
Concept explainers
A thin, diverging lens having a focal length of magnitude 45.0 cm has the same principal axis as a concave mirror with a radius of 60.0 cm. The center of the mirror is 20.0 cm from the lens, with the lens in front of the mirror. An object is placed 23.0 cm in front of the lens.
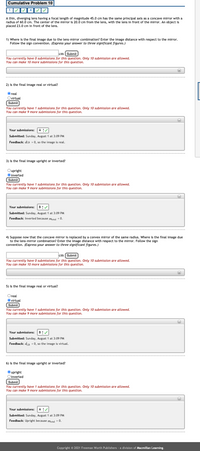
1)Where is the final image due to the lens–mirror combination? Enter the image distance with respect to the mirror. Follow the sign convention. (Express your answer to three significant figures.)
4)Suppose now that the concave mirror is replaced by a convex mirror of the same radius. Where is the final image due to the lens–mirror combination? Enter the image distance with respect to the mirror. Follow the sign convention. (Express your answer to three significant figures.)
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

- A concave mirror is placed 10 cm in front of an object. The image measures 6 cm, and the image-mirror distance is 40 cm. Solve completely and find: a) radius of curvature in meters or cm and focal length in meters or cm b) magnification and the size of the object in cm c) Say if the image is real or virtual, if the image is reduced, the same size or enlarged and if the image is erect or invertedarrow_forwardA convex mirror has a Radius of Curvature of 5.80 cm and is the second optical device (spherical mirror or thin lens) in an optical system. The image from the first optical device becomes an object for the second device. For the given convex mirror, a virtual image is located 39.7 cm away on the optical axis. Answer the following questions. All answer tolerance ±5 on the third significant digit. a) Calculate the mirror's focal length. Number b) Calculate the object distance. Number c) Is the object real or virtual? Real Virtual Units O Upright Units d) Calculate the maginification of the mirror. Number e) Relative to the image, is the object inverted or upright? Invertedarrow_forwardAll problems involve a concave (converging) mirror that has a radius of curvature of 18.0 m.For problems 1-4, an object of height 12.0 cm is placed 15.00 m in front of the mirror. Calculate the image distance, the image height, and the magnification(not necessarily in that order). 1) Calculate di. 2) Calculate hi. 3) Calculate the magnification m. 4) Where is the image formed? A) on the object side of the optic B) on the side of the optic opposite the object C) there is no image formedarrow_forward
- Box answers for A and C, keep getting it wrong.arrow_forwardYou are given a spherical mirror and wish to determine its properties. You place an object on its axis, 33.5 cm in front of it, and discover that the mirror creates a virtual image located 14.5 cm from the mirror. Determine the mirror's focal length / in centimeters. Calculate the mirror's radius of curvature C in centimeters. If it can be determined, is the mirror concave or convex? convex concave cannot be determined. cm cmarrow_forwardIn the figure below, a diverging lens and concave spherical mirror are positioned along an optical axis, with an object half way between the two. The distance between the lens and mirror is d = 23.6 cm. The magnitude of the mirror's radius of curvature is 20.1 cm, and the lens has a focal length of flens = -19.0 cm. Lens Object Mirror (a) Considering only the light that leaves the object and travels first toward the mirror, locate the final image formed by this system. (Give the magnitude of the image distance in cm, and select its location with respect to the lens.) image distance image location -Select--- (b) Is this image real or virtual? O real O virtual (c) Is it upright or inverted? O upright O inverted (d) What is the overall magnification? cmarrow_forward
- A student notices that the image produced from a large concave mirror of a distant skyscraper of height hs= 106 m is inverted and the magnitude of the height is |hiI = 1.46 m tall. The image is located di = 178 cm in front of the mirror. A)Write an expression for the distance between the mirror and the skyscraper, ds. B) What is the distance between the mirror and the skyscraper in meters? C) What is the focal length of the mirror, f, in centimeters?arrow_forwardAn object is 30.0 from a spherical mirror, 1 magnification is. The image produced is inverted. What is along the central axis. The absolute value of lateral 2 the focal length of the mirror?arrow_forward+ Mirror Equation: Si So M; = = - Yo So Principle Ray: the ray from object to mirror that is parallel to the principle (optical) axis will reflect in a path that intersects the image focal point. Radius Ray: the ray from the object whose path is aligned curvature center point will reflect directly back to the center point on the principle (optical) axis. Central Ray: the ray from the object whose path is directed towards the center of the mirror (intersection with the principle axis) will reflect from the lens in the opposite direction with respect the optical path. Conventions: Quantity Sign Positive (+) Negative (-) Object distance So Real object Virtual object Image distance Si Real image Virtual image Focal length Concave mirror Convex mirror (opposite side of o,i) Radius of curvature R Convex Concave Object height Yo Erect object Inverted object Image height Yi Erect image Inverted image Magnification (transverse) MT Erect image Inverted image For the following mirror…arrow_forward
- You have a concave spherical mirror (the same holds if you had a convex mirror) If the value of q(the distance from the image to the mirror along the principal axis of the mirror) is 1.45m and the distance of p (the distance from the object to the mirror along the principal axis of the mirror) is 4.11m, what is the focal length of the mirror? The magnification equation and the sign convention for q imply that real images of real objects are always inverted (if both p and q are positive, m is negative); virtual images of real objects are always upright (if p is positive and q is negative, m is positive). Keeping the signs of p and q straight in your mind is the most challenging aspect of mirrors (and lenses). Fortunately, table 23.2 summarizes when p and q are positive and when they are negative.arrow_forwardAn object 1.30 cm high is held 3.00 cm from a person's cornea, and its reflected image is measured to be 0.167 cm high. What is the magnification? magnification: Where is the image? image distance: cm Find the magnitude of the radius of curvature of the convex mirror formed by the cornea. magnitude of radius of curvature: cmarrow_forward
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON





