
Elements Of Electromagnetics
7th Edition
ISBN: 9780190698614
Author: Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher: Oxford University Press
expand_more
expand_more
format_list_bulleted
Concept explainers
Question
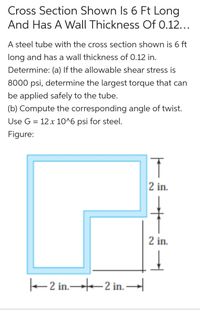
Transcribed Image Text:Cross Section Shown Is 6 Ft Long
And Has A Wall Thickness Of 0.12...
A steel tube with the cross section shown is 6 ft
long and has a wall thickness of 0.12 in.
Determine: (a) If the allowable shear stress is
8000 psi, determine the largest torque that can
be applied safely to the tube.
(b) Compute the corresponding angle of twist.
Use G = 12 x 10^6 psi for steel.
Figure:
2 in.
2 in.
e 2 in.-2 in. –
Expert Solution
This question has been solved!
Explore an expertly crafted, step-by-step solution for a thorough understanding of key concepts.
This is a popular solution
Trending nowThis is a popular solution!
Step by stepSolved in 2 steps with 4 images

Knowledge Booster
Learn more about
Need a deep-dive on the concept behind this application? Look no further. Learn more about this topic, mechanical-engineering and related others by exploring similar questions and additional content below.Similar questions
- An automobile engine develops a maximum torque of 162Nm. The low gear ratio of transmission is 2.75, while the back axle ratio is 4.25. The effective wheels radius is 0.325m and the co-efficient of friction between the tyre and the road surface is 0.6. If the permissible shear stress is 32373 X 104Pa. Determine the maximum shaft diameter. Assuming that the load is nearly torsional. What is maximum load permissible on each wheel?arrow_forwardPlease help. Do not just guess. Prove your answer. I will give a good feedback. thank you :)arrow_forwardA circular shaft of the dimensions shown in the following figure is subjected to three torques : T1 = 28 k-in, T2 = -8 k-in and T3 = 10 k-in. (a) What is the angle of twist of the right end due to the applied torque? (b) Plot the angle of twist diagram along the shaft. Let, G= 12×106 psi.arrow_forward
- A metal shaft ABCD with variable cross-section is subjected to three external torques (T₁=28 kip- in, T2=8 kip-in, and T3=10 kip-in) as shown in the figure below. Each torque is acting at the locations marked with circular points along the shaft. Note that a 16-inch long segment of the shaft at the free end (right) has a 1-inch diameter bore. The dimensions (lengths and diameters) of the shaft are given in the figure. Assume deformation is linear elastic and take G=12×106 psi. D [3" 16"- X C T₁ 2" -32"- T₂ 1" diam. bore B -16"- A T3 the bar has a uniform diameter d along its full length, but external torques remain the same and are applied at the same locations. If the failure shear stress for the material is equal to Tfail = 10 ksi, and the factor of safety is equal to 2, determine the required (uniform) diameter d for the bar. Assume that the bar is solid for its entire length.arrow_forwardAn irregular shaped hollow tube, with the dimensions shown in figure below, is subjected to a torque of 2.5 kN m. If the tube is fabricated from steel and is 4 m long, determine the maximum value of the average shearing stress and the angle of twist of the tube. Note that the wall thickness of vertical sides is 6 mm and the thickness of the horizontal sides is 5 mm. * Assume the following values: • L₁= 44 mm • L₂ = 50 mm • L3= 88 mm • LA = 25 mm Taug ++ S+ O - L₁ number (rtol-0.01, atol-1e-05) number (rtol-0.01, atol-1e-05) L3 MPa L2arrow_forwardPlease help. This problem involves torsional stress and strain. Thank you.arrow_forward
- The shaft in Figure below consists of a 3-in. -diameter aluminum segment that is rigidly joined to a 2-in. -diameter steel segment. The ends of the shaft are attached to rigid supports, Calculate the maximum shear stress developed in each segment when the torque T= 10 kip.in is applied. Use G = 4×106 psi for aluminum and G = 12×106 psi for steel. Aluminum 3-in. diameter 6 ft T Steel 2-in. diameter 3 ftarrow_forwardThe following data relate to a compound impulse turbine having two rows of moving blades and one row of fixed blades in between them. Steam velocity coming out of nozzle = 450 m/sec., Nozzle angle 15°, Moving blades tip discharge angles = 30°, Fixed blade discharge angle = 20°, Friction loss in each blade rows = 10% of the relative velocity. Find the blade velocity, blade efficiency and specific steam consumption for turbine.arrow_forward(2) The shaft consists of a 3-in diameter aluminum segment that is rigidly joined to a 2-in diameter steel segment. The ends of the shaft are attached to rigid supports, Calculate the angle of twist developed at the interface of the two segments when the torque T = 50 kip in is applied. Use G = 4×106 psi for aluminum and G = 12×106 psi for steel. | Aluminum 3-in. diameter 6 ft T Steel 2-in. diameter 3 ft Darrow_forward
arrow_back_ios
arrow_forward_ios
Recommended textbooks for you
 Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press
Elements Of ElectromagneticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9780190698614Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.Publisher:Oxford University Press Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON
Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9780134319650Author:Russell C. HibbelerPublisher:PEARSON Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education
Thermodynamics: An Engineering ApproachMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781259822674Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. BolesPublisher:McGraw-Hill Education Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY
Control Systems EngineeringMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118170519Author:Norman S. NisePublisher:WILEY Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning
Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)Mechanical EngineeringISBN:9781337093347Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. GerePublisher:Cengage Learning Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY
Engineering Mechanics: StaticsMechanical EngineeringISBN:9781118807330Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. BoltonPublisher:WILEY

Elements Of Electromagnetics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780190698614
Author:Sadiku, Matthew N. O.
Publisher:Oxford University Press

Mechanics of Materials (10th Edition)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9780134319650
Author:Russell C. Hibbeler
Publisher:PEARSON

Thermodynamics: An Engineering Approach
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781259822674
Author:Yunus A. Cengel Dr., Michael A. Boles
Publisher:McGraw-Hill Education

Control Systems Engineering
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118170519
Author:Norman S. Nise
Publisher:WILEY

Mechanics of Materials (MindTap Course List)
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781337093347
Author:Barry J. Goodno, James M. Gere
Publisher:Cengage Learning

Engineering Mechanics: Statics
Mechanical Engineering
ISBN:9781118807330
Author:James L. Meriam, L. G. Kraige, J. N. Bolton
Publisher:WILEY