
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
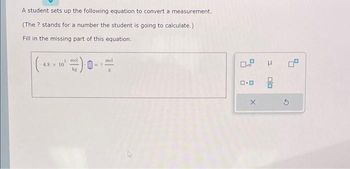
Transcribed Image Text:A student sets up the following equation to convert a measurement.
(The ? stands for a number the student is going to calculate.)
Fill in the missing part of this equation.
3 mol
kg
-4.8 x 10
mol
ロ・ロ
X
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 1 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- 39.6 g of carbon dioxide (CO2) is dissolved in a 2 L of water. 1 L of water is added. What is the new volume? What is the new molarity?arrow_forwardA chemistry student must write down in her lab notebook the concentration of a solution of sodium thiosulfate. The concentration of a solution equals the mass of what's dissolved divided by the total volume of the solution. Here's how the student prepared the solution: • The label on the graduated cylinder says: empty weight: 6.0 g • She put some solid sodium thiosulfate into the graduated cylinder and weighed it. With the sodium thiosulfate added, the cylinder weighed 94.86 g. • She added water to the graduated cylinder and dissolved the sodium thiosulfate completely. Then she read the total volume of the solution from the markings on the graduated cylinder. The total volume of the solution was 122.28 mL. What concentration should the student write down in her lab notebook? Be sure your answer has the correct number of significant digits. 山。 g.mL 1 x10 X Śarrow_forwardWhat is the molarity of a solution containing 36.3 g of NaOH in 1.40 L? The molar mass of NaOH is 40.0 g/mol. Suppose you add 600 mL of water to the NaOH solution in the question above. What is the new molarity of the dilute NaOH solution?arrow_forward
- Part C A solid mixture consists of 32.3 g of KNO3 (potassium nitrate) and 5.7 g of K2SO4 (potassium sulfate). The mixture is added to 130. g of water. If the solution described in the introduction is cooled to 0 °C what mass of K2SO4 will crystallize? Use this solubility curve (Figure 1) to answer the questions. Enter your answer numerically in grams. • View Available Hint(s) Nνα ΑΣφ ? Figure Submitarrow_forwardA student measures the initial volume of NaOH to be 0.56 mL. The final volume is measured to be 21.60 mL. If the concentration of NaOH used is 0.0877 M, how many moles of NaOH were used? Report your answer with four decimals. Enter numbers only; do not enter units.arrow_forwardThe excess reactant will always have the greater volume of the reactants. True/Falsearrow_forward
- Use the data below to determine the Molarity of KMnO4 to THREE decimal places. (MM sodium oxalate = 134 g/mol) mass of sodium oxalate (g) 0.099 initial buret reading (mL) 0.44 final buret reading (mL) 16.64 Type your answer...arrow_forwardThe following graph was created to determine the relationship between density and concentration of sugar solutions If it is found that 5.00 ml of a sample has a mass of 6.083 g, what is the density of the sample in g/mL?arrow_forward5. How would the following errors affect the empirical formula for the compound? a. The student ran out of time and did not do the second heating. Explain how this error will affect the calculation for the number of moles of water in the hydrate? Will the final answer be artificially high or low? How do you know? b. The student recorded the mass of the cup + sample incorrectly and started with 2.2 g of hydrated compound but used 2.0 g in the calculations. Explain how this error will affect the calculation for the number of moles of water in the hydrate? Will the final answer be artificially high or low? How do you know? BI U = E T O Word(s)arrow_forward
- 0.332 mL of 51.72 M of aqueous NaOH solution is diluted to a volume of 482.2 mL. What is the molarity of the diluted solution? Assume that all of the values have at least three significant units.arrow_forwardA solution of CaCl2 in water forms a mixture that is 37.5% calcium chloride by mass. If the total mass of the mixture is 551.7 g, what masses of CaCl2 and water were used? mass of CaCl2: mass of water:arrow_forwardSuppose 9.67g of sodium chloride is dissolved in 100.mL of a 0.50M aqueous solution of potassium carbonate. Calculate the final molarity of chloride anion in the solution. You can assume the volume of the solution doesn't change when the sodium chloride is dissolved in it. Round your answer to 3 significant digits.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY