
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A uniformly charged solid disk of radius R=0.25 m carries a uniform charge density of σ=225μC/m2. A point P is located a distance a=0.25 m from the center of the disk and perpendicular to the face of the disk.
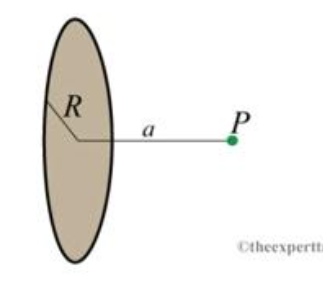
Transcribed Image Text:R
a
P
Ctheexpertta
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 5 steps with 10 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- The figure below shows a small, charged bead, with a charge of q = +41.0 nC, that moves a distance of d = 0.174 m from point A to point B in the presence of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 255 N/C, pointing right. A positive point charge q is initially at point A, then moves a distance d to the right to point B. Electric field vector E points to the right. (a) What is the magnitude (in N) and direction of the electric force on the bead? magnitude Ndirection (b) What is the work (in J) done on the bead by the electric force as it moves from A to B? J (c) What is the change of the electric potential energy (in J) as the bead moves from A to B? (The system consists of the bead and all its surroundings.) PEB − PEA = J (d) What is the potential difference (in V) between A and B? VB − VA = Varrow_forwardAn infinite line of positive charge lies along the y axis, with charge density = 1.30 μC/m. A dipole is placed with its center along the x axis at x = 22.0 cm. The dipole consists of two charges ±10.0 μC separated by 2.00 cm. The axis of the dipole makes an angle of 45.0° with the x axis, and the positive charge is farther from the line of charge than the negative charge. Find the net force exerted on the dipole. F -0.0683 N An infinite line of positive charge lies along the y axis, with charge density = 1.30 μC/m. A dipole is placed with its center along the x axis at x = 22.0 cm. The dipole consists of two charges ±10.0 μC separated by 2.00 cm. The axis of the dipole makes an angle of 45.0° with the x axis, and the positive charge is farther from the line of charge than the negative charge. Find the net force exerted on the dipole. -0.623 N Xarrow_forwardA circular plastic disk with radius R = 2.00 cm has a uniformly distributed charge Q = +(2.00 x 106)e on one face. A circular ring of width 30 µm is centered on that face, with the center of that width at radius r = 0.50 cm. In coulombs, what charge is contained within the width of the ring?arrow_forward
- An infinite line of positive charge lies along the y axis, with charge density A = 1.10 µC/m. A dipole is placed with its center along the x axis at x = 21.0 cm. The dipole consists of two charges ±10.0 µuC separated by 2.00 cm. The axis of the dipole makes an angle of 25.0° with the x axis, and the positive charge is farther from the line of charge than the negative charge. Find the net force exerted on the dipole.arrow_forwardIn the figure a small, nonconducting ball of mass m = 1.1 mg and charge q = 2.4 × 10-8 C (distributed uniformly through its volume) hangs from an insulating thread that makes an angle θ = 38° with a vertical, uniformly charged nonconducting sheet (shown in cross section). Considering the gravitational force on the ball and assuming the sheet extends far vertically and into and out of the page, calculate the surface charge density σ of the sheet.arrow_forwardYour answer is partially correct. The charges and coordinates of two charged particles held fixed in an xy plane are q1 = 2.13 µC, x1 = 4.35 cm, Y1 = 0.304 cm and 92 = -5.93 µC, x2 = -2.30 cm, y2 = 1.07 cm. Find the (a) magnitude and (b) direction (with respect to +x-axis in the range (-180°;180°]) of the electrostatic force on particle 2 due to particle 1. At what (c) x and (d) y coordinates should a third particle of charge q3 = 6.16 µC be placed such that the net electrostatic force on particle 2 due to particles 1 and 3 is zero? (a) Number 25.3 Units N (b) Number i 173.44 Units ° (degrees) (c) Number -3.6 Units m Number i 0.42 Units marrow_forward
- An infinitely long rod lies along the x-axis and carries a uniform linear charge density λ = 5 μC/m. A hollow cone segment of height H = 27 cm lies concentric with the x-axis. The end around the origin has a radius R1 = 8 cm and the far end has a radius R2 = 16 cm. Refer to the figure. a. Consider the conic surface to be sliced vertically into an infinite number of rings, each of radius r and infinitesimal thickness dx. Enter an expression for the electric flux differential through one of these infinitesimal rings in terms of λ, x, and the Coulomb constant k. b. Integrate the electric flux over the length of the cone to find an expression for the total flux through the curved part of the cone (not including the top and bottom) in terms of λ, H, and the Coulomb constant k. Enter the expression you find. c. Calculate the electric flux, in N•m2/C, through the circular end of the cone at x = 0. d. Calculate the electric flux, in N•m2/C, through the circular end of the cone at x = H. e.…arrow_forwardAn infinite sheet of charge is located in the y-z plane at x = 0 and has uniform charge denisity o1 = 0.62 µC/m². Another infinite sheet of charge with uniform charge density o2 = -0.29 µC/m² is located at x = c = 33 cm.. An uncharged infinite conducting slab is placed halfway in between these sheets ( i.e., between x = 14.5 cm and x = 18.5 cm). d a/2 a/2| a/2 1) What is Ex(P), the x-component of the electric field at point P, located at (x,y) = (7.25 cm, 0)? N/C Submit 2) What is oa, the charge density on the surface of the conducting slab at x = 14.5 cm? | µC/m² Submit 3) What is V(R) - V(P), the potentital difference between point P and point R, located at (x,y) = (7.25 cm, -18.5 cm)? Submit 4) What is V(S) - V(P), the potentital difference between point P and point S, located at (x,y) = (25.75 cm, -18.5 cm)? V submit + 5) What is Ex(T), the x-component of the electric field at point T, located at (x,y) = (40.25 cm, -18.5 cт)? N/C Submit R.arrow_forwardThe figure below shows a charged particle, with a charge of q = +38.0 nC, that moves a distance of d = 0.185 m from point A to point B in the presence of a uniform electric field E of magnitude 245 N/C, pointing right. A positive point charge q is initially at point A, then moves a distance d to the right to point B. Electric field vector E points to the right. (a) What is the magnitude (in N) and direction of the electric force on the particle? magnitude Ndirection ---Select--- toward the right toward the left The magnitude is zero. (b) What is the work (in J) done on the particle by the electric force as it moves from A to B? J (c) What is the change of the electric potential energy (in J) as the particle moves from A to B? (The system consists of the particle and all its surroundings.) PEB − PEA = J (d) What is the potential difference (in V) between A and B? VB − VA = Varrow_forward
- The electric field in an xy plane produced by a positively charged particle is 6.20(6.61 + 6.3) N/C at the point (4.1, 4.6) cm and 123 N/C at the point (3.8, 0) cm. What are the (a) x and (b) y coordinates of the particle? (c) What is the charge of the particle? (a) Number i Unitsarrow_forwardA conducting sphere is placed within a conducting spherical shell. The conductors are in electrostatic equilibrium. The inner sphere has a radius of 1.50 cm, the inner radius of the spherical shell is 2.25 cm, and the outer radius of the shell is 2.75 cm. The inner sphere has a charge of 228 nC and the spherical shell has zero net charge. What is the electric field at a point 3.80 cm from the center? Enter a positive answer if the electric field is directed away from the center and a negative answer if the electric field is directed toward the center.arrow_forwardA conducting sphere of radius r1 = 0.46 m has a total charge of Q = 2.9 μC. A second uncharged conducting sphere of radius r2 = 0.23 m is then connected to the first by a thin conducting wire. The spheres are separated by a very large distance compared to their size. r1 = 0.46 mr2 = 0.23 mQ = 2.9 μC What is the total charge on sphere two, Q2 in coulombs?arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON