
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
thumb_up100%
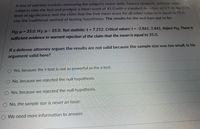
Transcribed Image Text:A test of sobriety involves measuring the subject's motor skills. Twenty randomly-selected sober
subjects take the test and produce a mean score of 41.0 with a standard deviation of 3.7. At the 0.01
level of significance, test the claim that the true mean score for all sober subjects is equal to 35.0.
Use the traditional method of testing hypotheses. The results for the test turn out to be:
Ho: H = 35.0. H1:µ/35.0. Test statistic: t 7.252. Critical values: t = -2.861, 2.861. Reject Ho. There is
sufficient evidence to warrant rejection of the claim that the mean is equal to 35.0.
If a defense attorney argues the results are not valid because the sample size was too small, is his
argument valid here?
Yes, because the t-test is not as powerful as the z-test.
No, because we rejected the null hypothesis.
Yes, because we rejected the null hypothesis.
O No, the sample size is never an issuc.
O We need more information to answer.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- You are testing the claim that the mean GPA of night students is different from the mean GPA of day students. You sample 35 night students, and the sample mean GPA is 2.68 with a standard deviation of 0.75. You sample 55 day students, and the sample mean GPA is 2.45 with a standard deviation of 0.49. Test the claim using a 5% level of significance. Assume the population standard deviations are unequal and that GPAs are normally distributed. Give answer to at least 4 decimal places. What are the correct hypotheses? Ho: Select an answer = Select an answer H₁: Select an answer ? Select an answer Based on the hypotheses, find the following: Test Statistic = Critical Values = ± (Just enter the positive CV.) The correct decision is to Select an answer The correct summary would be: [Select an answer night students is different from the mean GPA of day students. that the mean GPA ofarrow_forwardWhen you purchased your car, the dealer told you that your average gas mileage on your car was 30mpg, but you suspect that is might be lower than that. You conduct a sample over 30 days, and find that your sample average is only 28 mpg, with a standard deviation of 8.2 mpg. You conduct a hypothesis test, and find a P-value of 9.6%. What are your conclusions? Use an a level of 5% O Reject H, and accept H4. You have strong evidence that your car does get less than 28 mpg, on average. O Accept H.. You have strong evidence that your car gets 28 mpg, on average. O Reject H4. You have strong evidence that your car gets more than 28 mpg, on average. O Fail to reject Ho. You do not have strong evidence that your car gets less than 28 mpg, on average.arrow_forwardThe average American consumes 86 liters of alcohol per year. Does the average college student consume more alcohol per year? A researcher surveyed 11 randomly selected college students and found that they averaged 95.8 liters of alcohol consumed per year with a standard deviation of 20 liters. What can be concluded at the the a= 0.05 level of significance? a. For this study, we should use Select an answer b. The null and alternative hypotheses would be: Ho ? Select an answer H₁: ? Select an answer c. The test statistic ? C d. The p-value = e. The p-value is ? a f. Based on this, we should Select an answer the null hypothesis. g. Thus, the final conclusion is that ... (please show your answer to 3 decimal places.) (Please show your answer to 4 decimal places.) O The data suggest the population mean is not significantly more than 86 at a = 0.05, so there is statistically insignificant evidence to conclude that the population mean amount of alcohol consumed by college students is equal to…arrow_forward
- An automobile manufacturer claims that their van has a 51.4 miles/gallon (MPG) rating. An independent testing firm has been contracted to test the MPG for this van. After testing 250 vans they found a mean MPG of 51.5. Assume the standard deviation is known to be 2.2. Is there sufficient evidence at the 0.01 level that the vans outperform the manufacturer's MPG rating? Step 4 of 5: Enter the decision rule. Reject Ho if z >arrow_forwardPeople spend an average of $11 on entertainment. You believe that for people who live in Arizona, this number is significantly lower. To test, you randomly sampled n=100 Arizona residents and asked them how much they spend on entertainment. The sample average of these respondents was $10.74 with a sample standard deviation of $1.2. If you want to test the null hypothesis that H0: u=11 vs Ha: u<11, what is the value of the test statistic?arrow_forwardYou are testing the claim that the mean GPA of night students is different from the mean GPA of day students. You sample 60 night students, and the sample mean GPA is 2.16 with a standard deviation of 0.79. You sample 20 day students, and the sample mean GPA is 2.09 with a standard deviation of 0.93. Test the claim using a 1% level of significance. Assume the population standard deviations are unequal and that GPAs are normally distributed. Give answer to at least 4 decimal places. What are the correct hypotheses? Ho: ₁ H₁: M₁ Test Statistic = Critical Values Based on the hypotheses, find the following: = = H₁₂ ± #v OF H₂ (Just enter the positive CV.) The correct decision is to Fail to reject the null hypothesis The correct summary would be: There is not enough evidence to support the claim ✓ of night students is different from the mean GPA of day students. o that the mean GPAarrow_forward
