
College Physics
11th Edition
ISBN: 9781305952300
Author: Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher: Cengage Learning
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A string is vibrating back and forth as in Figure 17. l 8a. The
tension in the string is decreased by a factor of four, with the frequency and the length of the string remaining the same. Draw the
new standing wave pattern that develops on the string. Give your
reasoning.
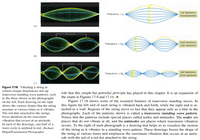
Transcribed Image Text:Frequency -
1st harmonic
(fundamental)
(a)
-Antinodes-
Frequency = 2j
2nd harmonic
(1st overtone)
(b)
3rd harmonic
(2nd overtone)
Frequency = 3ji
(c)
Figure 17.18 Vibrating a string at
certain unique frequencies sets up
transverse standing wave patterns, such
as the three shown in the photographs
on the left. Each drawing on the right
shows the various shapes that the string
assumes at various times as it vibrates.
role that this simple but powerful principle has played in this chapter. It is an expansion of
the charts in Figures 17.9 and 17.14. 4
Figure 17.18 shows some of the essential features of transverse standing waves. In
this figure the left end of each string is vibrated back and forth, while the right end is at-
tached to a wall. Regions of the string move so fast that they appear only as a blur in the
photographs. Each of the patterns shown is called a transverse standing wave pattern.
Notice that the patterns include special places called nodes and antinodes. The nodes are
places that do not vibrate at all, and the antinodes are places where maximum vibration
occurs. To the right of each photograph is a drawing that helps us to visualize the motion
of the string as it vibrates in a standing wave pattern. These drawings freeze the shape of
the string at various times and emphasize the maximum vibration that occurs at an antin-
ode with the aid of a red dot attached to the string.
The red dots attached to the strings
focus attention on the maximum
vibration that occurs at an antinode.
In each of the drawings, one-half of a
wave cycle is outlined in red. (Richard
Megna/Fundamenta! Photographs)
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, physics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- B AAN EE Tamat Parme Solving problems by relaung sinusordal wave and vector functions to their related engineering applications. You also must solve the problems of differential and integral calculus for your related works. Fart AaBb AaB AaE AD Cet Accide 1 Amg 1 Coe 1 Cor. 1 Part 1: A support beam, within an industrial building, is subjected to vibrations along its length; emanating from two machines situated at opposite ends of the bear. The displacement caused by the vibrations can be modelled by the following equations, x₁ = 4.2 sin(100nt +0.59) mm x₂ = 6.1 sin(100m - 0.42) mm O fype here to search Your senior engineer asked you the followings: (a) State the amplitude, periodic time, frequency and phase angle (in degrees) for each of these waves. Q Engah Sandad Complung IMGarrow_forwardDon't use chat gpt It Chatgpt means downvote pleasearrow_forwardA 1.1 m string oscillating at a frequency of 86 Hz generates the standing wave shown below. What is the wave speed on the string. What is the linear density on the string if the string tension is 5.6 N?arrow_forward
- If I tap a tuner fork on a block to get the form vibrating, then use another tuning fork of a higher frequency to do the same: a. which has the faster rate of vibration? b. What seems to determine the rate of vibration?arrow_forwardShown below are three waves that were sent down a string at different times. The tension in the string remains constant. Rank the waves from the smallest wavelength to the largest wavelength. 1. B, C, A 2. B, A, C 3. C, A, B 4. A, B, C 5. C, B, A 6. A, C, Barrow_forward3. The figure below shows various positions of a child on a swing moving toward Mr. Doig on the ground blowing a 3-kHz whistle. If the child starts from rest at Point A a height 0.75 m above the ground, calculate the frequency the child hears at Points A, C, and E, on the swing forward. Additionally, calcu- late the frequency the child hears at Point Con the swing back. When does the child hear the highest pitch? Hint: you might want to use energy conservation. Here are some equations from a past unit: KE = mv² and PE = mgh. A B C D Whistle Whistle Earrow_forward
- I need help with this physics question. I need a detailed explanation.arrow_forwardA stretched string is 2.03 m long and has a mass of 20.3 g. When the string oscillates at 440 Hz, which is the frequency of the standard A pitch, transverse waves with a wavelength of 15.5 cm travel along the string. Calculate the tension T in the string. T = terms of use contact us help careers privacy polícy about us Show All Free-Fall-Phet.docx V VS T.jpeg free fall.png VS T.jpegarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning
College PhysicsPhysicsISBN:9781305952300Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris VuillePublisher:Cengage Learning University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON
University Physics (14th Edition)PhysicsISBN:9780133969290Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. FreedmanPublisher:PEARSON Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press
Introduction To Quantum MechanicsPhysicsISBN:9781107189638Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.Publisher:Cambridge University Press Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning
Physics for Scientists and EngineersPhysicsISBN:9781337553278Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. JewettPublisher:Cengage Learning Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley
Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory AstronomyPhysicsISBN:9780321820464Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina BrissendenPublisher:Addison-Wesley College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON
College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...PhysicsISBN:9780134609034Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart FieldPublisher:PEARSON

College Physics
Physics
ISBN:9781305952300
Author:Raymond A. Serway, Chris Vuille
Publisher:Cengage Learning

University Physics (14th Edition)
Physics
ISBN:9780133969290
Author:Hugh D. Young, Roger A. Freedman
Publisher:PEARSON

Introduction To Quantum Mechanics
Physics
ISBN:9781107189638
Author:Griffiths, David J., Schroeter, Darrell F.
Publisher:Cambridge University Press

Physics for Scientists and Engineers
Physics
ISBN:9781337553278
Author:Raymond A. Serway, John W. Jewett
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Lecture- Tutorials for Introductory Astronomy
Physics
ISBN:9780321820464
Author:Edward E. Prather, Tim P. Slater, Jeff P. Adams, Gina Brissenden
Publisher:Addison-Wesley

College Physics: A Strategic Approach (4th Editio...
Physics
ISBN:9780134609034
Author:Randall D. Knight (Professor Emeritus), Brian Jones, Stuart Field
Publisher:PEARSON