
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
A study was conducted to measure the effectiveness of hypnotism in reducing pain. The measurements are centimeters on a pain scale before and after hypnosis. Assume that the paired sample data are simple random samples and that the differences have a distribution that is approximately normal. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the
a. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the mean of the "beforeminusafter" differences.
less than mu Subscript dless than
(Round to two decimal places as needed.)
b. Does hypnotism appear to be effective in reducing pain?
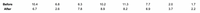
Transcribed Image Text:**Data Comparison: Before and After**
The table illustrates a comparison of numerical values before and after a specific event or intervention.
- **Before:**
- 10.4, 6.8, 6.3, 10.2, 11.3, 7.7, 2.0, 1.7
- **After:**
- 6.7, 2.6, 7.8, 8.9, 8.2, 6.9, 3.7, 2.2
These values may reflect measurements in a study, such as test scores, substance levels, or other quantifiable data, showing changes after applying certain conditions or treatments. By analyzing these values, one can draw conclusions on the effectiveness or impact of the intervention.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 6 steps

Knowledge Booster
Similar questions
- When you calculate a Confidence Interval (CI) for the difference between two population mean values, which of the following types of CIs indicate that the two mean values are significantly different? A. A Mixed CI B. A Negative CI C. A Positive CIarrow_forwardInsurance Company A claims that its customers pay less for car insurance, on average, than customers of its competitor, Company B. You wonder if this is true, so you decide to compare the average monthly costs of similar insurance policies from the two companies. For a random sample of 15 people who buy insurance from Company A, the mean cost is $150 per month with a standard deviation of $14. For 6 randomly selected customers of Company B, you find that they pay a mean of $157 per month with a standard deviation of $11. Assume that both populations are approximately normal and that the population variances are equal to test Company A's claim at the 0.05 level of significance. Let customers of Company A be Population 1 and let customers of Company B be Population 2. Step 2 of 3: Compute the value of the test statistic. Round your answer to three decimal places.arrow_forwardInsurance Company A claims that its customers pay less for car insurance, on average, than customers of its competitor, Company B. You wonder if this is true, so you decide to compare the average monthly costs of similar insurance policies from the two companies. For a random sample of 7 people who buy insurance from Company A, the mean cost is $150 per month with a standard deviation of $16. For 12 randomly selected customers of Company B, you find that they pay a mean of $160 per month with a standard deviation of $14. Assume that both populations are approximately normal and that the population variances are equal to test Company A's claim at the 0.10 level of significance. Let customers of Company A be Population 1 and let customers of Company B be Population 2. Step 1 of 3: State the null and alternative hypotheses for the test. Fill in the blank below. Ho:μ₁ = 1₂ Ha:M M₂arrow_forward
- A sociologist develops a test to measure attitudes about public transportation, and 20 randomly selected subjects are given the test. Their mean score is 85 and their standard deviation is 7.70. Construct 99% confidence interval for the mean score of all such subjects.arrow_forwardStatisic and prob . Sampling distributionarrow_forwardZoologists investigated the reproductive traits of spider mites with an infection. Male and female pairs of infected spider mites were mated in a laboratory and the number of eggs produced by each female recorded. Summary statistics for several samples are provided in the accompanying table. Assume that the sampled populations are approximately normal. Complete parts a and b. Click the icon to view the table. a. For each type of female-male pair, construct a 90% confidence interval for the population mean number of eggs produced by the female spider mite. The 90% confidence interval for both untreated pairs is (, ). (Round to the nearest hundredth as needed.) - X The 90% confidence interval for male treated pairs is Data table (Round to the nearest hundredth as needed.) The 90% confidence interval for female treated pairs is (Round to the nearest hundredth as needed.) Female- Sample Mean # Standard Male Pairs Size of Eggs Deviation The 90% confidence interval for both treated pairs is…arrow_forward
- Scores on an IQ test are normally distributed. A sample of 25 IQ scores had standard deviation s= 8. Construct a 95% confidence interval for the population variance σ2 .arrow_forwardFor each scenario listed on the left, determine whether the scenario represents an Independent Samples or Matched pairs situation by placing the appropriate letter in the box provided. ARR Comparing pain levels before and after treatment with magnetic therapy Comparing pain levels of a group receiving a placebo to a group receiving a medicine Comparing the number of speeding tickets received by men to the number received by women Comparing pre-test scores before training to post-test scores a. Independent Samples b. Matched Pairsarrow_forwardA professor at a large university believes that students take an average of 15 credit hours per term. A random sample of 22 students in her class of 250 students reported the following number of credit hours that they were taking: 12 12 12 13 13 14 14 14 14 15 15 15 16 16 16 16 16 17 17 18 19 21 Find a 95% confidence interval for the mean number of credit hours taken by the students in the professor’s class. Interpret your interval. Which method did you use to get your confidence interval? Give the error bound for mean.arrow_forward
- Insurance Company A claims that its customers pay less for car insurance, on average, than customers of its competitor, Company B. You wonder if this is true, so you decide to compare the average monthly costs of similar insurance policies from the two companies. For a random sample of 13 people who buy insurance from Company A, the mean cost is $150 per month with a standard deviation of $19. For 9 randomly selected customers of Company B, you find that they pay a mean of $157 per month with a standard deviation of $16. Assume that both populations are approximately normal and that the population variances are equal to test Company A’s claim at the 0.05 level of significance. Let customers of Company A be Population 1 and let customers of Company B be Population 2. Step 2 of 3: Compute the value of the test statistic. Round your answer to three decimal places. Step 3 of 3: Draw a conclusion and interpret the decision.arrow_forwardInsurance Company A claims that its customers pay less for car insurance, on average than customers of its competitor, Company B. You wonder if this is true, so you decide to compare the average monthly costs of similar insurance policies from the two companies. For a random sample of 11 people who buy insurance from Company A, the mean cost is $150 per month with a standard deviation of $14. For 14 randomly selected customers of Company B, you find that they pay a mean of $158 per month with a standard deviation of $12. Assume that both populations are approximately normal and that the population variances are equal to test Company A’s claim at the 0.10 level of significance. Let customers of Company A be Population 1 and let customers of Company B be Population 2. Step 2 of 3 : Compute the value of the test statistic. Round your answer to three decimal places.arrow_forwardResearchers conducted an experiment to test the effects of alcohol. Errors were recorded in a test of visual and motor skills for a treatment group of 28 people who drank ethanol and another group of 28 people given a placebo. The errors for the treatment group have a standard deviation of 2.20, and the errors for the placebo group have a standard deviation of 0.77. Assume that the two populations are normally distributed. Use a 0.05 significance level to test the claim that both groups have the same amount of variation among the errors. Let sample 1 be the sample with the larger sample variance, and let sample 2 be the sample with the smaller sample variance. What are the null and alternative hypotheses? OB. Ho: 0=02 O A. H₁: 0²12 = 0²/2 H₁:0² > 0²/2 H₁:0² <0² O C. Ho: 0²/02/ H₁:0² = 0² Identify the test statistic. (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Use technology to identify the P-value. (Round to three decimal places as needed.) What is the conclusion for this hypothesis test?…arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman