
Chemistry
10th Edition
ISBN: 9781305957404
Author: Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
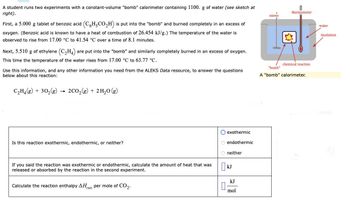
Transcribed Image Text:A student runs two experiments with a constant-volume "bomb" calorimeter containing 1100. g of water (see sketch at
right).
First, a 5.000 g tablet of benzoic acid (C6H-CO₂H) is put into the "bomb" and burned completely in an excess of
oxygen. (Benzoic acid is known to have a heat of combustion of 26.454 kJ/g.) The temperature of the water is
observed to rise from 17.00 °C to 41.54 °C over a time of 8.1 minutes.
Next, 5.510 g of ethylene (C₂H4) are put into the "bomb" and similarly completely burned in an excess of oxygen.
This time the temperature of the water rises from 17.00 °C to 63.77 °C.
Use this information, and any other information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions
below about this reaction:
C₂H₂(g) + 30₂(g) → 2CO₂(g) + 2H₂O(g)
Is this reaction exothermic, endothermic, or neither?
If you said the reaction was exothermic or endothermic, calculate the amount of heat that was
released or absorbed by the reaction in the second experiment.
Calculate the reaction enthalpy AHxn per mole of CO₂.
exothermic
O endothermic
Oneither
KJ
0
kJ
mol
stirrer
0
thermometer
chemical reaction
"bomb"
"bomb" calorimeter.
water
insulation
match
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps with 3 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, chemistry and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- What is the enthalpy change for the first reaction? CH4(g) + 1/2O2(g) → CH3OH(g) ΔH = CH4(g) + 2O2(g) → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ΔH = -806.5 CH3OH(l) + 3/2 O2 → CO2(g) + 2H2O(g) ΔH = -676.7arrow_forward[2] When 1.045 g of CaO is added to 50.0 ml of water at 22.0 °C in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature of the water increases to 29.3 °C. Assume that the specific heat and density of the solution is 4.184 J/g-°C and 1.00g/ml, respectively. The heat capacity of the calorimeter is 18.0 J/°C. Calculate AH for the reaction. CaO(s) + H2O(1) –→ Ca(OH)2(aq); AH =arrow_forwardWhen 1.836 grams of sucrose (Molar mass 342.3 g/mol) is burned in a bomb calorimeter, the temperature of the calorimeter increases from 22.41°C to 26.63°C. If the heat capacity of the calorimeter is 4.900 kJ/°C, what is the heat of combustion of sucrose?arrow_forward
- 6, A 0.213 g sample of an organic compound with a molar mass of 386.0 g/mol was burned in the bomb calorimeter with a heat capacity of 2.54 kJ/K. The temperature in the calorimeter increased by 4.12 K. Calculate the energy of combustion of the compound in kJ/mol. A, –1.896 x103 B, –4.90 x102 C, 0.00937 D, –1.90 x104 E, -531arrow_forwardmetal X =51.0g; specific heat capacity =0.44 J/C If metal X is heated to 86C and put into a calorimeter containing water (she=4.18 J/g°C ) at 23C. The final temperature of the water becomes 31C. What is the mass of water?arrow_forward[11] A 10.00 g sample of a metal alloy was heated to 88.99 °C. It is then quickly dropped into 40.0 g of water in a calorimeter. The water temperature rises from 19.73 °C to 24.23 °C. Calculate the specific heat of the alloy. [Specific Heat of Water = 4.184 J/g °C and Heat Capacity of Calorimeter = 12.6 J/°C]arrow_forward
- A 5.1-gram piece of gold jewelry isremoved from water at 100.0°C and placed in a coffee-cup calorimeter containing 16.9 gof water at 22.5°C (specific heat of water is 4.184 J/g · °C). The equilibrium (final)temperature of the water and jewelry is 23.2°C. The calorimeter constant is known fromcalibration experiments to be 1.54 J/°C. What is the specific heat (in J/g · °C) of this pieceof jewelry? If the tabulated value of the specific heat of gold is 0.129oC, is the jewelrypure gold?arrow_forwardPlease don't provide handwriting solutions....arrow_forward25.00 mL of 0.200 M sulfuric acid was added to 25.00 mL of 0.200 M NAOH, in a constant volume calorimeter. The density of the resulting solution is 1.225 g/mL and its specific heat is 5.321 J/g-°C. As the reaction took place, the temperature of the solution rose from 22.0 °C to 31.3 °C. What is AH (in units of kJ/mol) for the reaction, per mole of water formed? This is a limiting reactant problem and your choice of limiting reactant must be justified through stoichiometric calculations. 21.arrow_forward
- First, a 5.500 g tablet of benzoic acid (C6H₂CO₂H) is put into the "bomb" and burned completely in an excess of oxygen. (Benzoic acid is known to have a heat of combustion of 26.454 kJ/g.) The temperature of the water is observed to rise from 19.00 °C to 45.03 °C over a time of 12.0 minutes. Next, 4.840 g of acetylene (C₂H₂) are put into the "bomb" and similarly completely burned in an excess of oxygen. This time the temperature of the water rises from 19.00 °C to 56.59 °C. Use this information, and any other information you need from the ALEKS Data resource, to answer the questions below about this reaction: Is this reaction exothermic, endothermic, or neither? If you said the reaction was exothermic or endothermic, calculate the amount of heat that was released or absorbed by the reaction in the second experiment. Calculate the reaction enthalpy ΔΗ per mole of C₂H₂. rxn 2C₂H₂(g) + 50₂ (8) 4C0₂(g) + 2 H₂O (g) Be sure any of your answers that are calculated from measured data are…arrow_forward5.00 × 10−2 mol KOH and an excess of hydrochloric acid are combined in 100.0 mL of water initially at 25.0 °C, leading to a final measured temperature of 31.1 °C. (a) What is the heat flow for the water in the calorimeter, qH2O, in Joules? (b) Assuming the calorimeter constant Ccal = 50.0 J °C , what is the heat flow for the calorimeter, qcal, in Joules? (c) What is the amount of heat given off by the reaction, qrxn, in Joules? (d) What is the molar enthalpy of the neutralization reaction (shown below) as measured in the calorimeter, ∆H◦ rxn in kilojoules per mole? H3O + (aq) + OH– (aq) → 2H2O (l)arrow_forwardIn a calorimeter, a 2.0 g sample of magnesium is burned to form MgO. In doing so, 25.5 kJ of energy are released. What is the Heat of Combustion in kJ/mol of magnesium? с 306.2 1.54 x 1025 0.0392 514 25.5arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781305957404Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCostePublisher:Cengage Learning ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
ChemistryChemistryISBN:9781259911156Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby ProfessorPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning
Principles of Instrumental AnalysisChemistryISBN:9781305577213Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. CrouchPublisher:Cengage Learning Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Organic ChemistryChemistryISBN:9780078021558Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning
Chemistry: Principles and ReactionsChemistryISBN:9781305079373Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. HurleyPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY
Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...ChemistryISBN:9781118431221Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. BullardPublisher:WILEY

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305957404
Author:Steven S. Zumdahl, Susan A. Zumdahl, Donald J. DeCoste
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9781259911156
Author:Raymond Chang Dr., Jason Overby Professor
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Principles of Instrumental Analysis
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305577213
Author:Douglas A. Skoog, F. James Holler, Stanley R. Crouch
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Organic Chemistry
Chemistry
ISBN:9780078021558
Author:Janice Gorzynski Smith Dr.
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Chemistry: Principles and Reactions
Chemistry
ISBN:9781305079373
Author:William L. Masterton, Cecile N. Hurley
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Principles of Chemical Processes, Bind...
Chemistry
ISBN:9781118431221
Author:Richard M. Felder, Ronald W. Rousseau, Lisa G. Bullard
Publisher:WILEY