
MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
6th Edition
ISBN: 9781119256830
Author: Amos Gilat
Publisher: John Wiley & Sons Inc
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
Transcribed Image Text:i
Rates of Return
Financial
Energy
Utilities
10.73
12.72
11.98
15.05
13.91
5.86
17.01
6.43
13.67
5.03
11.19
9.90
19.50
18.93
3.95
8.16
20.73
3.44
10.38
9.60
7.11
6.75
17.40
15.70

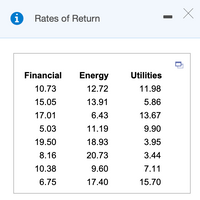
Transcribed Image Text:A stock analyst wondered whether the mean rate of return of financial, energy, and utility stocks differed over the past 5 years. He obtained a simple random sample of eight companies from each of the three sectors and obtained the 5-year rates
of return shown in the accompanying table (in percent). Complete parts (a) through (d) below.
Click the icon to view the data table.
(a) State the null and alternative hypotheses. Choose the correct answer below.
O A. Ho: Hfinancial = Peneray and H,: the means are different
O B. Ho: Hfinancial = Penergy = Hutilities and H1: at least one of the means is different
%3D
%3D
O C. Ho: Hfinancial = Henergy = Hutilities and H,: Hfinancial <Penergy <Hutilities
O D. Ho: at least one of the means is different and H1: Hfinancial = Penergy = Putilities
%3D
(b) Normal probability plots indicate that the sample data come from normal populations. Are the requirements to use the one-way ANOVA procedure satisfied?
O A. No, because there are k=3 simple random samples, one from each of k populations, the k samples are independent of each other, and the populations are normally distributed and have the same variance.
B. Yes, because there are k= 3 simple random samples, one from each of k populations, the k samples are independent of each other, and the populations are normally distributed and have different variances.
O C. No, because the largest sample standard deviation is more than twice the smallest sample standard deviation.
D. Yes, because there are k=3 simple random samples, one from each of k populations, the k samples are independent of each other, and the populations are normally distributed and have the same variance.
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 4 steps with 2 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, statistics and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- Can you help me with this question from my business statistics class?arrow_forwardThe British Department of Transportation studied to see if people avoid driving on Friday the 13th. They did a traffic count on a Friday and then again on a Friday the 13th at the same two locations. The data for each location on the two different dates is in the table. Do the data show that on average fewer people drive on Friday the 13th? Test at the 10% level. Traffic Count 6th 13th 1990, July 138998 138877 1990, July 135438 136187 1991, September 132918 129920 1991, September 136810 133914 1991, December 124545 120192 1991, December 128339 125776 1992, March 122024 118128 1992, March 124013 120800 1992, November 136759 134911 1992, November 123410 122447 Dates State the null and alternative hypotheses. Ho: Hd ? ✓ Ha: Hd ? ✓ Calculate the test statistic. Round to four decimal places. d= Calculate the standardized test statistic. Round three decimal places. t = Find the p-value. Round to four decimal places. p-value = State your decision. O Since the p-value is greater than .10,…arrow_forwardIn this problem, we explore the effect on the mean, median, and mode of adding the same number to each data value. Consider the data set 2, 2, 3, 6, 10. In USE SALT (a) Compute the mode, median, and mean. (Enter your answers to one decimal place.) mode median mean (b) Add 3 to each of the data values. Compute the mode, median, and mean. (Enter your answers to one decimal place.) mode median mean (c) Compare the results of parts (a) and (b). In general, how do you think the mode, median, and mean are affected when the same constant is added to each data value in a set? Adding the same constant c to each data value results in the mode, median, and mean remaining the same. Adding the same constant c to each data value results in the mode, median, and mean increasing by c units. There is no distinct pattern when the same constant is added to each data value in a set. Adding the same constant c to each data value results in the mode, median, and mean decreasing by c units.arrow_forward
- At the end of a certain year, the variance in the semiannual yields of overseas government bond was o? = 0.70. A group of bond investors met at that time to discuss future trends in overseas bond yields. Some expected the variability in overseas bond yields to increase and others took the opposite view. The following table shows the semiannual yields for 12 overseas countries as of March 6 of the following year. Country Yield (%) Australia 3.98 Belgium 3.78 Canada 2.95 Denmark 3.55 France 3.44 Germany 3.08 Italy 4.51 Japan 1.32 Netherlands 3.53 Spain 3.90 Sweden 2.48 United Kingdom 3.76 (a) Compute the mean (in percent), variance, and standard deviation (in percent) of the overseas bond yields as of the March 6 date. (Round your answers to four decimal places.) mean % variance standard deviation % (b) Develop hypotheses to test whether the sample data indicate that the variance in bond yields has changed from that at the end of the initial year. O Ho: o 2 0.70 H: o2 0.70 H: o2 s 0.70…arrow_forwardA traffic safety company publishes reports about motorcycle fatalities and helmet use. In the first accompanying data table, the distribution shows the proportion of fatalities by location of injury for motorcycle accidents. The second data table shows the location of injury and fatalities for 2073 riders not wearing a helmet. Complete parts (a) and (b) below. Click the icon to view the tables. S alternative hypotheses? A. Ho: The distribution of fatal injuries for riders not wearing a helmet foll H₁: The distribution of fatal injuries for riders not wearing a helmet do B. Ho: The distribution of fatal injuries for riders not wearing a helmet do H₁: The distribution of fatal injuries for riders not wearing a helmet do OC. None of these. Compute the expected counts for each fatal injury. Observed Count Location of injury Multiple Locations 1042 865 37 84 45 Head Neck Thorax Abdomen/Lumbar/Spine (Round to two decimal places as needed.) Expected Count Distribution of fatalities by…arrow_forwardIn regression, the best-fitting line through a scatterplot is known as the ______. A. Regression line B. Correlation line C. Variance line D. Scatterplot linearrow_forward
- Consider a sample with data values of 29, 27, 22, 17, 32, 38, 30, and 27. Compute the 20th, 25th, 65th, and 75th percentiles. Step 1 Recall that a percentile gives insight to how data are spread between the smallest and largest values. The pth percentile of a set of data indicates that p% of the data are below that value, and (100 − p)% are above that value. There are two components of the pth percentile: the location within the data and the actual value. The formula for finding the location of the percentile, denoted Lp, follows where p is the percentile and n is the number of observations in the ordered data set. Lp = p 100 (n + 1) The first step in calculating a percentile is to order the data in ascending order. The ordered data are below. 17 22 27 27 29 30 32 38 There are n = 8 observations in the data. Find the location of the p = 20th percentile. Lp = p 100 (n + 1) L20 = 20 100 + 1 =arrow_forwardFind the (a) mean, (b) median, (c) mode, and (d) midrange for the data and then (e) answer the given questions. Listed below are selling prices (dollars) of TVs that are 60 inches or larger and rated as a "best buy" by a popular magazine. Are the resulting statistics representative of the population of all TVs that are 60 inches and larger? If you decide to buy one of these TVs, what statistic is most relevant, other than the measures of central tendency? 1850 1000 1600 1000 1300 1150 1000 1100 1150 1350 1000 1450 a. Find the mean. The mean is $ (Type an integer or a decimal rounded to one decimal place as needed.)arrow_forwardIn the world population, 81.2% of all people have dark brown or black hair, 10.3% have brown hair, 6.3% have blond hair and 2.2% have red, gray, or white hair. A researcher wants to see if the distribution of hair color is different for the residents of Nashville. The table below shows the results of a random sample of 568 residents in Nashville. What can be concluded at the significant level of a = 0.01.arrow_forward
- Absenteeism: Absenteeism can be a serious employment problem. It is estimated that absenteeism reduces potential output by more than 10%. Two economists launched a research project to learn more about the problem. They randomly selected 100 organizations to participate in a 1-year study. For each organization, they recorded the average number of days absent per employee and several variables thought to affect absenteeism. Management’s goal here is to analyze the data and determine which factors may be helpful in predicting absenteeism. Perform a two-sample t-test analysis to determine if mean absenteeism is different between organizations which have a good Union management and those that do not. I have provided the F-test for two variances below: Copy and paste the Two sample t-test output below AND provide a clear conclusion supported by key statistics in the output about how absenteeism is affected by the Union Management Relationship. (I just need to know how to perform the two…arrow_forwardThe analysis of variance is a procedure that allows statisticians to compare two or more population: Select one: a. proportions b. variances c. standard deviations d. means e. none of thesearrow_forwardA sales team's statistical staff doesn't understand why their top salesperson's sales decreased 50% during holiday months. They bring him to the director's office, where they direct him to change his advertisement strategy. The salesperson changes his advertisement strategy and logs sales records for the months of November, December and January. This is an example of an Group of answer choices Observational Study Experiment None of the abovearrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
SEE MORE QUESTIONS
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc
MATLAB: An Introduction with ApplicationsStatisticsISBN:9781119256830Author:Amos GilatPublisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning
Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...StatisticsISBN:9781305251809Author:Jay L. DevorePublisher:Cengage Learning Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning
Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...StatisticsISBN:9781305504912Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. WallnauPublisher:Cengage Learning Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON
Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...StatisticsISBN:9780134683416Author:Ron Larson, Betsy FarberPublisher:PEARSON The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman
The Basic Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319042578Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. FlignerPublisher:W. H. Freeman Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman
Introduction to the Practice of StatisticsStatisticsISBN:9781319013387Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. CraigPublisher:W. H. Freeman

MATLAB: An Introduction with Applications
Statistics
ISBN:9781119256830
Author:Amos Gilat
Publisher:John Wiley & Sons Inc

Probability and Statistics for Engineering and th...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305251809
Author:Jay L. Devore
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Statistics for The Behavioral Sciences (MindTap C...
Statistics
ISBN:9781305504912
Author:Frederick J Gravetter, Larry B. Wallnau
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Elementary Statistics: Picturing the World (7th E...
Statistics
ISBN:9780134683416
Author:Ron Larson, Betsy Farber
Publisher:PEARSON

The Basic Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319042578
Author:David S. Moore, William I. Notz, Michael A. Fligner
Publisher:W. H. Freeman

Introduction to the Practice of Statistics
Statistics
ISBN:9781319013387
Author:David S. Moore, George P. McCabe, Bruce A. Craig
Publisher:W. H. Freeman