- A researcher claims that the amounts of acetaminophen in a certain brand of cold tablets have a mean different than the 600mg claimed by the manufacturer. Test this claim at the .01 significance level. The mean acetaminophen content for a random sample of n = 29 tablets is 597.9 mg with a standard deviation of 3.8 mg. What are the hypotheses? What is the test statistic? Is it a z or a t? Find the P-value for this test statistic. How does it compare to the significance level? On the normal curve, indicate the location of the test statistic and the p-value. (label them on the graph) Write a conclusion in statistical terms and relate it to the parameters of this problem.arrow_forwardBrooke is interested in whether art classes improve students’ attitudes about school. She collects a sample of students who are enrolled in art class and finds that they report a mean of M = 19 on a school-attitudes scale. She knows that the school-attitudes scale has a mean of μ = 15 and a standard deviation of σ = 3. What type of test would you use to test the hypothesis that art classes improve school attitudes? Would you use a one-tailed or two-tailed test? What would be an appropriate measure of effect size to report?arrow_forwardA recent report claims that Americans spend an average of $11 per day on lunch. You believe that people who live in Philadelphia, PA spend significantly less on lunch per day than that. In order to test this, you randomly sampled n=100 Philadelphia residents and asked them how much they spend on lunch everyday. The sample average of these respondents was $10.92 with a sample standard deviation of $1.07. If you want to test the null hypothesis that H0: mean=11 vs Ha: mean <11.what is the value of the test statistic?arrow_forward
- 10. Gravetter/Wallnau/Forzano, Essentials - Chapter 9 - End-of-chapter question 15 Weinstein, McDermott, and Roediger (2010) report that students who were given questions to be answered while studying new material had better scores when tested on the material compared to students who were simply given an opportunity to reread the material. In a similar study, an instructor in a large psychology class gave one group of students questions to be answered while studying for the final exam. The overall average for the exam was u = 73.4, but the n = 16 students who answered questions had a mean of M = 78.3 with a standard deviation of s = 8.4. For this study, did answering questions while studying produce significantly higher exam scores? Use a one-tailed test with a = .01 and the Distributions tool to help. (Round your answers to three decimal places, when needed.) t Distribution Degrees of Freedom = 21 -3.0 -2.0 -1.0 0.0 1.0 2.0 3.0 SM %3D t-critical %3Darrow_forwardYou are testing the claim that the mean GPA of night students is different from the mean GPA of day students. You sample 45 night students, and the sample mean GPA is 2.63 with a standard deviation of 0.81. You sample 40 day students, and the sample mean GPA is 3.02 with a standard deviation of 0.59. Test the claim using a 5% level of significance. Assume the population standard deviations are unequal and that GPAS are normally distributed. Give answer to at least 4 decimal places. What are the correct hypotheses? Ho: M₁ = μ₂ H₁: M₁ Based on the hypotheses, find the following: Test Statistic = -0.7918 X O μ₂ Critical Values=2.0154 x (Just enter the positive CV.) The correct decision is to Reject the null hypothesis The correct summary would be: There is enough evidence to support the claim of night students is different from the mean GPA of day students. o that the mean GPAarrow_forwardJustine is an analyst for a sleep study center. She believes that the average adult in a certain city spends more than 7.2 hours sleeping daily. To test this claim, she selects a random sample of 63 adults from the city. The following is the data from this study: The alternative hypothesis Ha:μ>7.2. The sample mean number of hours slept per night by the 63 adults is 7.52 hours. The sample standard deviation is 1.14 hours. The test statistic is calculated as 2.23. Using the information above and the portion of the t− table below, choose the correct p− value and interpretation for this hypothesis test. Values for right-tail areas under the t-distribution curve Probability 0.10 0.05 0.025 0.01 0.005 Degrees of Freedom 60 1.296 1.671 2.000 2.390 2.660 61 1.296 1.670 2.000 2.389 2.659 62 1.295 1.670 1.999 2.388 2.657 63 1.295 1.669 1.998 2.387 2.656 64 1.295 1.669 1.998 2.386 2.655 65 1.295 1.669 1.997 2.385 2.654 66 1.295 1.668 1.997 2.384 2.652…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman