
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
A strain gauge mounted at a potentially critical point in a steel part has recorded the stress history shown below during 20 seconds of typical use. Identical parts have been fatigue tested under constant amplitude loading with R = -1 to give an endurance limit of 60 ksi and a fatigue strength of 140 ksi at N = 1000 cycles. The steel used has an ultimate strength of 165 ksi. Estimate the fatigue life of the part under typical use.
How much will the fatigue life in problem 3 (above) be reduced if a mean stress of 10 ksi is added to the stress history given?
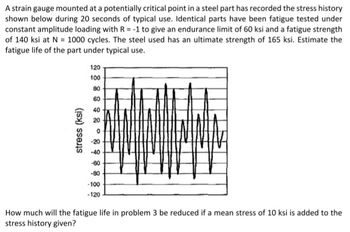
Transcribed Image Text:A strain gauge mounted at a potentially critical point in a steel part has recorded the stress history
shown below during 20 seconds of typical use. Identical parts have been fatigue tested under
constant amplitude loading with R = -1 to give an endurance limit of 60 ksi and a fatigue strength
of 140 ksi at N = 1000 cycles. The steel used has an ultimate strength of 165 ksi. Estimate the
fatigue life of the part under typical use.
stress (ksi)
120
100
80
60
40
20
0
-20
-40
-60
-80
-100
-120
How much will the fatigue life in problem 3 be reduced if a mean stress of 10 ksi is added to the
stress history given?
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 3 steps

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A point in a brittle material of ultimate strength equal to 600 MPa 0, and has the following state of stress: 0xx = 150 MPa, oyy Txy = 60 MPa. Determine the safety factor used in the design. =arrow_forwardQuestion: 8-2. Determine the material's fatigue properties for the given d... 8-2. Determine the material's fatigue properties for the given data. Shown the plots to obtain the properties. Smooth Specimen-Cyclic Data Plastic Strain Amplitude. Ae./2" Total Strain Stress Amplitude. Reversals to Amplitude. Ac/2 As, Δσ A0/2 (ksi) Failure. 2N, Basquin Equation: 2 2E E 0.0393 0.0393 0.02925 0.01975 0.0196 0.01375 162.5 0.0336 50 162 0.0336 0.0238 68 155 143.5 Δε, 122 = 6,(2N,} Coffin-Manson Equation: 0.0147 256 143.5 0.0145 350 2 136.5 130.5 126.5 121 0.00894 488 0.00521 1,364 1.386 3,540 3.590 9.100 35.200 140.000 0.00980 0.00980 0.00655 0.00630 0.00460 0.00360 0.00295 0.00534 0.00229 0.00211 0.00059 119 Δε Δε, 114 %3D 106 84.5 0.00000 2 2E E 0.00000 Ao All information is givenarrow_forwardFor the given fluctuating fatigue load,the values of stress amplitude and stress ratio are respectively???arrow_forward
- The track curves on the Transnet railway line between Belfast and Steelport in the Limpopo province are heavily corrugated. Explain how you would use FEM to determine the following parameters: i) Total corrugation frequency. ii) Lateral vibrations. ii) Fatigue stresses on the rails.arrow_forwardQUESTION 1 Predict the fatigue strength (ksi) at N=1000 cycles for a fatigue test specimen of a steel whose tensile strength is 125 ksiarrow_forwardFor a given homogeneous, isotropic, linearly elastic material, E = 15e6 psi and v = 0.3. Solve for the shear modulus. 2.1.1 Homogeneous, isotropic, linearly elastic materials For specimens undergoing small deformations, the stress-strain diagram often ex- hibits a linear behavior. Although this is a very crude approximation to the behavior of actual materials, it is a convenient assumption that is often used for preliminary evaluation. A linear relationship between stress and strain can be expressed as 01 = E €1, (2.1) where the coefficient of proportionality, E, is called Young's modulus or modulus of elasticity. Since strains are non-dimensional quantities, this coefficient has the same units as stress quantities, i.e., Pa. This linear relationship is known as Hooke's law. The elongation of a bar in the direction of the applied stress is accompanied by a lateral contraction that is also proportional to the applied stress. The resulting defor- mations for this uniaxial state of stress…arrow_forward
- a rectangular stepped bar is shown. the bar is loaded in bending. determine the fatigue stress concentration factor if the ultimate stress of the material is 690 mPa. please inlcude how to calculate the notch sensitivity.arrow_forward1. A steel rotating-beam specimen has an ultimate strength of 1600 MPa. It is tested at a completely reversed stress amplitude of 900 MPa. The life of the specimen is ( _) cycles.arrow_forwardA steel rotating-beam test specimen has an ultimate strength, Sut, of 120 kpsi. Estimate the life of the specimen if it is tested at a completely reversed stress amplitude, Orev, of 74 kpsi. Take the value of the fatigue strength fraction, f, from Fig. 6-23. The life of the specimen is cycles.arrow_forward
- A resistance, wire strain gauge with a gauge factor of 3 is bonded to a steel structural e subjected to a stress of 200 MN/m² The modulus of elasticity of steel is 400 GN/m² Calculate the % change in the value of the gauge resistance due to the applied stressarrow_forwardA cylindrical steel bar 8 mm in diameter is loaded 1000 cycles per day with a load of 15560 N. How long until fatigue failure takes place? Note: stress = force/area Group of answer choices The bar should not fatigue. The bar will fail in one cycle. 100 days 1000 daysarrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY