
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Topic Video
Question
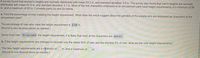
Transcribed Image Text:A survey found that women's heights are normally distributed with mean 63.3 in. and standard deviation 3.9 in. The survey also found that men's heights are normally
distributed with mean 67.4 in. and standard deviation 3.1 in. Most of the live characters employed at an amusement park have height requirements of a minimum of 56
in. and a maximum of 62 in. Complete parts (a) and (b) below.
a. Find the percentage of men meeting the height requirement. What does the result suggest about the genders of the people who are employed as characters at the
amusement park?
The percentage of men who meet the height requirement is 4.08 %.
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
Since most men do not meet the height requirement, it is likely that most of the characters are women.
b. If the height requirements are changed to exclude only the tallest 50% of men and the shortest 5% of men, what are the new height requirements?
The new height requirements are a mnimum of in. and a maximum of in.
(Round to one decimal place as needed.)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- In this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer. Suppose that at five weather stations on Trail Ridge Road in Rocky Mountain National Park, the peak wind gusts (in miles per hour) for January and April are recorded below. Wilderness District 1 2 3 4 January April 130 127 122 64 78 105 97 108 88 61 Does this information indicate that the peak wind gusts are higher in January than in April? Use a = 0.01. Solve the problem using the critical region method of testing. (Let d = January - April. Round your answers to three decimal places.) test statistic = critical value = Interpret your conclusion in the context of the application. O Reject the null hypothesis, there is insufficient evidence to claim average peak…arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer.At five weather stations on Trail Ridge Road in Rocky Mountain National Park, the peak wind gusts (in miles per hour) for January and April are recorded below. Weather Station 1 2 3 4 5 January 137 124 128 64 78 April 104 115 102 88 61 Does this information indicate that the peak wind gusts are higher in January than in April? Use ? = 0.01. (Let d = January − April.) (a) What is the level of significance? What is the value of the sample test statistic?arrow_forwardFor a data set of the pulse rates for a sample of adult females, the lowest pulse rate is 38beats per minute, the mean of the listed pulse rates is x =73.0 beats per minute, and their standard deviation is sequals=23.2 beats per minute. a. What is the difference between the pulse rate of 38 beats per minute and the mean pulse rate of the females? b. How many standard deviations is that [the difference found in part (a)]? c. Convert the pulse rate of 38 beats per minutes to a z score. d. If we consider pulse rates that convert to z scores between minus−2 and 2 to be neither significantly low nor significantly high, is the pulse rate of 38 beats per minute significant?arrow_forward
- In this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer. Suppose that at five weather stations on Trail Ridge Road in Rocky Mountain National Park, the peak wind gusts (in miles per hour) for January and April are recorded below. Wilderness District 1 2 3 4 5 January 122 122 130 64 78 April 114 115 114 88 61 Does this information indicate that the peak wind gusts are higher in January than in April? Use ? = 0.01. Solve the problem using the critical region method of testing. (Let d = January − April. Round your answers to three decimal places.) test statistic = critical value =arrow_forwardAssume that males have a mean hieght of 69.1 in. with a standard deviation of 2.9 in., and females have a mean height of 63.7 in. with a standard deviation of 2.7 in. Based on Z scores, would a 5'4" male or a 4'10" female be taller compared to the rest of their gender?arrow_forwardThe data set of size 40 has mean 15 and standard deviation 2. Approximately how many observations lie between 13 and 17?arrow_forward
- A survey found that women's heights are normally distributed with mean 63.4 in. and standard deviation 2.5 in. The survey also found that men's heights are hormally distributed with mean 68.3 in. and standard deviation 3.7 in. Most of the live characters employed at an amusement park have height requirements of a minimum of 57 in. and a maximum of 62 in. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. a. Find the percentage of men meeting the height requirement. What does the result suggest about the genders of the people who are employed as characters at he amusement park? The percentage of men who meet the height requirement is %. Round to two decimal places as needed.)arrow_forwardAssume that the Leaf Area Index over a management area is normally distributed with a mean of 3 and a standard deviation of 0.2. One sample area shows a LAI of 2.76. How many standard deviations is this measurement from the mean?arrow_forwardIn this problem, assume that the distribution of differences is approximately normal. Note: For degrees of freedom d.f. not in the Student's t table, use the closest d.f. that is smaller. In some situations, this choice of d.f. may increase the P-value by a small amount and therefore produce a slightly more "conservative" answer.The artifact frequency for an excavation of a kiva in Bandelier National Monument gave the following information. Stratum Flaked Stone Tools Nonflaked Stone Tools 1 10 2 2 10 3 3 9 2 4 1 3 5 4 7 6 38 32 7 51 30 8 25 12 What is the value of the sample test statistic? (Round your answer to three decimal places.)arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman