
Modern Physics
3rd Edition
ISBN: 9781111794378
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
thumb_up100%
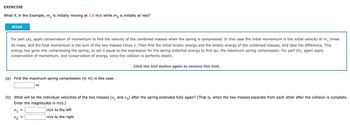
Transcribed Image Text:EXERCISE
What if, in the Example, m₁ is initially moving at 3.8 m/s while m2 is initially at rest?
Hint
For part (a), apply conservation of momentum to find the velocity of the combined masses when the spring is compressed. In this case the initial momentum is the initial velocity of m₁ times
its mass, and the final momentum is the sum of the two masses times v. Then find the initial kinetic energy and the kinetic energy of the combined masses, and take the difference. This
energy has gone into compressing the spring, so set it equal to the expression for the spring potential energy to find Ax, the maximum spring compression. For part (b), again apply
conservation of momentum, and conservation of energy, since the collision is perfectly elastic.
(a) Find the maximum spring compression (in m) in this case.
m
Click the hint button again to remove this hint.
(b) What will be the individual velocities of the two masses (V₁ and 2) after the spring extended fully again? (That is, when the two masses separate from each other after the collision is complete.
Enter the magnitudes in m/s.)
V1
=
m/s to the left
=
m/s to the right

Transcribed Image Text:A Two-Body Collision with a Spring
A block of mass m₁ = 1.50 kg initially moving to the right with a speed of 5.00 m/s on a frictionless, horizontal track collides with a light spring attached to a second block of mass m₂
initially moving to the left with a speed of 2.50 m/s as shown in figure (a). The spring constant is 550 N/m. (Assume the positive direction points to the right.)
Before a moving block collides with another
moving block with a spring attached.
a
m
k
V2i
m2
At one instant during the collision.
k
m1
m2
wwwwww
b
= 6.50 kg
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- A hockey puck of mass 150 g is sliding due east on a frictionless table with a speed of 10 m/s. Suddenly, a constant force of magnitude 5 N and direction due north is applied to the puck for 1.5 s. Find the north and east components of the momentum at the end of the 1.3-s interval.arrow_forwardA 2.00-kg object hangs, at rest, on a 1.00-m-long string attached to the ceiling. A 100-g mass is fired with a speed of 20 m/s at the 2.00-kg mass, and the 100.00-g mass collides perfectly elastically with the 2.00-kg mass. Write an equation for the motion of the hanging mass after the collision. Assume air resistance is negligible.arrow_forwardA skater of mass 40 kg is carrying a box of mass 5 kg. The skater has a speed of 5 m/s with respect to the floor and is gliding without any friction on a smooth surface. a. Find the momentum of the box with respect to the floor. b. Find the momentum of the box with respect to the floor after she puts the box down on the frictionless skating surface.arrow_forward
- A space probe, initially at rest, undergoes an internal mechanical malfunction and breaks into three pieces. One piece of mass ml = 48.0 kg travels in the positive x-direction at 12.0 m/s, and a second piece of mass m2 = 62.0 kg travels in the xy-plane at an angle of 105 at 15.0 m/s. The third piece has mass m3 = 112 kg. (a) Sketch a diagram of the situation, labeling the different masses and their velocities, (b) Write the general expression for conservation of momentum in the x- and y-directions in terms of m1, m2, m3, v1, v2 and v3 and the sines and cosines of the angles, taking to be the unknown angle, (c) Calculate the final x-components of the momenta of m1 and m2. (d) Calculate the final y-components of the momenta of m1 and m2. (e) Substitute the known momentum components into the general equations of momentum for the x- and y-directions, along with the known mass m3. (f) Solve the two momentum equations for v3 cos and v3 sin , respectively, and use the identity cos2 + sin2 = 1 to obtain v3. (g) Divide the equation for v3 sin by that for v3 cos to obtain tan , then obtain the angle by taking the inverse tangent of both sides, (h) In general, would three such pieces necessarily have to move in the same plane? Why?arrow_forwardA particle is suspended from a post on top of a can by a light string of length L. as shown in Figure P9.57a. The can and particle are initially moving to the right at constant speed the with the string vertical. The can suddenly comes to rest when it runs into and sticks to a bumper as shown in Figure P9.57b. The suspended panicle swings through an angle . (a) Show that the original speed of the cart can be computed from. vi=2gL(1cos) (b) If the bumper is still exerting a horizontal force on the cart when the hanging panicle is at its maximum angle forward from the vertical. at what moment does the bumper stop exerting a horizontal force?arrow_forwardThe momentum of an object is increased by a factor of 4 in magnitude. By what factor is its kinetic energy changed? (a) 16 (b) 8 (c) 4 (d) 2 (e) 1arrow_forward
- A ball of mass 250 g is thrown with an initial velocity of 25 m/s at an angle of 30 with the horizontal direction. Ignore air resistance. What is the momentum of the ball after 0.2 s? (Do this problem by finding the components of the momentum first, and then constructing the magnitude and direction of the momentum vector from the components.)arrow_forwardTwo identical particles, each of mass 1 000 kg, are coasting in free space along the same path, one in front of the other by 20.0 m. At the instant their separation distance has this value, each particle has precisely the same velocity of 800 m/s. What are their precise velocities when they are 2.00 m apart? Figure P13 74arrow_forwardA cannon is rigidly attached to a carriage, which can move along horizontal rails but is connected to a post by a large spring, initially unstretchcd and with force constant k = 2.00 104 N/m, as shown in Figure P8.60. The cannon fires a 200-kg projectile at a velocity of 125 m/s directed 45.0 above the horizontal. (a) Assuming that the mass of the cannon and its carriage is 5 000 kg, find the recoil speed of the cannon. (b) Determine the maximum extension of the spring. (c) Find the maximum force the spring exerts on the carriage. (d) Consider the system consisting of the cannon, carriage, and projectile. Is the momentum of this system conserved during the firing? Why or why not?arrow_forward
- A block of mass m1 = 20.0 kg is connected to a block of mass m2 = 30.0 kg by a massless string that passes over a light, frictionless pulley. The 30.0-kg block is connected to a spring that has negligible mass and a force constant of k = 250 N/m as shown in Figure P7.73. The spring is un-stretched when the system is as shown in the figure, and the incline is frictionless. The 20.0-kg block is pulled a distance h = 20.0 cm down the incline of angle = 40.0 (so that the 30.0-kg block is 40.0 cm above the floor) and released from rest. Find the speed of each block when the 30.0-kg block is 20.0 cm above the floor (that is, when the spring is unstretched). Figure P7.73arrow_forwardIn a laboratory experiment, 1 a block of mass M is placed on a frictionless table at the end of a relaxed spring of spring constant k. 2 The spring is compressed a distance x0 and 3 a small ball of mass m is launched into the block as shown in Figure P11.22. The ball and block stick together and are projected off the table of height h. Find an expression for the horizontal displacement of the ballblock system from the end of the table until it hits the floor in terms of the parameters given. FIGURE P11.22arrow_forwardGeorge of the Jungle, with mass m, swings on a light vine hanging from a stationary tree branch. A second vine of equal length hangs from the same point, and a gorilla of larger mass M swings in the opposite direction on it. Both vines are horizontal when the primates start from rest at the same moment. George and the gorilla meet at the lowest point of their swings. Each is afraid that one vine will break, so they grab each other and hang on. They swing upward together, reaching a point where the vines make an angle of 35.0 with the vertical. Find the value of the ratio m/M.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning
Modern PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781111794378Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. MoyerPublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University
University Physics Volume 1PhysicsISBN:9781938168277Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff SannyPublisher:OpenStax - Rice University Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based TextPhysicsISBN:9781133104261Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...PhysicsISBN:9781133939146Author:Katz, Debora M.Publisher:Cengage Learning College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...PhysicsISBN:9781305116399Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning

Modern Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781111794378
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Clement J. Moses, Curt A. Moyer
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics Volume 1
Physics
ISBN:9781938168277
Author:William Moebs, Samuel J. Ling, Jeff Sanny
Publisher:OpenStax - Rice University

Principles of Physics: A Calculus-Based Text
Physics
ISBN:9781133104261
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers: Foundations...
Physics
ISBN:9781133939146
Author:Katz, Debora M.
Publisher:Cengage Learning

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Physics for Scientists and Engineers, Technology ...
Physics
ISBN:9781305116399
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning