
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
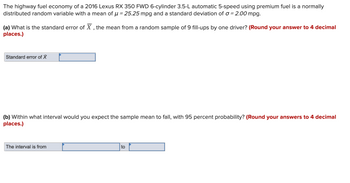
Transcribed Image Text:The highway fuel economy of a 2016 Lexus RX 350 FWD 6-cylinder 3.5-L automatic 5-speed using premium fuel is a normally
distributed random variable with a mean of μ = 25.25 mpg and a standard deviation of a = 2.00 mpg.
(a) What is the standard error of X, the mean from a random sample of 9 fill-ups by one driver? (Round your answer to 4 decimal
places.)
Standard error of X
(b) Within what interval would you expect the sample mean to fall, with 95 percent probability? (Round your answers to 4 decimal
places.)
The interval is from
to
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A random sample of 10,000 bottles of cola was taken to see whether the mean weight was 16 fluid ounces, as marked on the container. The null hypothesis is that the population mean is 16 ounces. Use the read-out below to test the hypothesis that the colas do not have a population mean of 16 fluid ounces. You do not have to do any calculations; just interpret the given data clearly and thoroughly in the context of the problem. | One-Sample T: ounces Test of u = 16 vs = 16 Variable Mean StDev SE Mean 95 CI T P ounces 10000 15.9988 0.0985 0.0010 (15.9969, 16.0007) -1.21 0.225arrow_forwardA sample of n = 6 scores has a mean of M = 5. One person with a score of X= 12 is added to the distribution. What is the mean for the new set of scores? O M= 8arrow_forwardSuppose in 2000, the science scores for female students had a mean of 146 with a standard deviation of 35. Assume that these scores are normally distributed with the given mean and standard deviation. _________________ of the female students scored between 76 and 216arrow_forward
- What value of x is two standard deviation to the right of the mean if X - N(10, 1)? 1 2 4 8 10 12arrow_forwardA population of N = 8 scores has a mean of M = 10. After one score is removed, the mean is found to be M = 5 What is the value of the score that was added? A X = 45 B X = 35 C X = 50 D X = 80arrow_forwardYou determine that the standard deviation for a sample of test scores is 0. This tells you that 1 all the test scores must be 0. 2 all the test scores must be the same value. 3 there is no straight-line association. 4 the mean test score must also be 0. 5 you made a mistake because the standard deviation can never be 0.arrow_forward
- Withdrawal symptoms may occur when a person using a painkiller suddenly stops using it. For a special type of painkiller, withdrawal symptoms occur in 1% of the cases. A random sample of 1100 people who have stopped using the painkiller is going to be taken. Let p be the proportion of people in the sample who experience withdrawal symptoms. Answer the following. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a) Find the mean of P. 0 (b) Find the standard deviation of p. 0 (c) Compute an approximation for P<0.02), which is the probability that fewer than 2% of the people in the sample experience withdrawal symptoms. Round your answer to four decimal places. 0 Xarrow_forwardA researcher wants to investigate the effects of environmental factors on IQ scores. For an initial study, she takes a sample of 400 people who grew up as the only child. She finds that 51.5% of them have an IQ score over 100. It is known that 50% of the general population has an IQ score exceeding 100. Answer the following. (If necessary, consult a list of formulas.) (a)Find the mean of p, where p is the proportion of people with IQ scores over 100 in a random sample of 400 people. (b)Find the standard deviation of p. (c)Compute an approximation for P≥p0.515, which is the probability that there will be 51.5% or more individuals with IQ scores over 100 in a random sample of 400. Round your answer to four decimal places.arrow_forwardWhat is the formula for finding the z-score? The z-score of the mean is always Z =arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman