEFT at an acceleration of 1.5 m/s^2? 2.34 kg 1.66 kg 10.38 kg 5.97 kgarrow_forward
- A 5.0-kg box is on a horizontal surface. The coefficients of static and kinetic friction between the box and the surface are 0.40 and 0.20, respectively. A 15-N push is applied to the box horizontally, what is the friction on the box?arrow_forwardAn 11 kg block is being pushed forward on a flat surface with a force of magnitude 45 N. The coefficient of static friction on the block is 0.15 and the coefficient of kinetic friction on the block is 0.12 (only one of these needs to be used). (a) Draw a free body diagram of the block. (b) What is the net force acting on the block? (c) What is the acceleration of the block? FN Eaarrow_forwardA child of mass 30 kg sits on a sled of mass 10kg which is pulled along the ice at a constant speed by a rope inclined at 30 °to the horizontal. The coefficient of friction for the ice and sled, HK, is 0.05. Calculate the pulling force in the rope. Pulling force F, pull 30° Gravity FG Normal i Friction farrow_forward
- A 5.1 kg box is slid across the floor at constant speed by a force of 25 N (40o above horizontal) as shown in the figure below. (a) How large a friction force impedes the motion of the box? (b) How large is the normal force? (c) Find the coefficient of kinetic friction.arrow_forwardA horizontal force, Fm, is applied to a book that is on a rough horizontal tabletop. As a result the book is accelerating to the right. If necessary, use Fs for the force of static friction and Fk as the force of kinetic friction. Draw a free body diagram for the bookarrow_forwardThe upper leg muscle (quadriceps) exerts a force of 1180 N, which is carried by a tendon over the kneecap (the patella) at the angles shown in Figure 5.43. Find the magnitude and direction of the force exerted by the kneecap on the upper leg bone (the femur). N ° (counter-clockwise from an axis directed to the left)arrow_forward
- Please Asaparrow_forwardA 50 kg box is pushed with a force of 200 N along a horizontal surface. If the coefficient of friction between the box and the surface is 0.3, calculate the acceleration of the box. (Note: The gravitational acceleration can be assumed to be 9.8 m/s² unless stated otherwise.)arrow_forwardConsider the 65.0 kg Ice skater being pushed by two others shown In the figure. Frot F2 Free-body diagram F, F, F, (a) Find the direction (in degrees) and magnitude (in N) of F,et, the total force exerted on her by the others, glven that the magnitudes F, and F, are 25.2 N and 15.4 N, respectively. direction o (counterclockwise from the direction of F, is positive) magnitude (b) What is her initial acceleration (in m/s?) if she is initlally stationary and wearing steel-bladed skates that point in the direction of F? (c) What is her acceleration (in m/s2) assuming she is already moving in the direction of Fot? Remember that friction is always in the opposite direction of motion or attempted motion between surfaces in contact. m/s? (in the direction of Frot)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON