
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Question
-
A straight horizontal pipe 100 mm in diameter terminates in a short, tapering nozzle from which a jet of water 50 mm in diameter is discharged to atmosphere. If the gauge pressure immediately before the nozzle is 50 kPa and friction in the nozzle is negligible, calculate the tensile force between the nozzle and pipe.
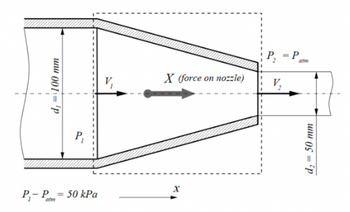
Transcribed Image Text:www 001 P
P₁
P₁-P= 50 kPa
atm
V₁
X (force on nozzle)
X
P₂
V₂
d₂ = 50 mm
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- A horizontal 300-mm pipe contracts to a 150-mm diameter. If the flow is 0.127 m3/s of oil (s.g.=0.88) and the pressure in the smaller pipe is 265 kPa what force is exerted on the contraction, neglecting friction?arrow_forwardPlease draw and label the diagram correctly.arrow_forwardOn the head side of a hydraulic cylinder, the rod is 1/2 inch in diameter and the piston is 2 inches in diameter. Calculate the force applied while retracting the rod and the speed at which it moves if the operating pressure is 150 psi and the flow rate is 6.5 gpm. Answer is incomplete without units.arrow_forward
- A jet of water impinges on a single smooth flat vane at its centre. The velocity of the jet is 70 m/s and the diameter 120 mm.Calculate the force on the vane, if it is moving with a velocity of 30 m/s in the direction of jet. Determine the power and efficiency. Also, find the speed of plate at which maximum efficiency may occur.arrow_forwardThe diameter of a pipe changes gradually from 75 mm at a point A, 6 m above datum, to 150 mm at B, 3 m above datum. The pressure at A is 103 kPa and the velocity of flow is 3.6 m/s. Neglecting losses, with the aid of a neat sketch, determine the pressure at Barrow_forwardThe diameter of a pipeline is 6-in at A and 18-in at B. A is 11 ft. lower than B. If the pressure at A is 10 lb per sq. in and at B 7 lb per sq. in when the flow is 2.5 cfs, determine the frictional loss between A and B when the liquid is water. Topic: FUNDAMENTALS OF FLUID FLOWarrow_forward
- Q5: A converging-diverging nozzle, which is shown in the figure, is supplied with air from a large tank where the pressure is Po and exhausts to the atmosphere with a pressure of Po. The area A at distance x from the throat is given by (A = At (1 + 0.75x/L)), where At is the throat cross- sectional area and Lis the total length of the diverging part of the nozzle. At a certain pressure ratio PoPb, a normal shock wave stands in the nozzle at a point where the Mach number before the shock is 1.7. Find the position of the normal shock wave from the throat, and the pressure ratio P/Po. Ans.: 0.45 L = 0.753 Р. Psarrow_forwardQ1. What would be the effect on the calculated force on the flat plate if the jet were to leave the plate not horizontal but inclined upwards at an angle of 1 °? If the experiment were to be repeated with the vane in the form of a cone with an included angle of 60° (half angle 30°), how would you expect the results to appear?arrow_forwardA high-pressure washing system's pump supplies 1 gallon of water persecond at 100 psi pressure. The nozzle should be designed so that the static pressureof the water as it exits the nozzle is the same as the atmospheric pressure. If theinside diameter of the hose leading from the pump to the nozzle is 2 in., whatshould the diameter of the nozzle exit be? What will be the velocity of the waterat the exit of the nozzle?arrow_forward
- Section 1 is the image below the problemarrow_forward3. A horizontal nozzle reduces from 100 mm bore diameter at inlet to 50 mm at exit. It carries liquid of density 1000 kg/m3 at a rate of 0.05 m3/s. The pressure at the wide end is 500 kPa (gauge). Calculate the pressure at the narrow end neglecting friction. (196 kPa)arrow_forwardWater steam is running through the nozzle. Inlet pressure is P1=25 bars; T1=300C; V1=90m/s; A1=0.2m2. The exit parameters are: P2=11bars; T2=210C. The mass flow rate is m=2 kg/s. Determine: a.Exit velocity V2=?; b.Inlet and outlet diameters D1 and D2.arrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY